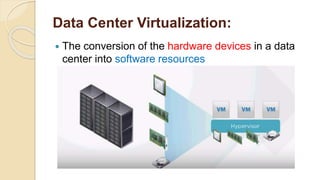
Data center virtualization (DCV) involves converting hardware resources like servers, storage and networking equipment in a data center into virtual resources that can be easily managed and allocated. This allows several virtual machines to run on a single physical server, reducing costs associated with power, cooling and hardware. DCV provides benefits like energy savings, easier backups, reduced costs and vendor independence by using a hypervisor to manage virtual machines independently of underlying hardware. However, issues with DCV include increased security risks, potential performance issues with certain applications, and increased licensing costs.