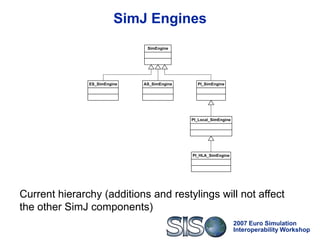
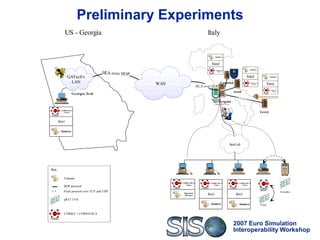
The document discusses advancements in distributed simulation interoperability, focusing on High-Level Architecture (HLA) standards and software solutions. It presents two technologies, CORBA-HLA and SIMJ, aimed at enhancing interoperability, reusability, and adaptability of distributed simulators. The conclusions highlight that current distributed simulation software doesn't fully utilize advancements in distributed software, emphasizing the need for improved quality attributes.














![2007 Euro Simulation
Interoperability Workshop
Improving interoperability through …
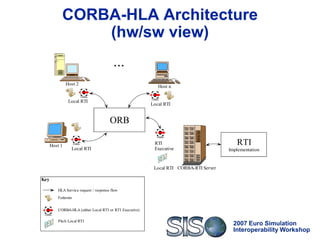
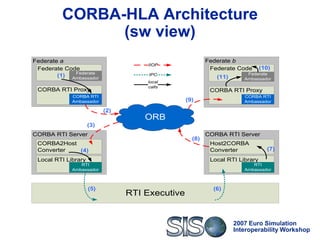
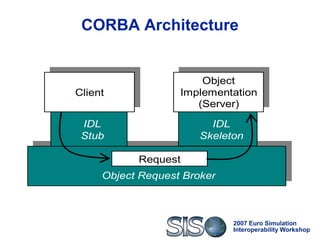
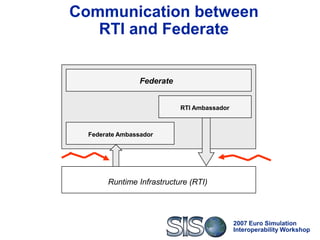
Standard, open and highly interoperable protocols to vehicle
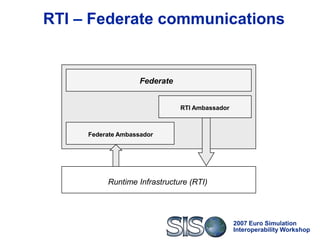
HLA service calls and data
Thus:
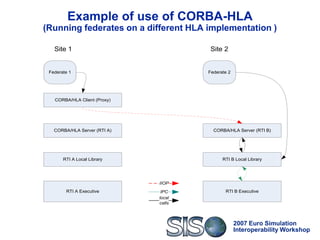
Federates using CORBA-HLA can switch to any HLA
implementation that exposes its services through IDL
interfaces, i.e. achieves technical interoperability [Tolk]
[Tolk] A. Tolk, J. Muguira, “The Level of Conceptual Interoperability”, The 2003 Fall Simulation
Interoperability Workshop, 03F-SIW-07](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07e-siw-053-111225150534-phpapp01/85/Software-Technologies-for-the-Interoperability-Reusability-and-Adaptability-of-Distributed-Simulators-18-320.jpg)