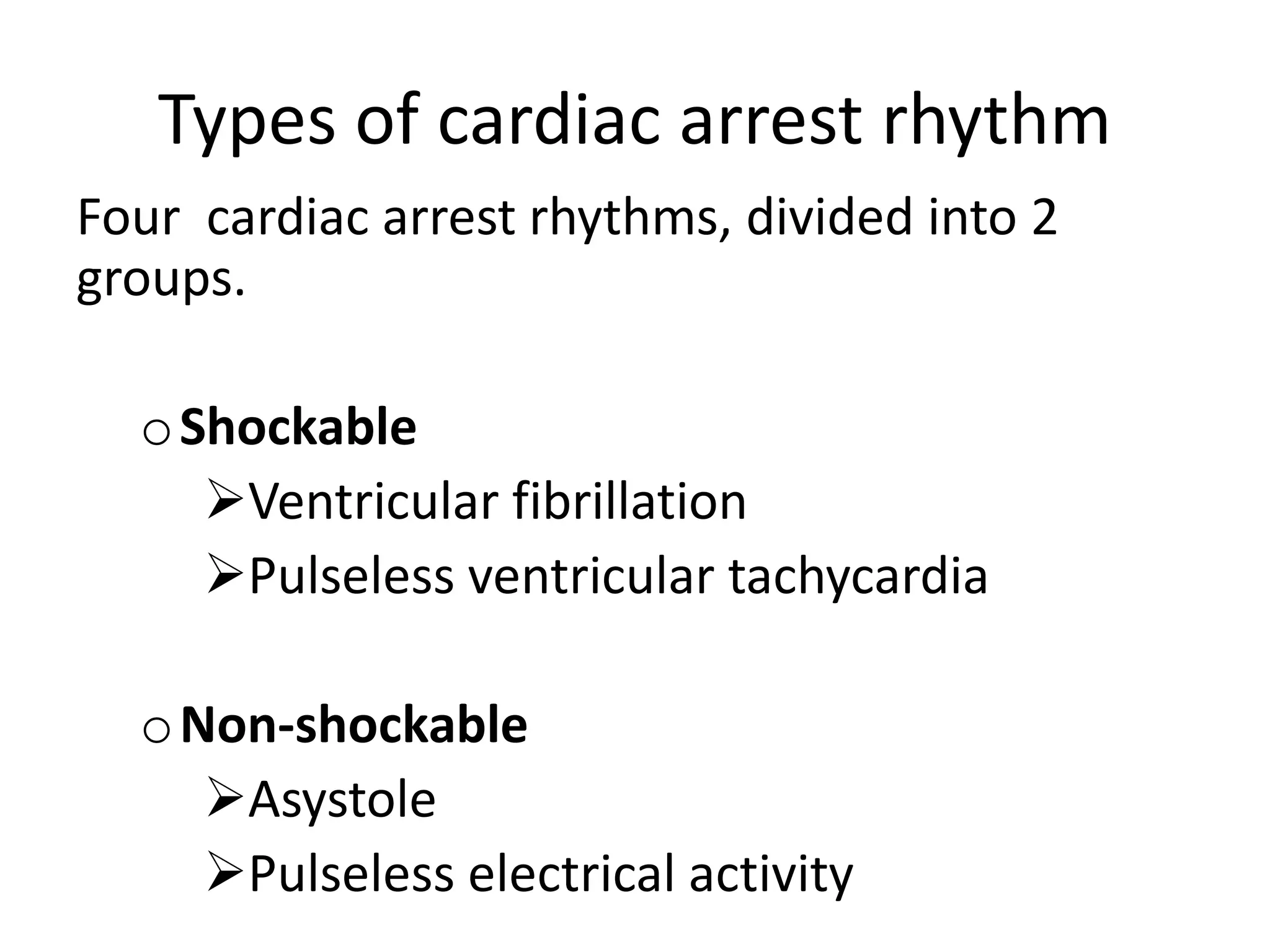
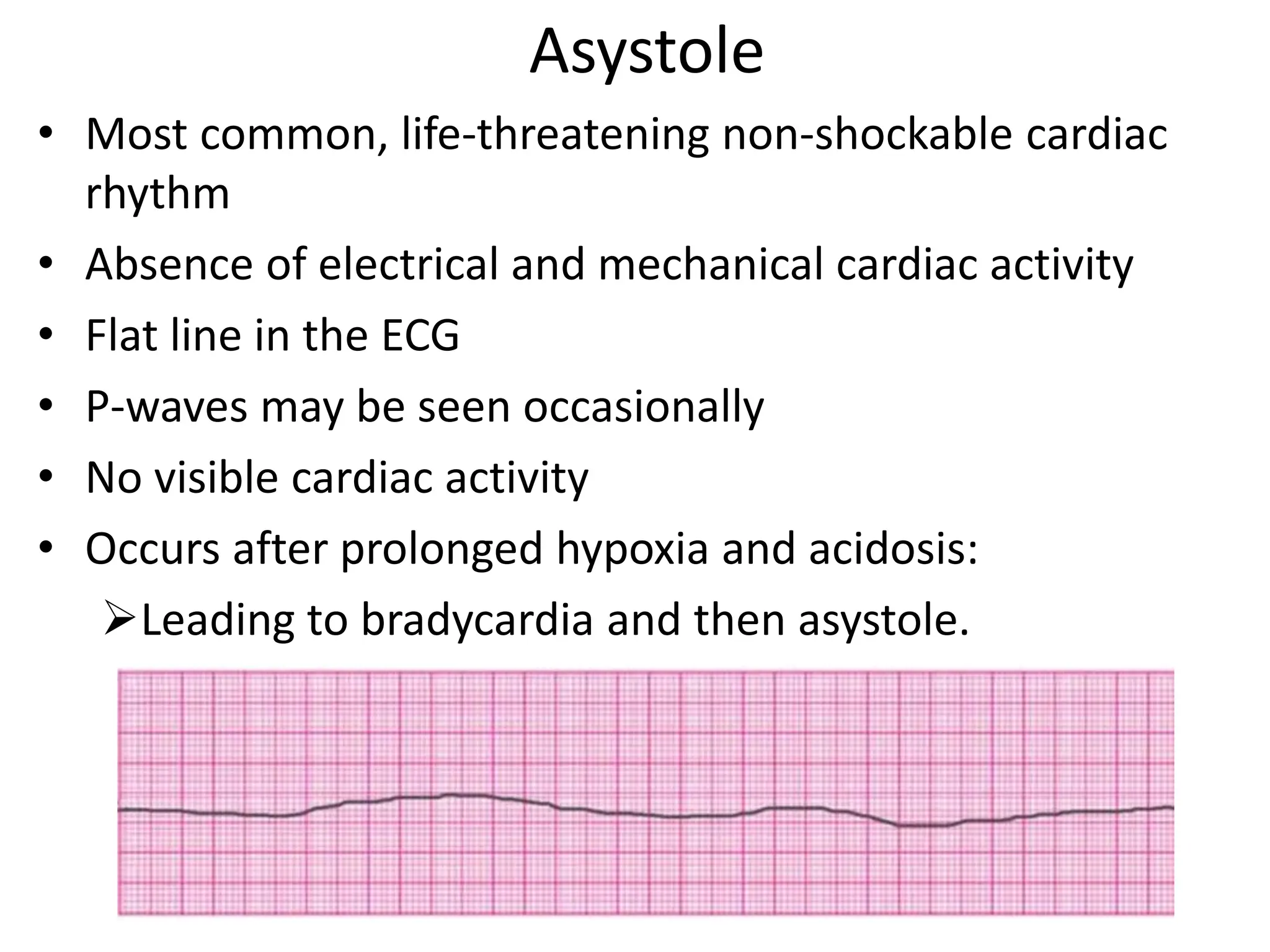
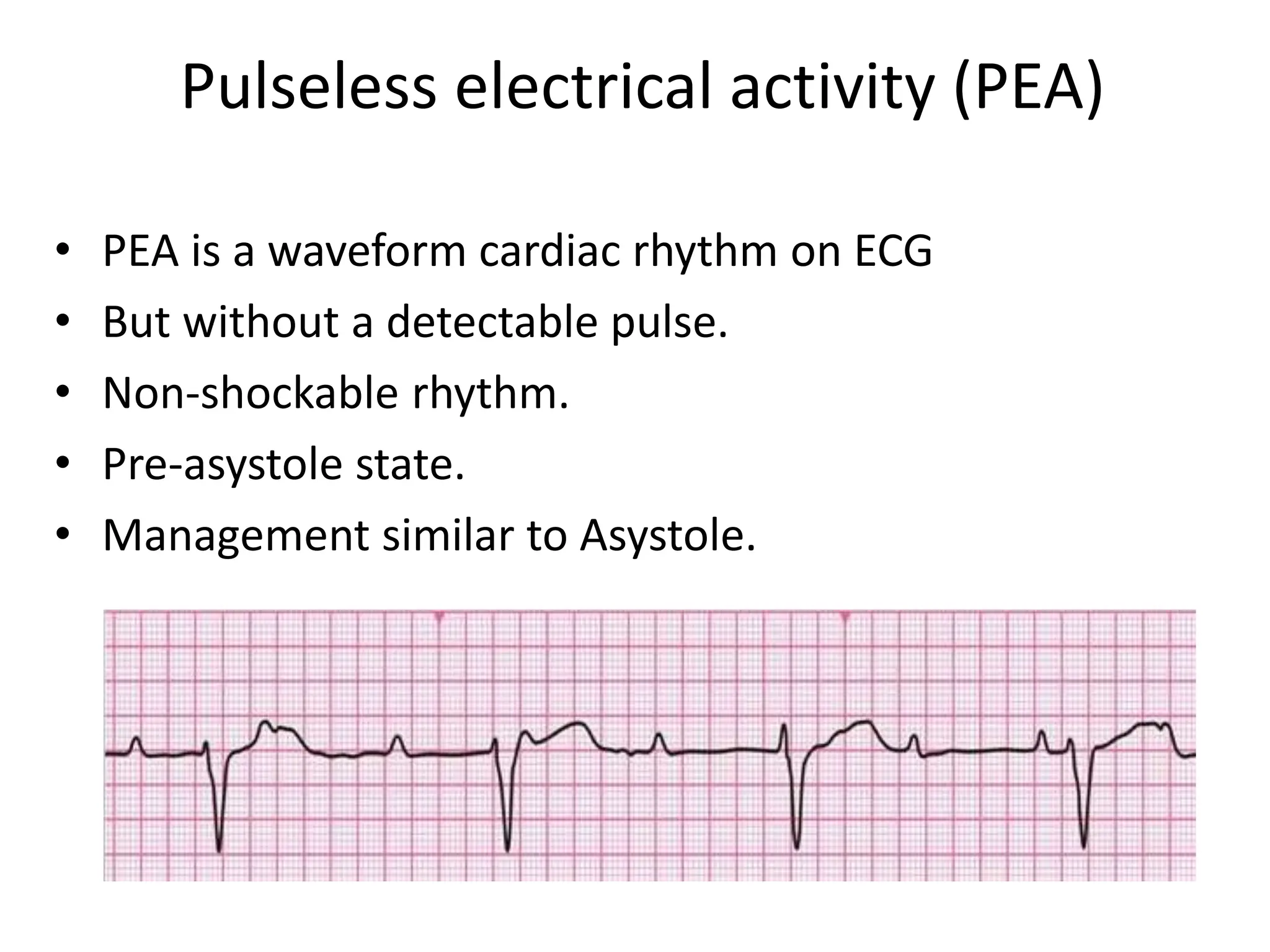
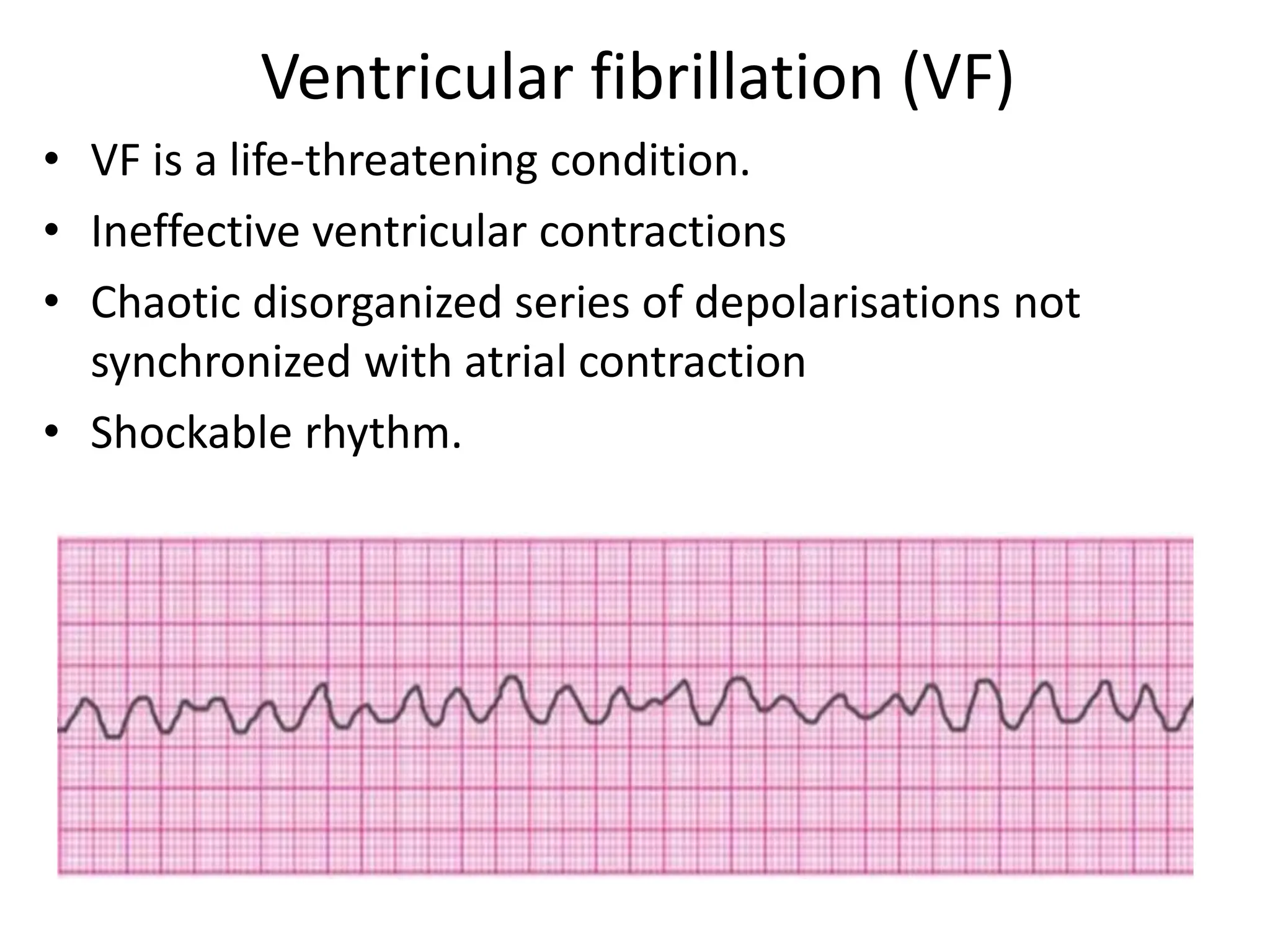
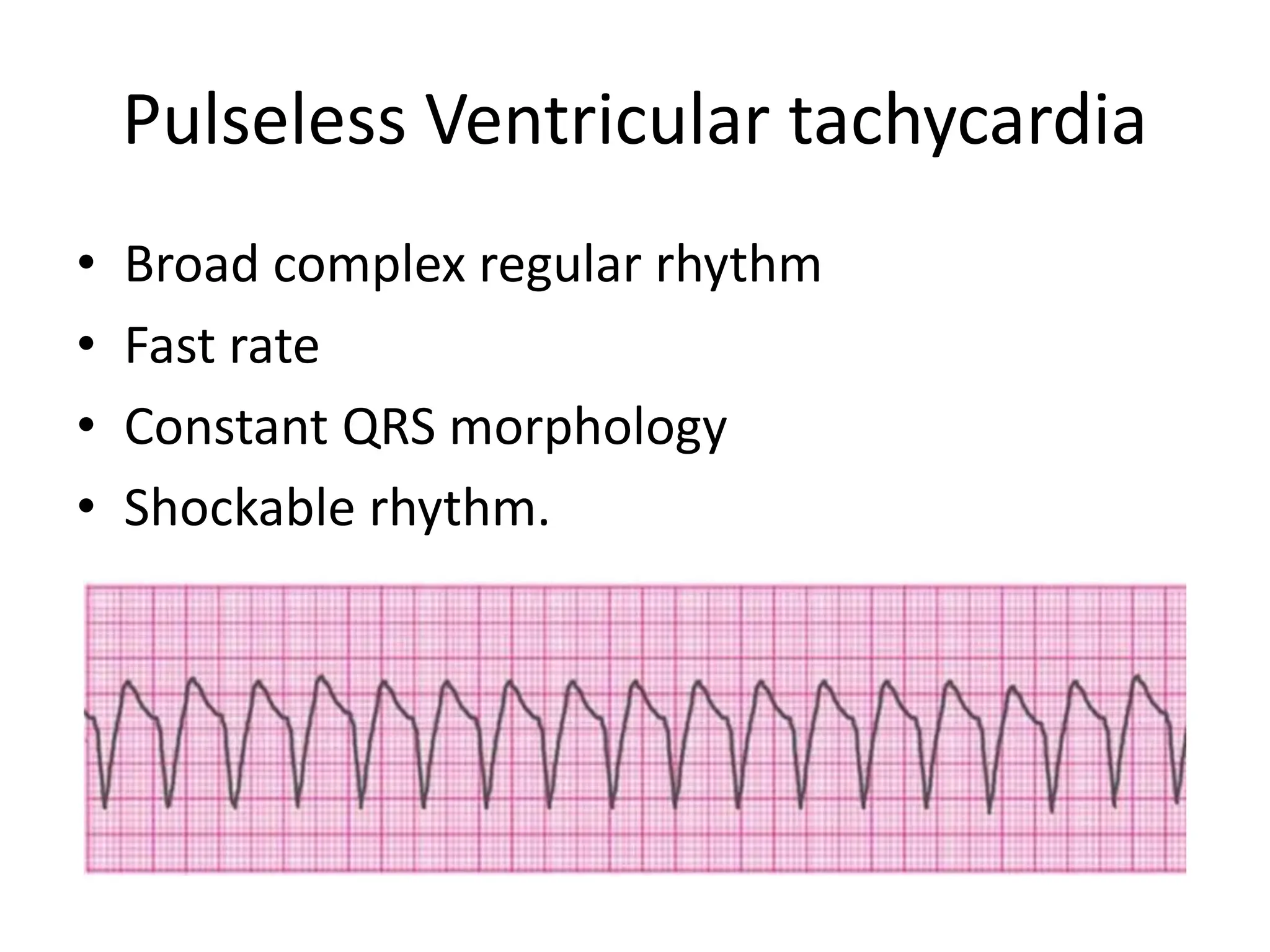
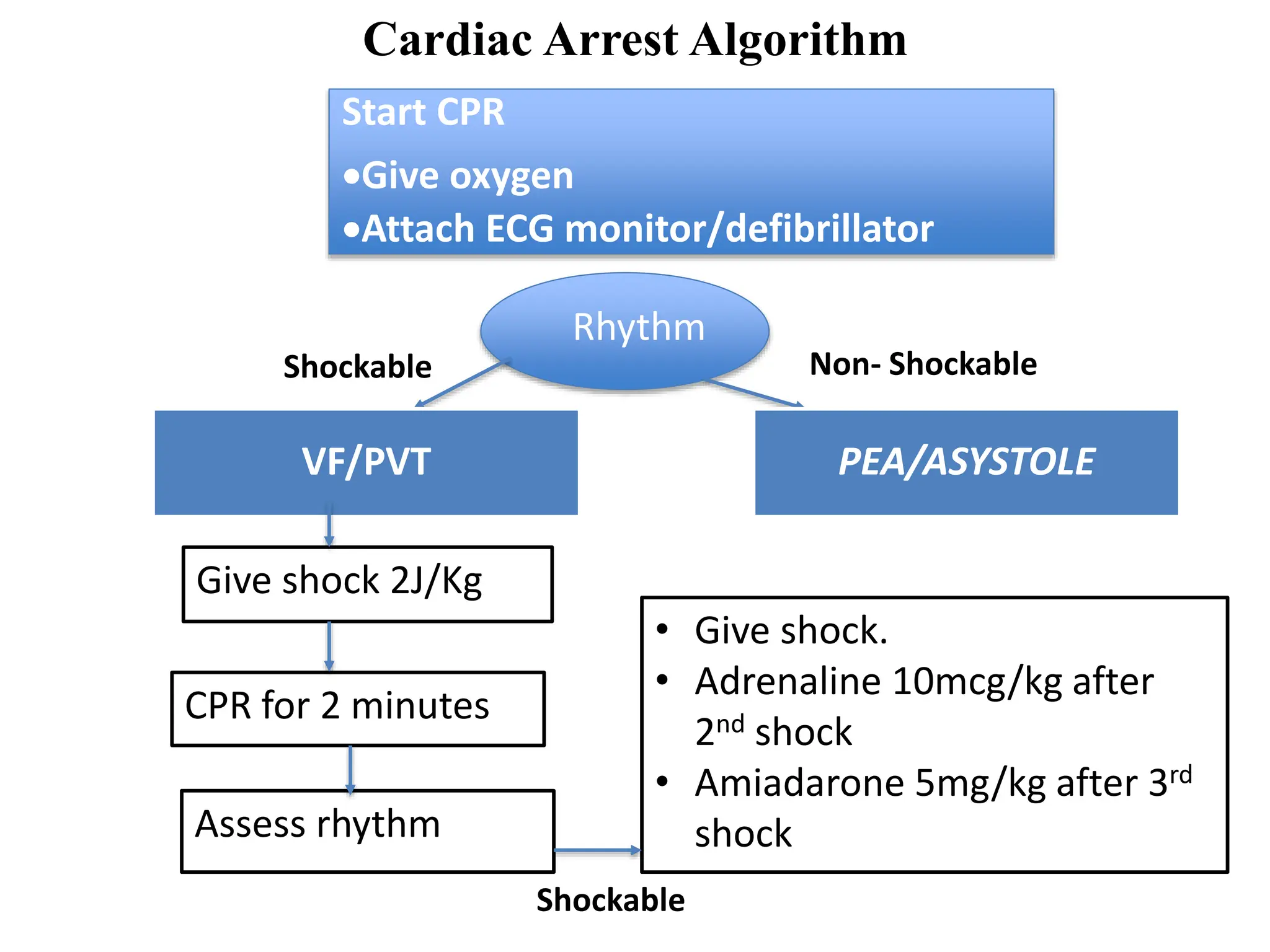
Cardiac arrest is the sudden cessation of cardiac activity where the victim becomes unresponsive with no breathing or pulse. There are two main types of cardiac arrest rhythms - shockable rhythms including ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia, and non-shockable rhythms such as asystole and pulseless electrical activity. For shockable rhythms, the protocol is to give a shock, then perform CPR for 2 minutes before reassessing the rhythm. For non-shockable rhythms like asystole, the protocol is to perform CPR for 2 minutes and then give epinephrine every 3-5 minutes without interrupting CPR.