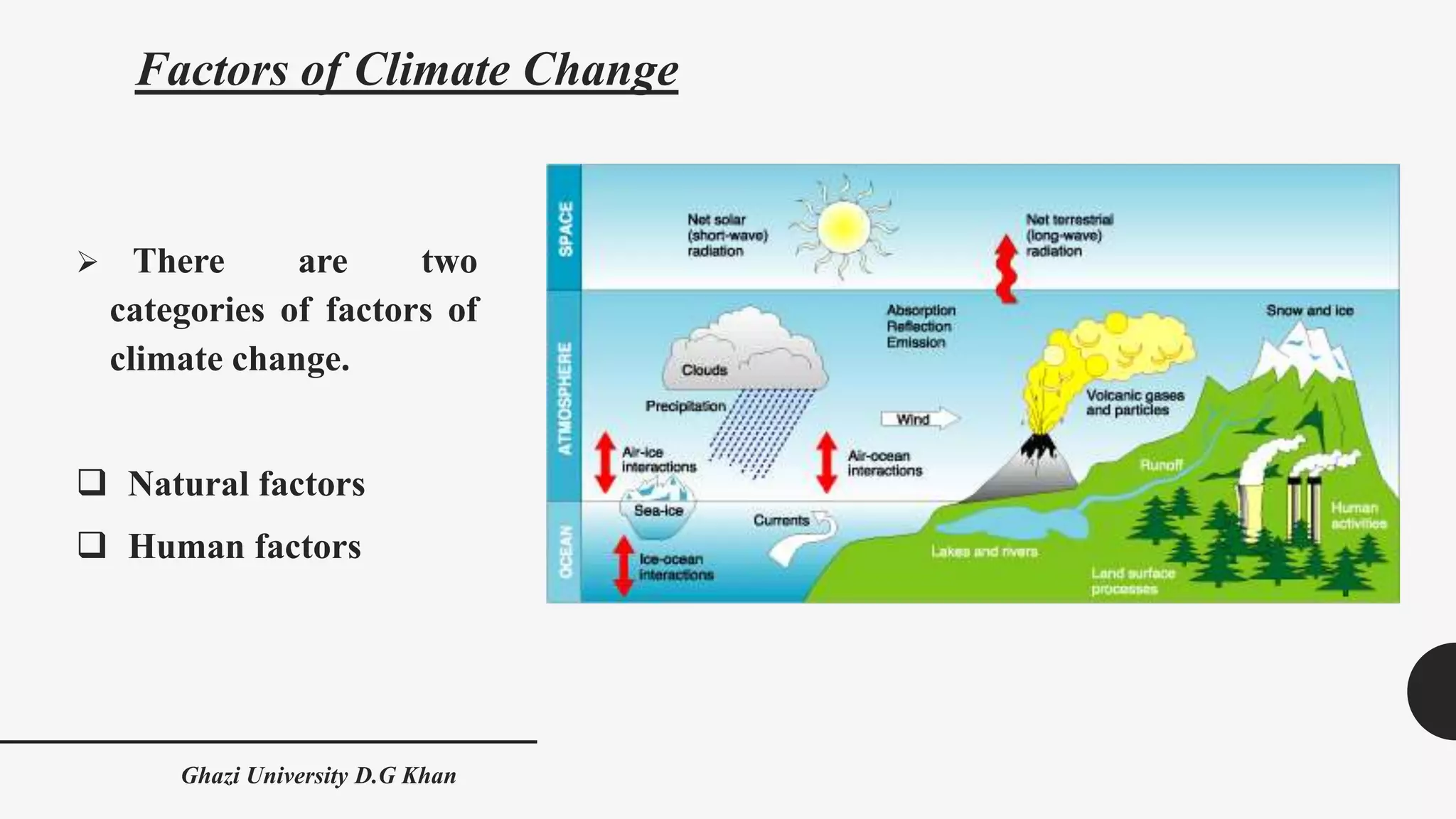
The document presents an overview of climate change, defining it as a long-term alteration in weather patterns influenced by both natural and human factors. Key contributors to climate change include greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, primarily due to human activities such as deforestation, livestock farming, and industrial practices. It also discusses natural factors like solar irradiance, volcanic eruptions, and ocean currents that can impact climate variability.