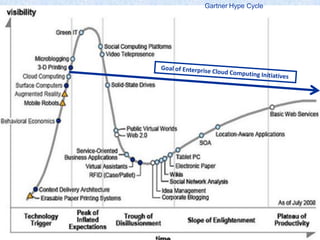
This document discusses key issues for enterprises adopting cloud computing. It identifies the need for standardization of APIs between cloud layers and across clouds to ensure interoperability. The document also discusses requirements for robust cloud operations including security, availability, and governance. It proposes several efforts could help including industry associations, user groups, and open initiatives to develop best practices, use cases, and software/services to guide enterprises in their cloud migrations.