This document discusses various applications of PCR cloning including its advantages over traditional cloning methods. It provides details on:
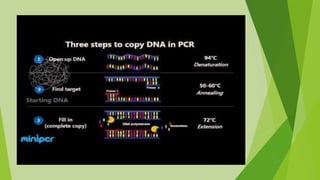
1) PCR cloning allows cloning of DNA fragments without restriction enzymes and works well for projects requiring high throughput. It can clone DNA fragments that are not available in large amounts.
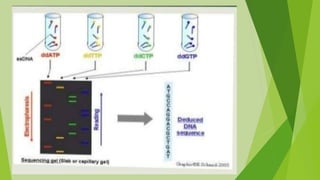
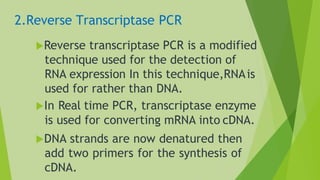
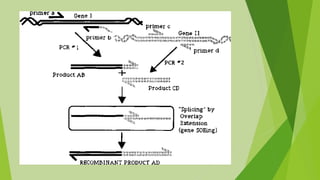
2) Common types of PCR like real-time PCR, reverse transcriptase PCR, and applications like paternity testing, mutation detection, gene recombination through addition, deletion, and site-specific mutagenesis.
3) The role of proofreading enzymes in ensuring faithful DNA replication by identifying and removing mismatched bases.