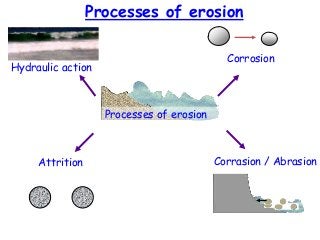
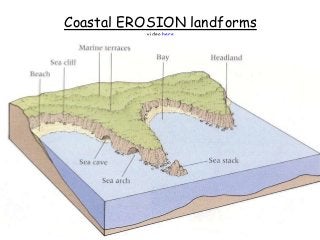
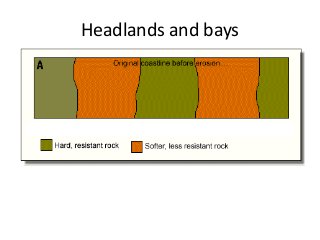
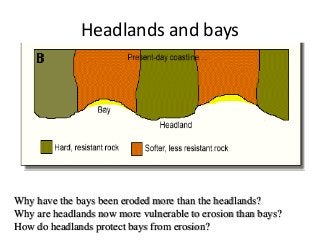
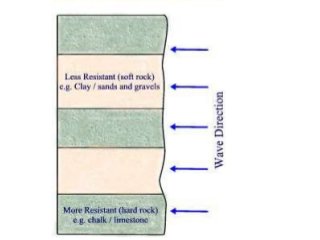
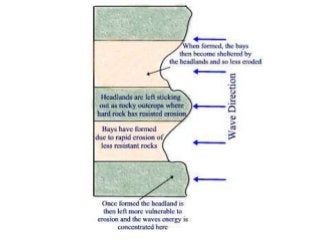
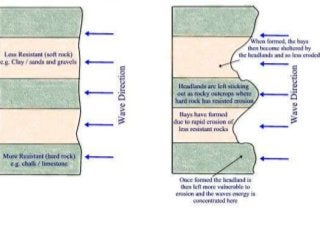
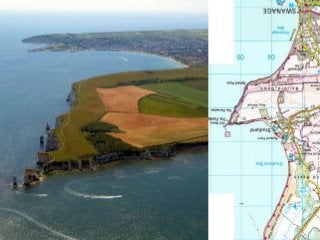
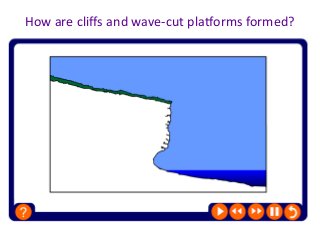
This document discusses various coastal landforms formed by erosion processes. It describes attrition as the breaking down of material into smaller particles when carried by waves. Corrasion and hydraulic action involve material carried by waves wearing away coastlines through impacts or air pressure within cracks. Solution slowly dissolves rocks through chemical reactions with acid in seawater. Headlands project out and are more resistant to erosion, forming bays between them. Cliffs and wave-cut platforms are formed as waves erode the cliff base and notch it, eventually leaving a platform when the cliff collapses. Caves, arches, stacks and stumps form through the continued erosion of weaknesses in the cliff and eventual collapse of eroded sections.