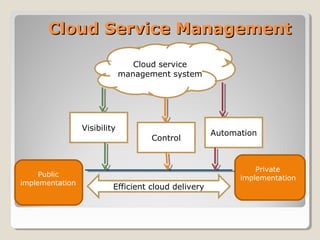
Cloud service management tools provide visibility, control, and automation to efficiently manage cloud services across public and private implementations. They allow monitoring of cloud performance, continuity, and efficiency in virtual environments. Cloud service management also simplifies user interactions, accelerates time to value through self-service catalogs, and lowers costs by automatically allocating and de-allocating resources according to provisioning policies.