IC Engine.pptx
- 1. Farm Machinery and Power Engine systems
- 2. Out line Introduction Classification of I.C. Engine Four stroke and two stroke Engine I.C. Engine terminology , Difference between petrol engine and diesel engine , Two stroke cycle engines , Difference between two stroke and four stroke cycle engines
- 3. Fuel System Lubrication System Ignition System Cooling System Governor Engine system Engine system Power transmission system Steering system Brake system Noise and vibration control Hydraulic system Tractor system
- 4. Introduction Heat engine is a mechanical device or machine which converts the heat energy to mechanical work. Or Heat engine is an equipment which generate thermal energy and transforms it into mechanical energy. Mechanical work Heat Energy Engine
- 5. Internal Combustion Engine the working fluid consists of a combustible fluid placed inside a cylinder these engines, the fluid undergoes combustion inside the cylinder and expands. External Combustion Engine The combustion takes place outside the cylinder. Heat then needs to be transferred to the cylinder where work is done. Steam engines are an example of external combustion engines.
- 6. Classification of Engine 2- stroke 4 -stroke 1. Air cooled 2. Water cooled 1.Spark ignition 2. Compression ignition Internal combustion IC – Engine External combustion EC - Engine
- 7. I. C. ENG INES E. C. ENGINES Fuel combustion take place inside the cylinder. Fuel combustion take place outside the cylinder. Compact in size and more efficient. Larger in size and less efficient. Low initial cost. More initial cost. Working fluid is mixture of air and fuel. Working fluid is steam. Easier and quick starting of these engines. Starting is difficult and more time is required. Costly fuels are required like petrol and diesel. Cheaper fuel may be used like coal. More suitable for mobile applications. Less suitable for mobile applications.
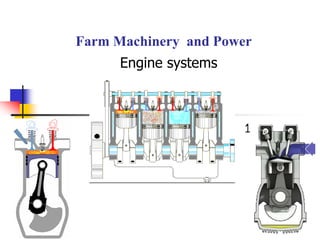
- 8. Cylinder Piston Piston rings Connecting rod Crank and crankshaft Valves Flywheel Crankcase Camshaft Timing gear Engine Component
- 9. Cylinder Part of the engine where fuel is burnt and power is developed. Inside diameter is called as bore. Sleeve is fitted tightly in the cylinder to prevent wearing of block.
- 10. Close fitting hollow – cylinder plunger moving to and fro in the cylinder. Function – power developed by the combustion of fuel is transmitted by piston to the crank-shaft through the connecting rod. Piston
- 11. Piston Rings Metallic rings inserted into groves provided at top end of the piston. Function – it maintains a gas-tight joint between the piston and the cylinder. Piston Rings are of two type 1. Compression Ring 2. Oil Ring
- 12. Connecting Rod Link that connects the piston and crankshaft by means of pin joint. Function – A connecting rod, also called a con rod, is the part of a piston engine which connects the piston to the crankshaft. Together with the crank, the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotation of the crankshaft
- 13. Crankshaft The crankshaft is a moving part of the internal combustion engine (ICE). It's main function is to transform the linear motion of the piston into rotational motion. The pistons are connected to the crankshaft through the connecting rods. The crankshaft is mounted within the engine block. Camshaft A camshaft is a rotating object— usually made of metal— that contains pointed cams, which converts rotational motion to reciprocal motion. Camshafts are used in internal combustion engines (to operate the intake and exhaust valves), mechanically controlled ignition systems and early electric motor speed controllers. Valves These are devices which control the flow of intake and exhaust gases.
- 14. Fly wheel Flywheel, heavy wheel attached to a rotating shaft so as to smooth out delivery of power from a motor to a machine. The inertia of the flywheel opposes and moderates fluctuations in the speed of the engine and stores the excess energy for intermittent use. Mounted on crankshaft to maintain uniform rotation of crankshaft. Crankcase Enclosure for crankshaft and sump for lubricating oil.
- 17. In four stroke Petrol engine the vale operating for inlet is called inlet valve and the valve operating for exhaust is called Exhaust valve. In Petrol engine SPARK plug fitted at the top of cylinder head initiates the ignition of the air fuel mixture. The piston performs four strokes to complete one working cycle. The four different strokes are ; (1) SUCTION STROKE (2) COMPRESSION STROKE (3) POWER STROKE (4) EXHAUST STROKE. Otto cycle engine
- 18. Four stroke Petrol Engine
- 19. Pistons Position Du rin g The Four Stroke Cycle
- 20. The four stroke Diesel engine is also consists of SUCTION, COMPRESSION,POWER and EXHAUST strokes. The basic construction of a four stroke diesel engine is same as that of four stroke petrol engine, except instead of spark plug, a fuel injector is mounted in its place .
- 21. Fo u r Stroke Diesel E n g i n e
- 22. Suction stroke Compression stroke Power stroke Exhaust stroke Four stroke petrol engine
- 23. SUCTION STROKE Inlet is open exhaust is closed. Piston moves from TDC to BDC. Crankshaft revolves half the rotation. Cranking Petrol air mixture drawn into cylinder due to pressure difference.
- 24. COMPRESSION STROKE Both inlet and exhaust are closed. Piston moves from BDC to TDC. Crankshaft revolves half the rotation. Cranking Petrol air mixture is compressed to a ratio of 1:11. This mixture is ignited by spark plug.
- 25. POWER STROKE Piston moves from TDC to BDC. Crankshaft revolves half the rotation. burnt gases generate energy and force the piston to move down.
- 26. EXHAUST STROKE exhaust is open and inlet is closed. Piston moves from BDC to TDC. crankshaft revolves half the rotation. energy for this stroke is supplied by flywheel. Burnt gases are expelled out through outlet port.
- 27. Four Stroke Petrol Engine
- 28. Four Stroke Diesel Engine
- 29. Inlet is open exhaust is closed. Piston moves from TDC to BDC and crankshaft revolves half the revolution. Cranking during first cycle. Due to the pressure difference air enters the cylinder through air filter. Suction stroke
- 30. Inlet and exhaust are closed. Piston moves from BDC to TDC. Cranking required in first cycle. Air will be compressed to a ratio of 1:20. Diesel oil is sprayed into cylinder by injector and auto-ignition takes place. Compression stroke
- 31. Piston moves from TDC to BDC. Inlet and exhaust valves are closed. burnt gases generate energy and force the piston to move down till injection of fuel is complete. Power stroke
- 32. Exhaust is open and inlet is closed. Piston moves from BDC to TDC. Crankshaft revolves half the rotation. Energy for this stroke is supplied by flywheel. Burnt gases are expelled out through outlet port. Exhaust stroke
- 33. Four Stroke Diesel Engine
- 35. PETROL ENGINE DIESEL ENGINE Works on Otto cycle . Works on Diesel Cycle . Petrol is used as fuel . Diesel is used as fuel . Air and fuel mixture enters in cylinder during suction stroke . Only Air is drawn during the suction stroke Low compression ratio ranging from 4:1 to 8:1 . High compression ratio ranging from14:1 to 22:1 . The compressed charge is ignited by the spark plug. The fuel injector is used in Diesel engine. High engine speed of about 3000 RPM . Low to medium engine speed ranging from 500 to 1500 RPM. The Thermal efficiency is 25-32 % and is lower due to lower Compression ratio . The Thermal efficiency is 32-38 % and is higher due to high Compression ratio . Lighter in weight because maximum pressure and Temperature is less . Heavier in Weight because maximum pressure and temperature is high . Less Costlier . More Costlier . Maintanence cost is Less . Maintanence cost is Slightly higher . Easier starting even in cold weather . Difficult to start in cold weather . Running cost Higher because petrol is Costlier . Running cost is Less because diesel is Cheaper .
- 38. Two stroke Engine Four stroke Engine
- 39. STROKE ENGINE TWO STROKE ENGINE • Fourpistonstrokesrequiretocompleteonecycle . • Twocompleterevolutionsofcrankshaftisrequiredto completeone cycle. • Equaltohalfofthespeedofenginecrankshaft. Number ofpower stroke/min. n=N/2 • Powerisdevelopedineveryalternaterevolutionof crank shaft. • Thepowerisdevelopedineveryalternaterevolution, henceheavy flywheelisrequired. • TheseenginesareHeavier,largerandrequiredmore space. • Theinletandexhaustvalvearerequireandtheyare operatedby valveoperatedbyvalveoperating mechanism. • Lubricatingoilconsumptionisless . • Thermalefficiencyishigher. • MechanicalefficiencyisLowbecauseofmorenumber ofmoving parts. • TheseEnginesareusedbasicallyinHighPower ApplicationWhere more spaceisavailablelikeCars, Truck,Tractors , Busesetc. • Onlytwopistonstrokesrequiredtocompleteonecycle . • Onlyonecompleterevolutionofcrankshaftisrequiredto complete onecycle . • Equaltothespeedofenginecrankshaft. Numberof power stroke/min. n=N • Powerisalsodevelopedineveryrevolutionofcrankshaft hencefor samecylinder. • Thepowerisdevelopedineveryrevolution, hencelighter flywheel isrequired . • Theseenginearelightermorecompactandrequireless space. • Inplaceofvalve,portsareusedwhichopensandcloseby motion ofpiston itself. • Lubricatingoilconsumptionismorebecauselubricatingoil ismixed withfuel • LessThermalefficiency. • MechanicalefficiencyisHighbecauseoflessnumberof moving parts. • TheseEnginesareusedbasicallyinLowPowerApplication Where lessspaceisavailablelikeMopeds,Scooters,Motor cycleetc. FOUR STROKE ENGINE
- 40. I.P. B.P. mech I.P. mf C.V it B.P. mf C.V bt a ir it re l
- 41. 1 (r) air 1 1 1 (1) 1 1 (r) air 1 mf kg /kWh B.P. SFC
- 42. Fuel : It is a substance consumed by the engine to produce energy Eg. Petrol, Diesel, kerosene etc. Fuel system s. no. Name of the fuel API degree Specific Gravity Calorific value (Kcal/kg) 1. Light diesel oil (LDO) 22 0.920 10300 2. High speed diesel (HSD) 31 0.820 10550 3. Power Kerosene 40 0.827 10850 4. Petrol 63 0.730 11100 Important properties of oil
- 43. Quality of the fuel Volatility Calorific value of fuel Ignition quality Cetane number (Diesel fuel) Ocatne number ( Petrol fuel) Fuel test Gravity test (API degree) Distillation test Vapour pressure test Sulphur content Carbon residue test Colour test Gum test
- 44. Type of fuel system Spark Ignition Mixture of air and fuel compressed and ignited by spark Compression Ignition Air alone is compressed and fuel is injected at the end of compression stroke
- 45. Fuel system of spark ignition engine (petrol engine) 1. Fuel tank 2. Sediment bowl 3. Fuel filters 4. Fuel lift pump 5. Carburettor 6. Spark plug 7. Inlet manifold
- 46. Working of the spark ignition system
- 47. Carburettor
- 48. Fuel tank Fuel Filters Fuel Filter
- 49. Fuel supply system of diesel engine Fuel tank Fuel lift pump Fuel filters Fuel injection pump High pressure pipeline Overflow valve Fuel injectors Fig. Flow diagram Of fuel system in diesel engine
- 50. Working of Fuel system of diesel engine