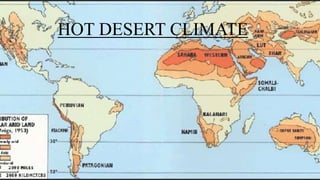
This document summarizes the major climate regions of the world. It discusses factors that influence climate such as latitude, altitude, proximity to seas, air currents and land formations. It then describes the key climatic characteristics of several climate regions including equatorial, tropical monsoon, hot desert, Mediterranean, temperate continental, Siberian, and Arctic climates. For each region it discusses location, climatic conditions such as temperature and rainfall patterns, and influencing seasonal winds.