Embed presentation
Downloaded 359 times


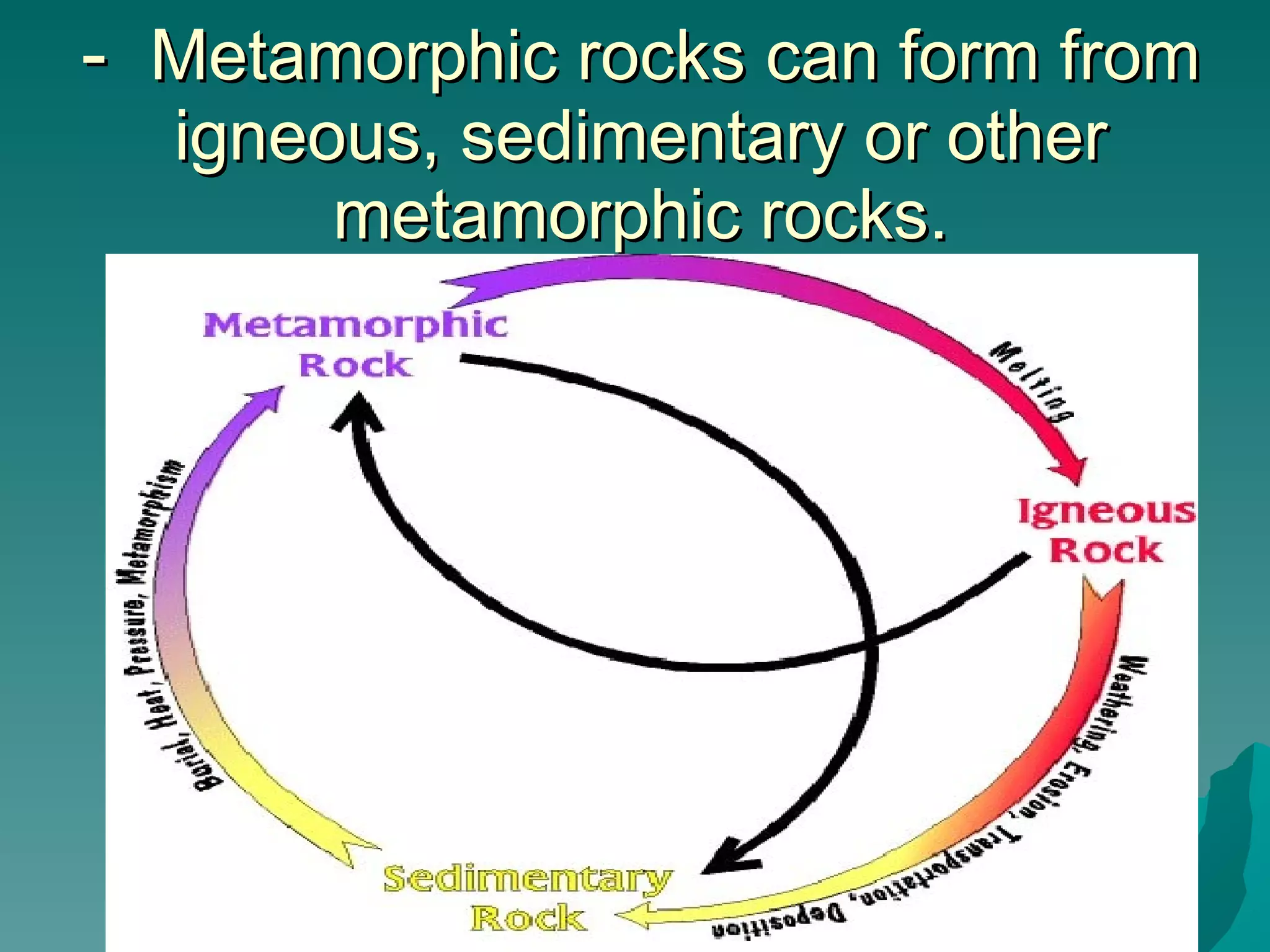














Metamorphic rocks are formed by heat and pressure acting on older igneous, sedimentary, or other metamorphic rocks. Earthquakes and volcanic activity apply this heat and pressure, which can melt rock into magma or flatten and rearrange mineral grains without melting. Metamorphic rocks are classified based on their texture as either foliated, with flattened and aligned mineral grains, or nonfoliated, with rearranged but not layered grains. Common metamorphic rocks include slate, gneiss, marble, and quartzite formed from their igneous or sedimentary protoliths under metamorphism.
















