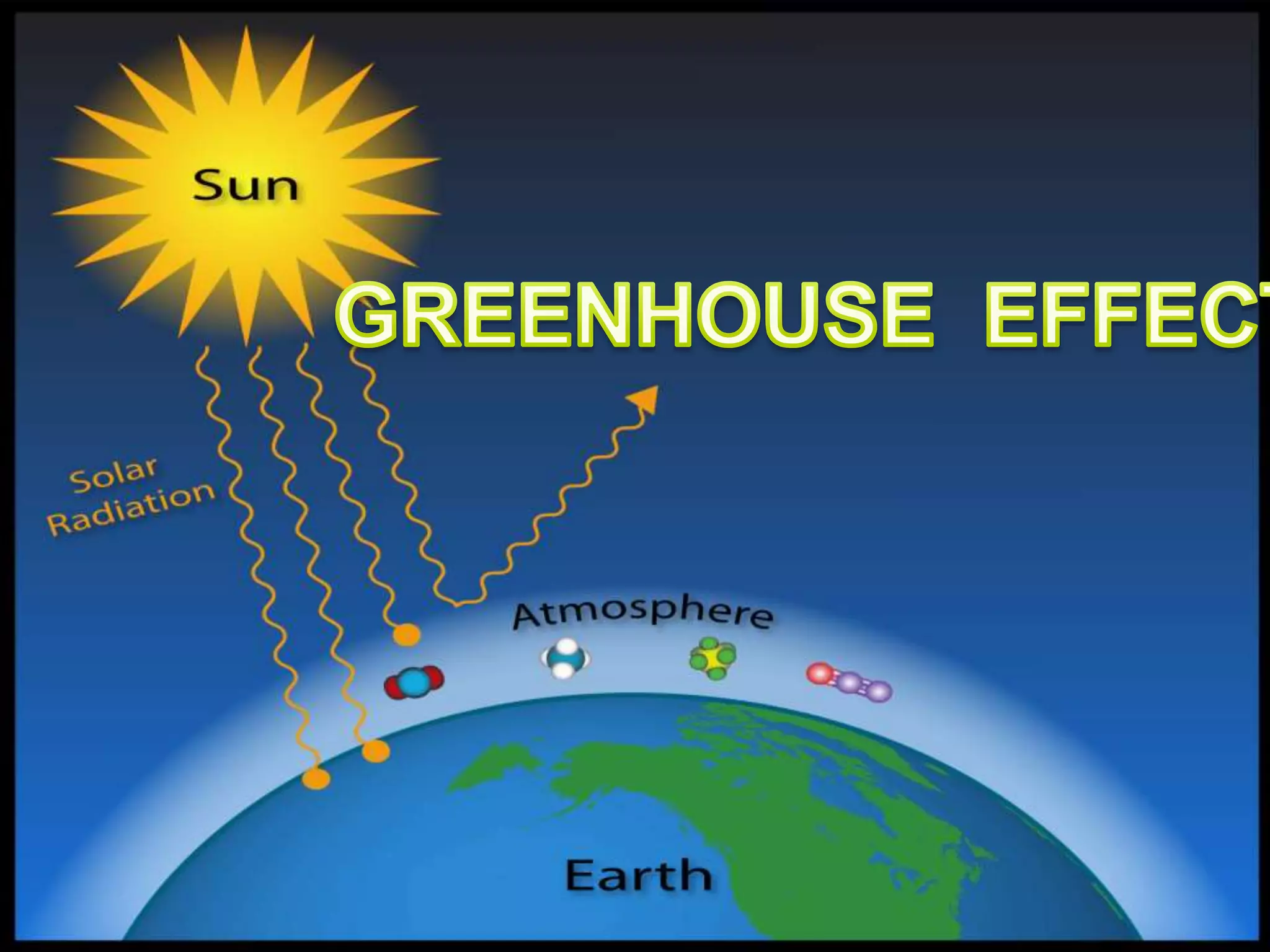
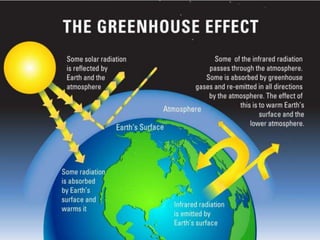
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface, with greenhouse gases like water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and ozone contributing to this effect. Climate change, driven by an increase in these gases, is expected to lead to approximately 250,000 additional deaths per year between 2030 and 2050 due to various health issues. While mainstream scientists agree on the seriousness of global warming, there are some dissenting opinions regarding its trajectory and urgency.