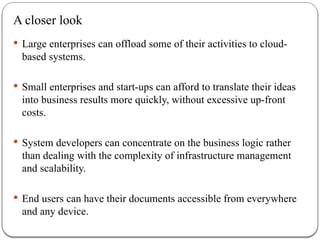
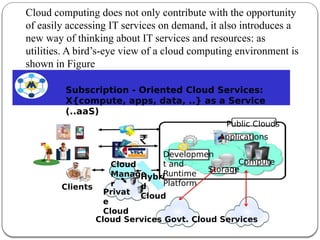
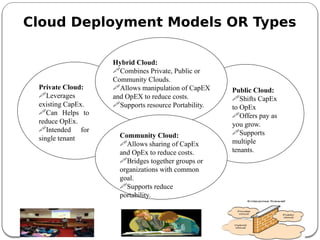
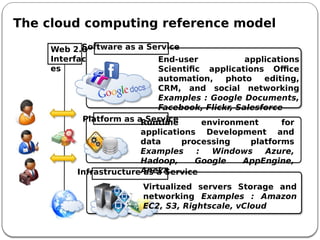
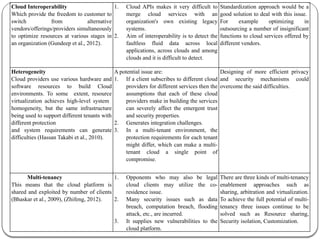
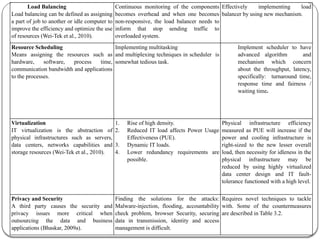
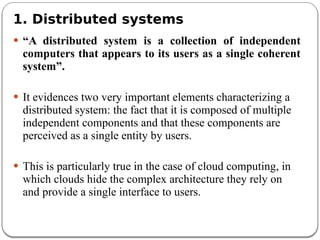
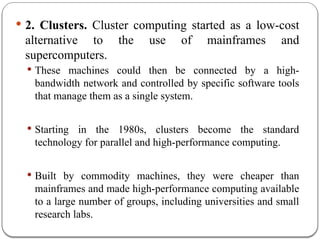
The document provides an introduction to cloud computing. It discusses how computing is transitioning to a utility-based model where resources are accessed on-demand via the internet. Cloud computing allows users to access applications, storage, and other services from any device. Early computer scientists envisioned this type of computing utility. The document outlines characteristics of cloud computing like multi-tenancy, scalability, and the various deployment models. It also discusses some of the technical aspects that enabled cloud computing such as virtualization, distributed systems, and web technologies. Challenges of cloud computing are security, privacy, outsourcing, and heterogeneity between provider platforms.









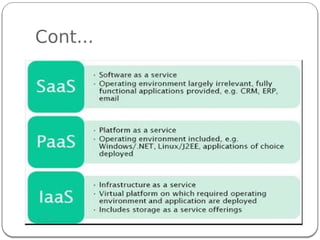



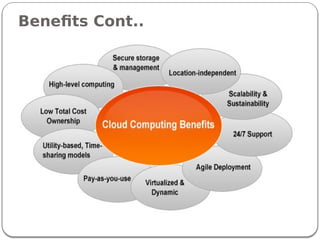
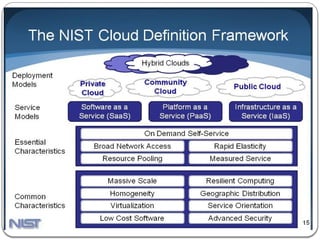


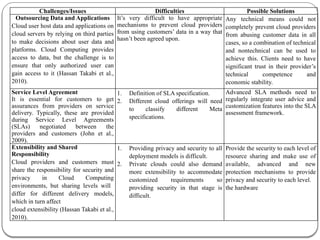











![Cont..
One of the most popular expressions of service orientation is represented
by Web Services (WS) [21]. These introduce the concepts of SOC into
the World Wide Web, by making it consumable by applications and not
only humans.
Web services are software components that expose functionalities
accessible using a method invocation pattern that goes over the
HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
The interface of a Web service can be programmatically inferred by meta
data expressed through the Web Service Description
Language(WSDL); this is an XML language that defines the
characteristics of the service and all the methods, together with
parameters, descriptions, and return type, exposed by the service.
Using SOAP and WSDL over HTTP, Web services become platform
independent and accessible to the World Wide Web.
The standards and specifications concerning Web services are controlled
by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). Among the most popular
architectures for developing Web services we can note ASP.NET [24]
and Axis [25].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch-1-introduction1-230526074620-ef253371/85/Ch-1-INTRODUCTION-1-pdf-43-320.jpg)