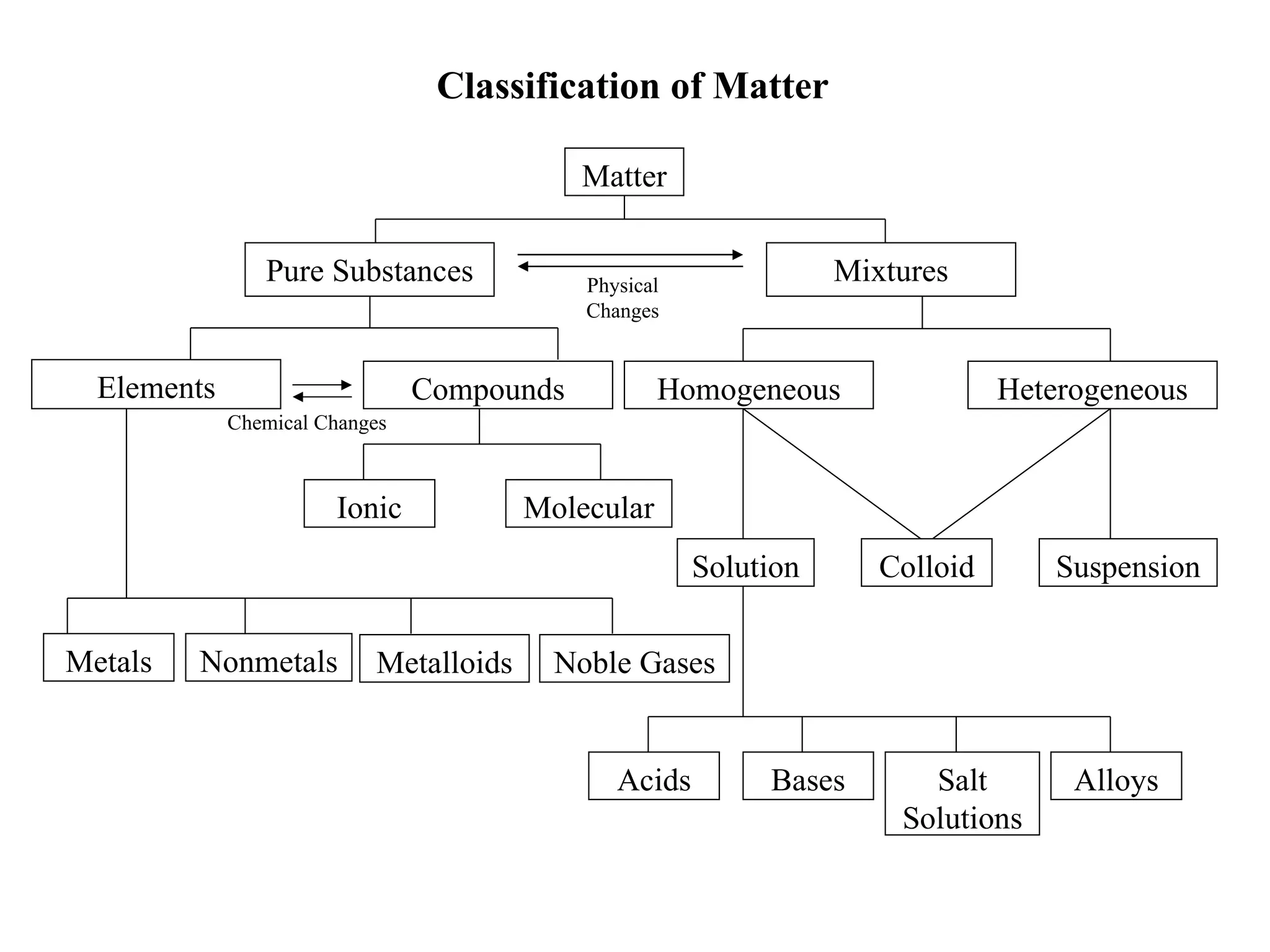
This document defines and classifies different types of matter. It describes elements as substances made of single atoms and compounds as bonded groups of elements. Pure substances include elements and compounds, while mixtures contain two or more substances mixed without chemical bonding. Mixtures can be homogeneous, appearing uniform, or heterogeneous, with distinct phases. Special types of mixtures include colloids, ores, alloys, and plated metals. The document provides examples to illustrate each classification of matter.