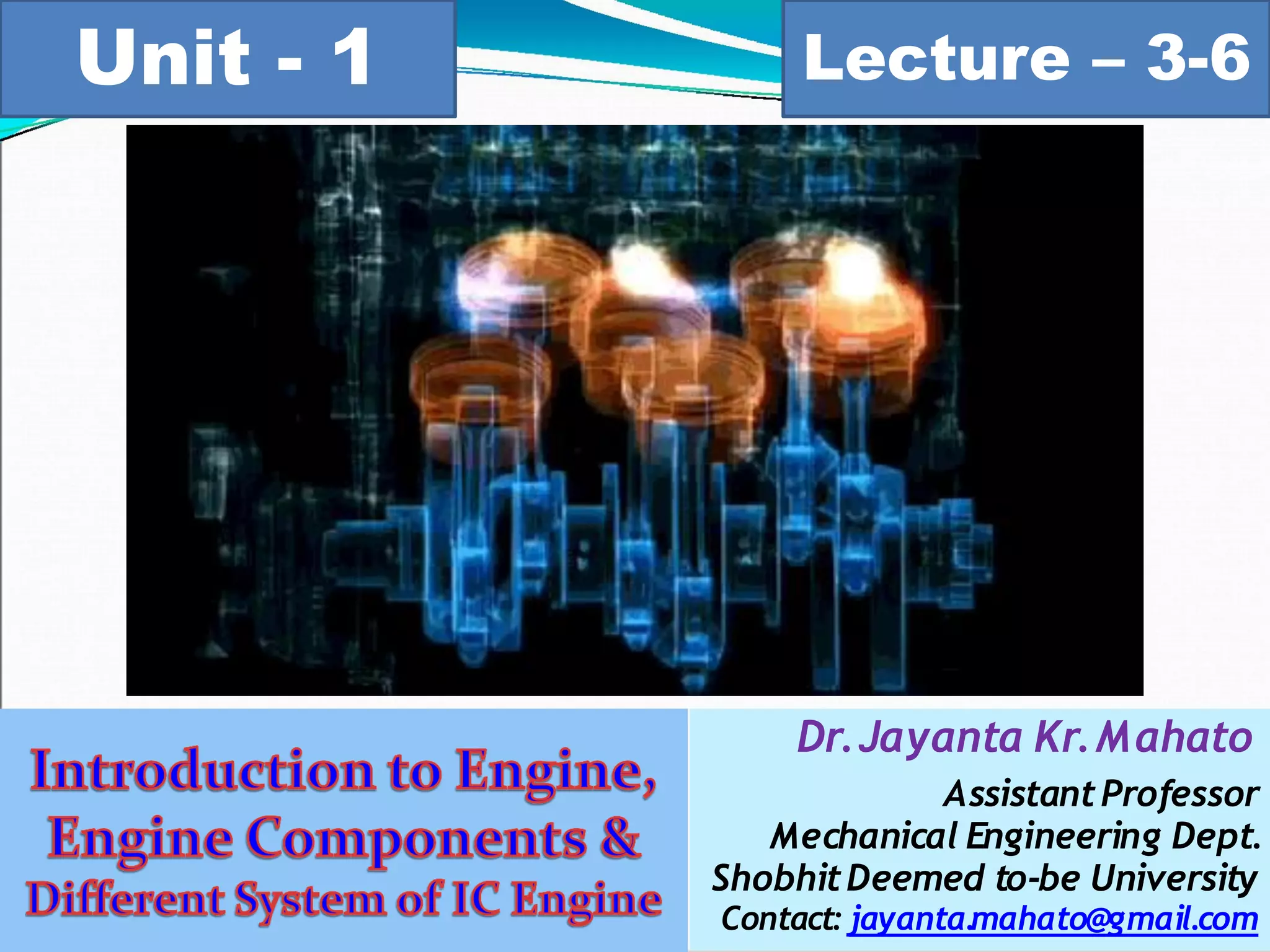
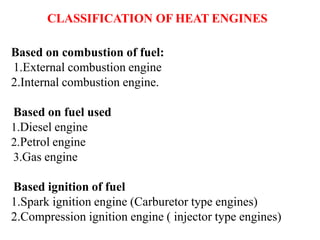
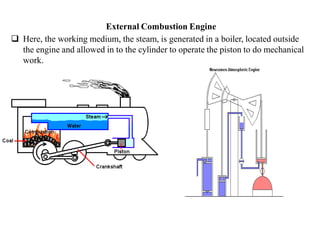
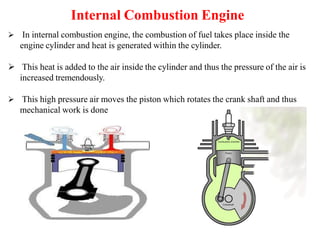
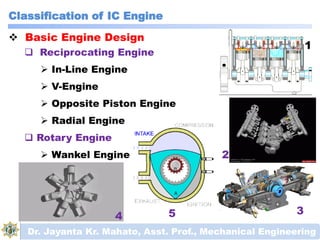
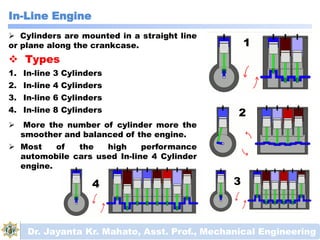
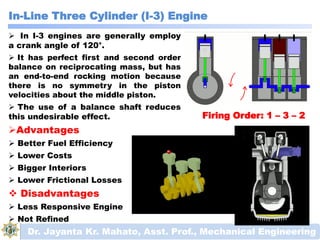
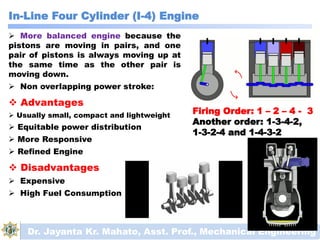
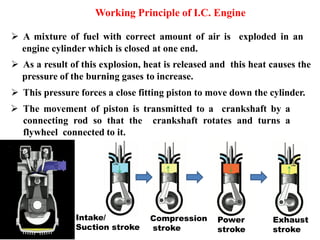
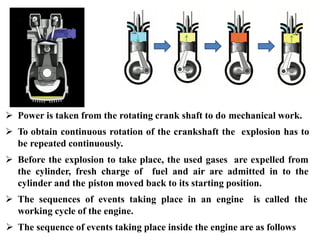
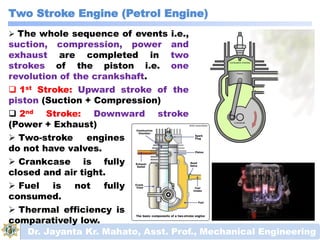
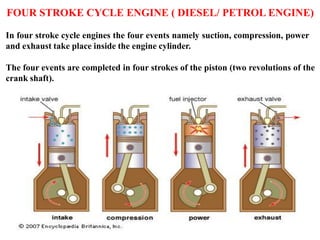
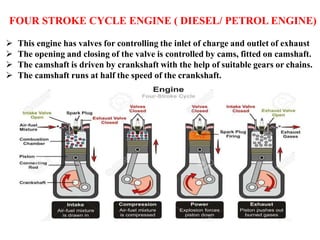
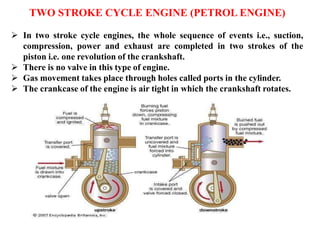
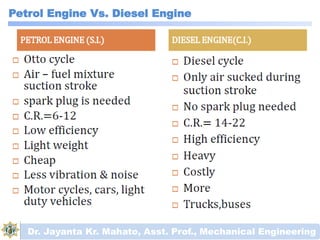
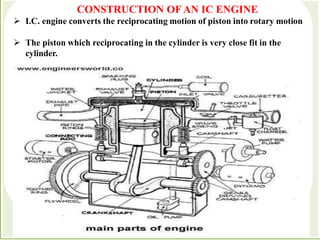
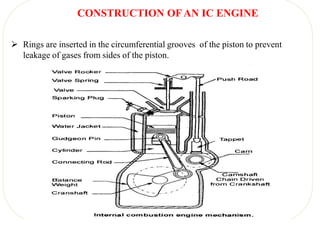
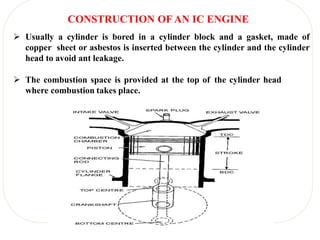
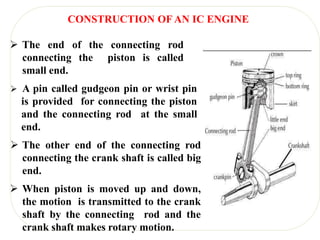
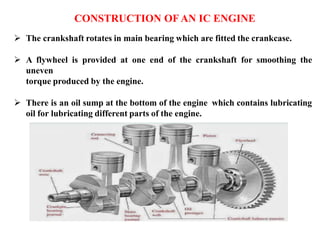
The document discusses engines and their classification. It begins by defining an engine as a device that converts chemical energy to mechanical energy. It then classifies heat engines based on whether combustion occurs externally or internally. Internal combustion engines are further classified based on the fuel used (diesel, petrol, gas), ignition type (spark ignition, compression ignition), and engine design (reciprocating, rotary). Reciprocating engines include inline, V-shaped, opposed piston, and radial configurations. The document also discusses two-stroke and four-stroke cycles and compares petrol and diesel engines. It concludes by describing the basic construction of an internal combustion engine.