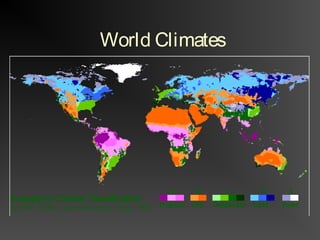
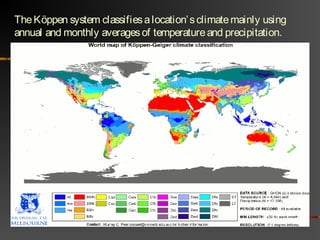
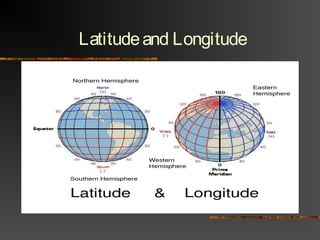
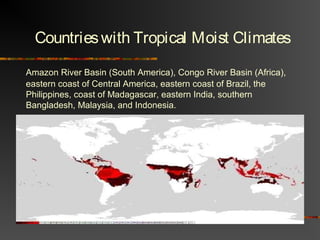
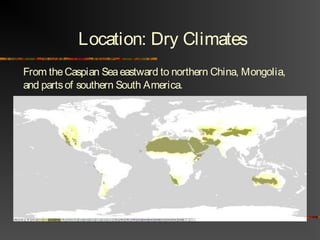
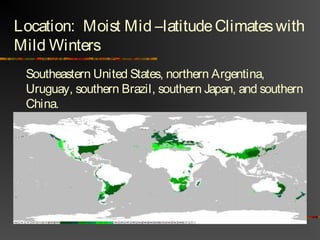
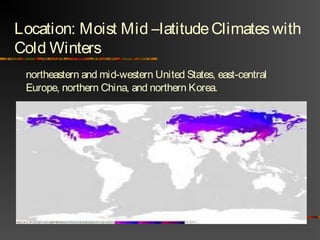
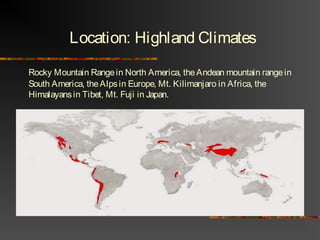
The document discusses climate as the long-term atmospheric conditions of a region, emphasizing its impact on biomes, plant growth, and animal habitation. It outlines the Köppen climate classification system, which categorizes the world's climates based on temperature and precipitation patterns, detailing major categories such as tropical moist, dry, moist mid-latitude, polar, and highland climates. Each climate type is associated with specific geographical locations around the world.