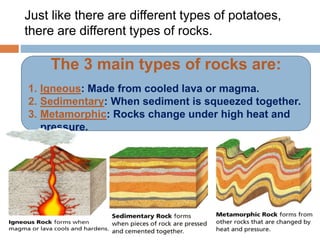
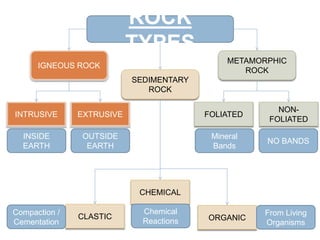
Geologists classify rocks based on their mineral composition, color, and texture. When studying a rock sample, they observe which minerals it contains, its color, and properties like grain size and shape. There are three main types of rocks: igneous rocks formed from cooled lava or magma, either intrusively underground or extruded onto the surface; sedimentary rocks formed by compaction or cementation of sediments or chemical/organic processes; and metamorphic rocks formed from changes to existing rocks through heat and pressure.