1) The document is a PowerPoint presentation about coastal features created by erosion. It contains sections on objectives, rationale, waves, coastal erosion, and various landforms created by erosion like headlands and bays, cliffs and wave-cut platforms, and caves, arches, stacks and stumps.
2) It explains the two types of waves - constructive waves that build beaches and destructive waves that erode coastlines. Coastal erosion occurs as wind and water wear away sediments from the land.
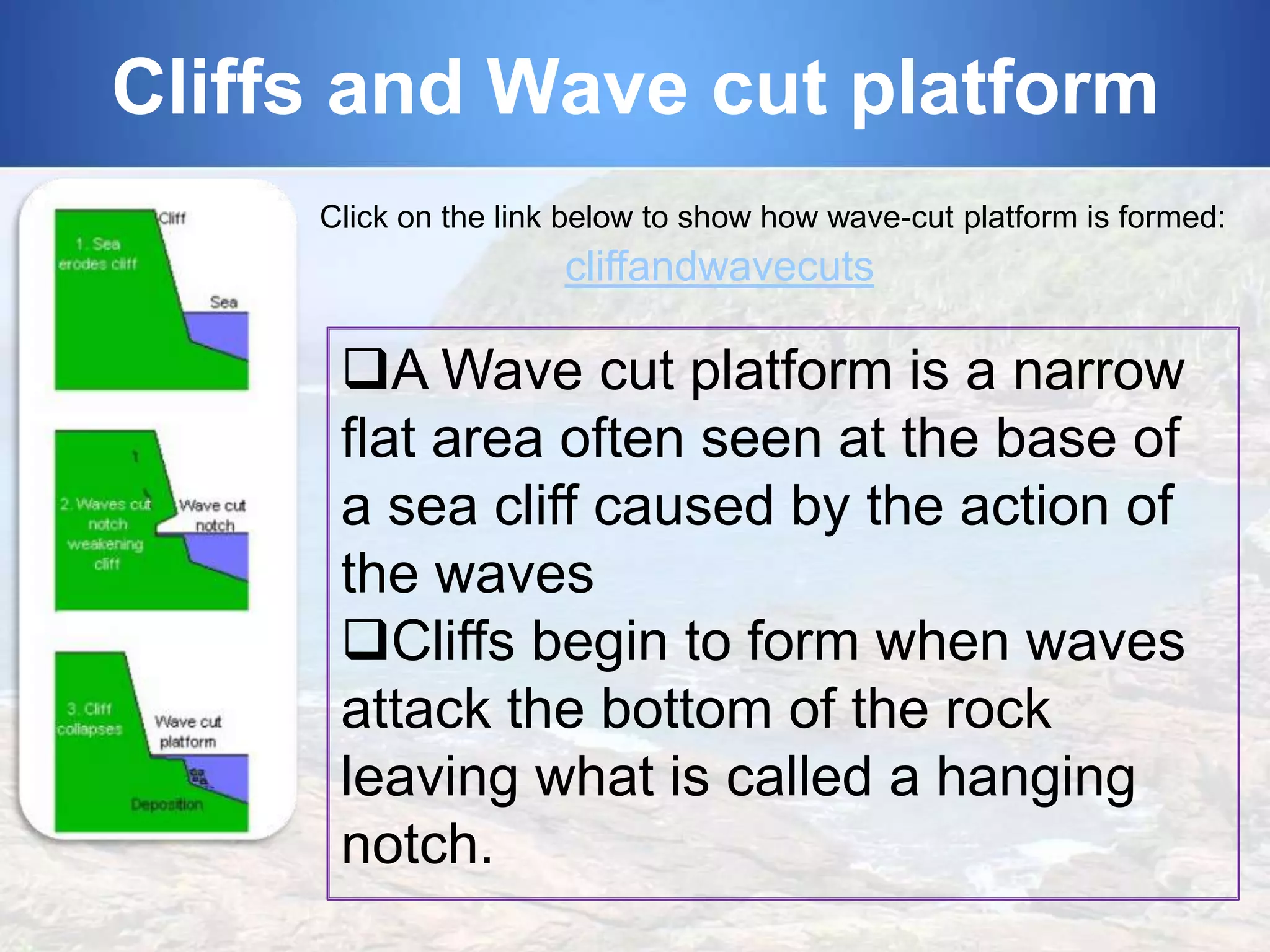
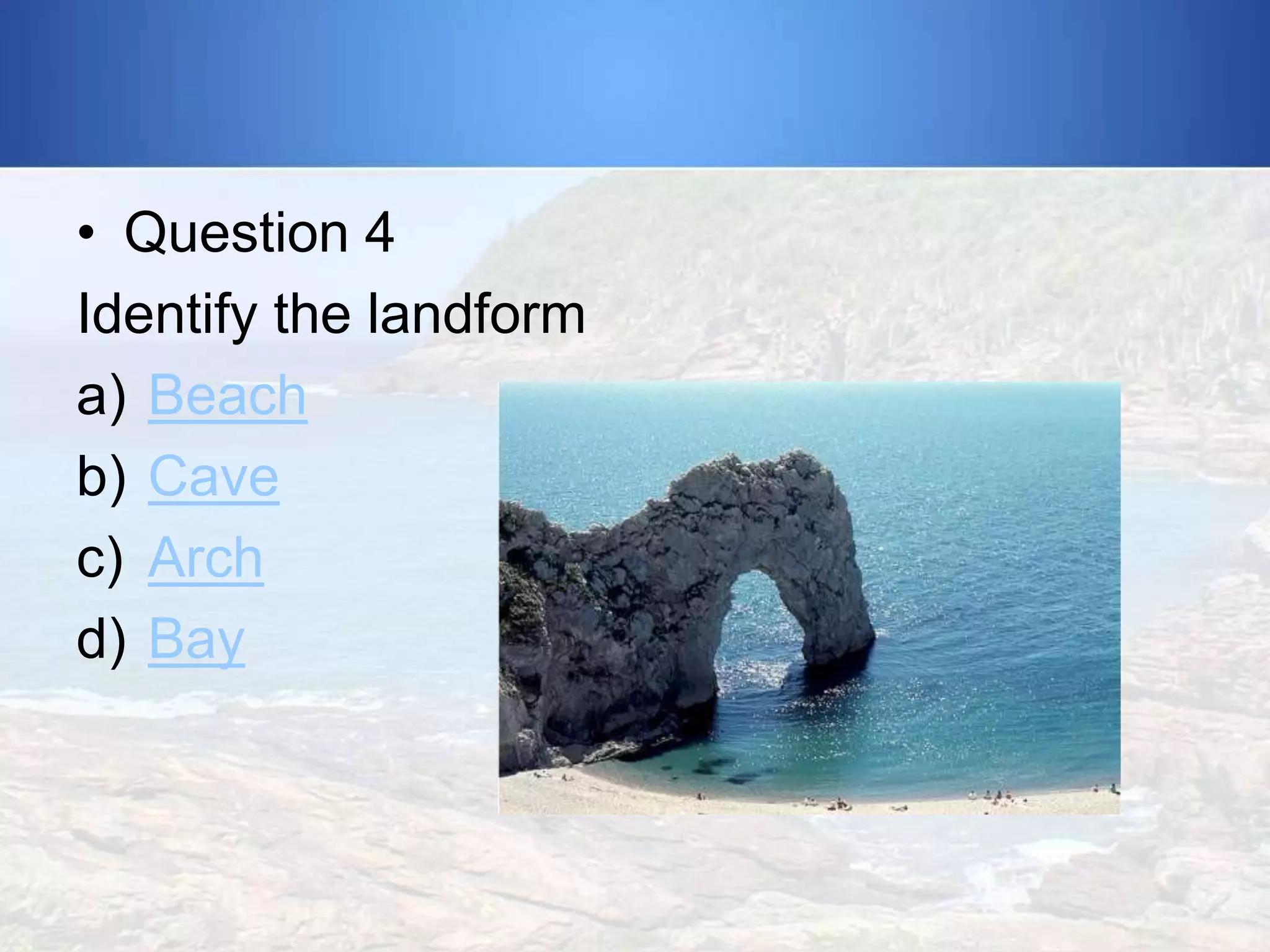
3) Various landforms along coastlines have been formed by these erosive processes, including headlands that jut into the sea and indented areas between them called bays, cliffs and the flat areas