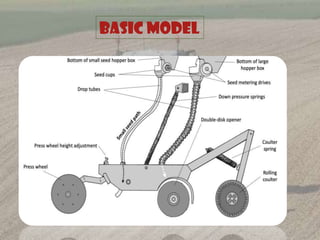
The document discusses components and calibration of a seed drill. It provides details on:
1) The main components of a seed drill including the frame, seed box, seed metering mechanism, furrow openers, covering device, and transport wheels.
2) The process of calibrating a ground wheel driven seed drill which involves determining the drill width and length to cover a hectare, revolutions to cover that length, collecting seeded amounts, and adjusting the rate control until the desired rate is reached.
3) Additional details on calculating seeding rates based on drill specifications and adjusting row spacing using the planting disc configuration.