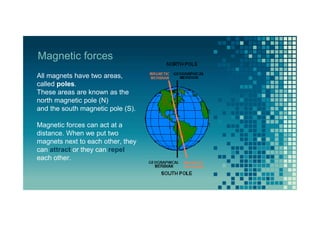
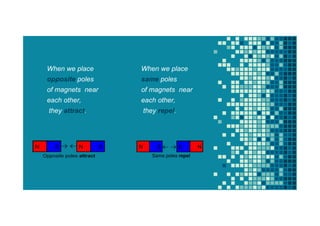
Electrical charges can build up on objects when they are rubbed together. This document discusses electricity, magnetism, and energy. It defines electricity as the flow of electrical charges and describes how materials can be conductors or insulators. Magnets attract other magnetic materials and have north and south poles that can attract or repel each other. There are different forms of energy including chemical, light, mechanical, thermal, and electrical. Energy sources can be renewable, like the sun, wind, water, and biomass, or non-renewable, like fossil fuels and nuclear fuels.