- Crystallography is the study of crystal shapes and symmetry based on how atoms combine to form geometric patterns on the smallest scale.
- There are 5 main symmetry functions that determine the 32 possible crystal classes: axis of rotation, mirror plane, center of symmetry, axis of rotoinversion, and crystal forms.
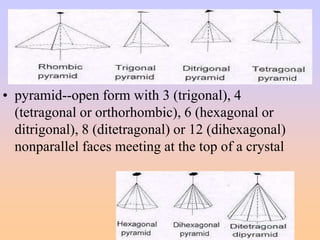
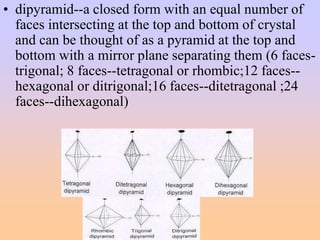
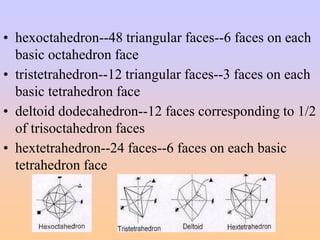
- Crystal forms include pinacoids, prisms, pyramids, dipyramids, and others that are characteristic of specific crystal classes and systems. Identifying crystal forms is important for determining the crystal's symmetry and class.