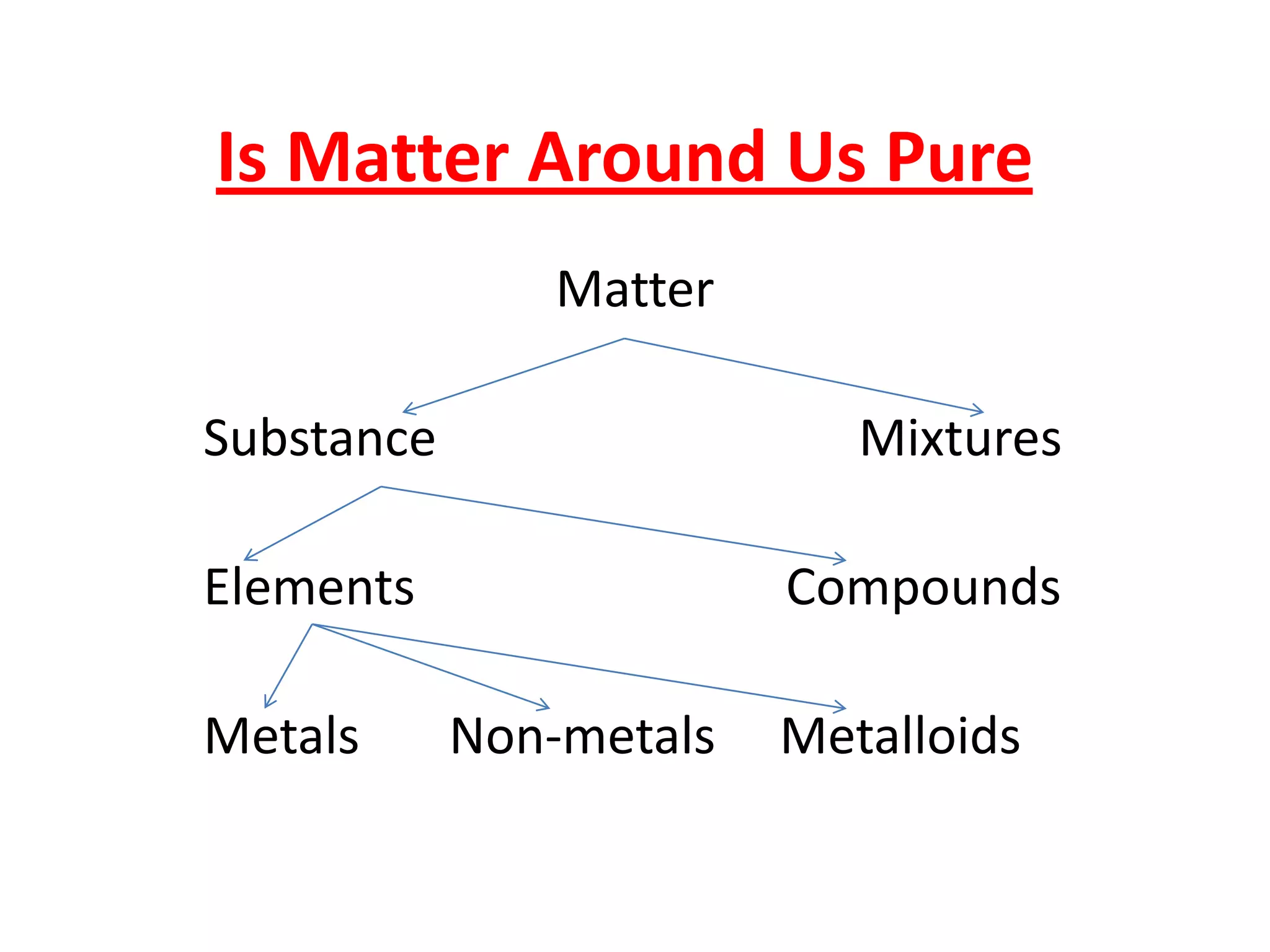
This document discusses the classification of matter into pure substances and mixtures. It defines elements, compounds, and mixtures. Elements are the simplest form of matter and cannot be broken down further. Compounds are combinations of elements that have distinct properties. Mixtures maintain the properties of their components and can be separated physically. Mixtures include solutions, suspensions, and colloids, which differ based on the size of particles and whether they are homogeneous. The document provides examples and characteristics of each type of pure substance and mixture.