The document discusses various factors that influence weather and climate:
- Weather refers to short-term atmospheric conditions over a small area, while climate describes average conditions over a larger area for an extended period.
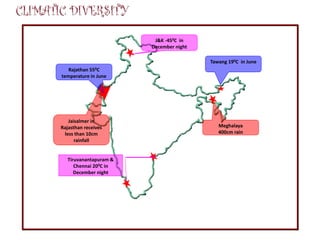
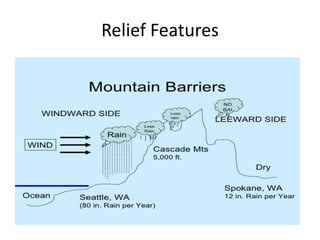
- Key climate determinants in India include latitude, altitude, pressure systems, distance from the sea, ocean currents, and relief features. The monsoon climate brings seasonal reversal of winds and heavy rainfall to much of the country.