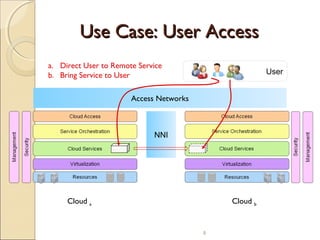
The document discusses cloud interoperability, which is the ability of IT systems to exchange data across different cloud platforms, enabling seamless communication and process integration. It outlines the importance of interoperability in fostering customer choice, competition, and innovation, while also detailing various use cases including resource sharing and B2B procurement. The text highlights the necessity of standards at multiple levels to achieve effective interoperability in the cloud ecosystem.