Embed presentation
Downloaded 572 times

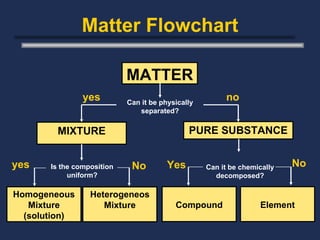











The document discusses the classification of matter into pure substances and mixtures. Pure substances are either elements or compounds, both of which have a uniform composition. Mixtures contain two or more substances mixed together, and can be either homogeneous, with a uniform composition throughout, or heterogeneous, with a non-uniform composition. Common examples of pure substances and mixtures are provided.












