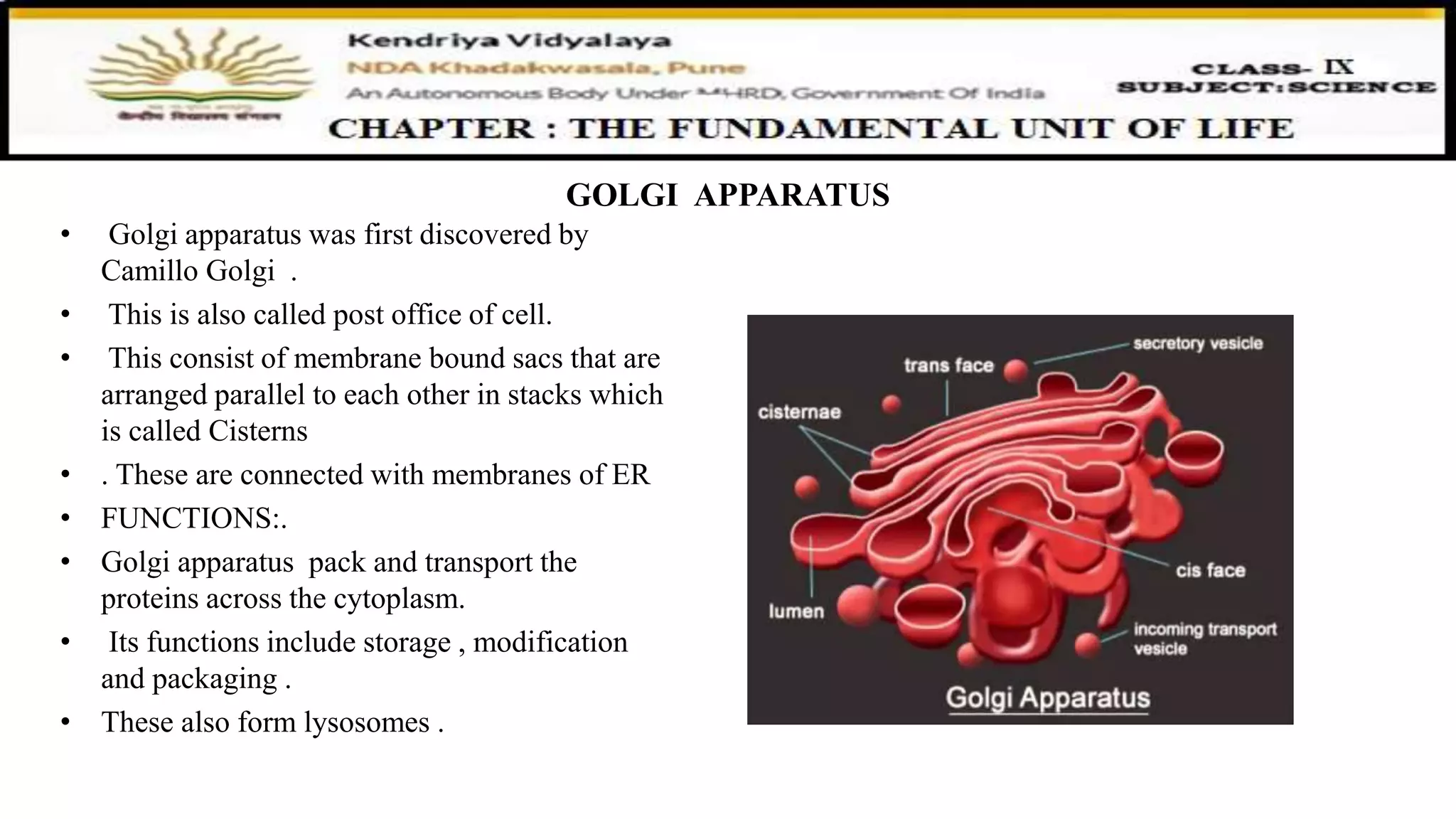
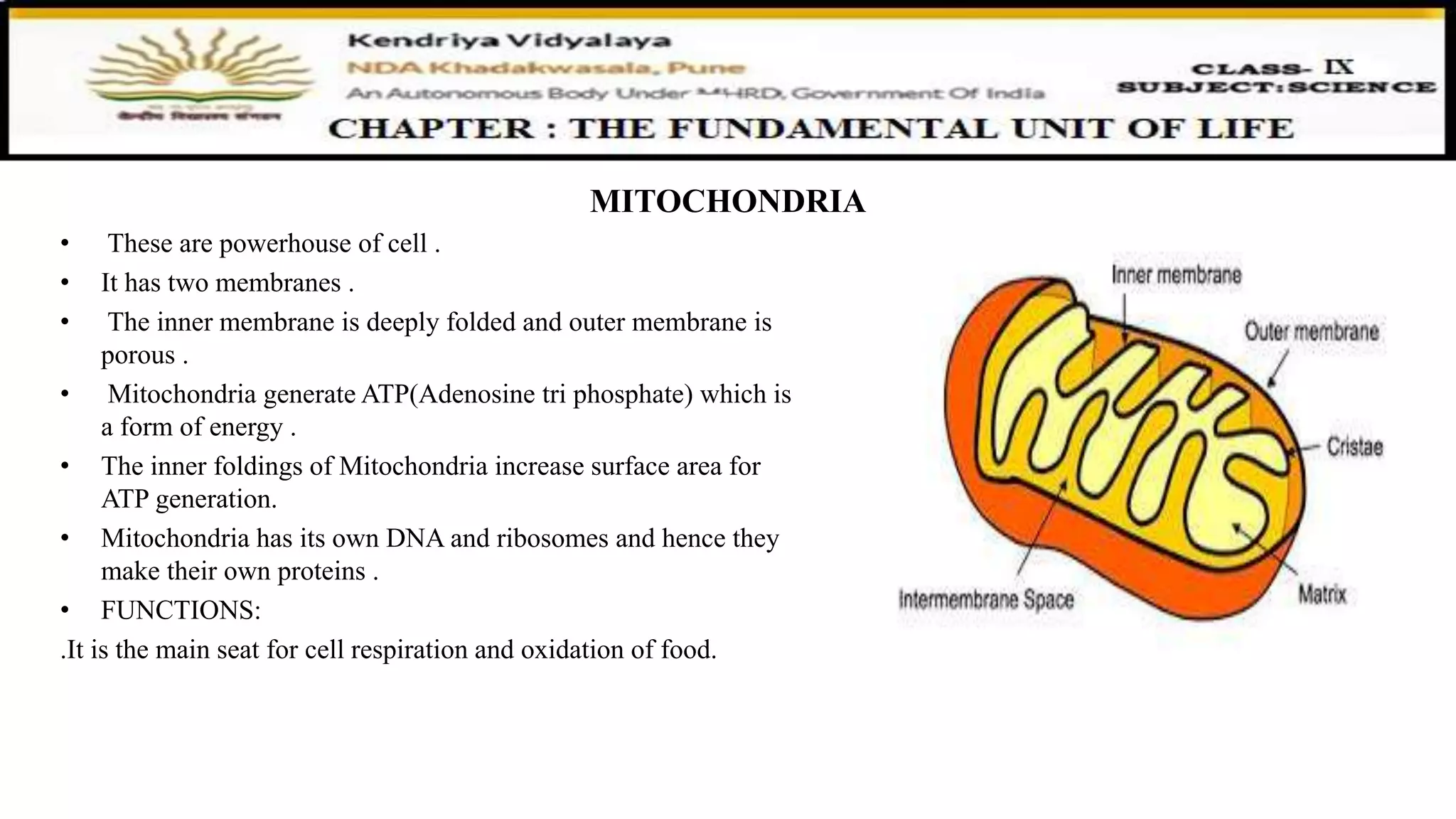
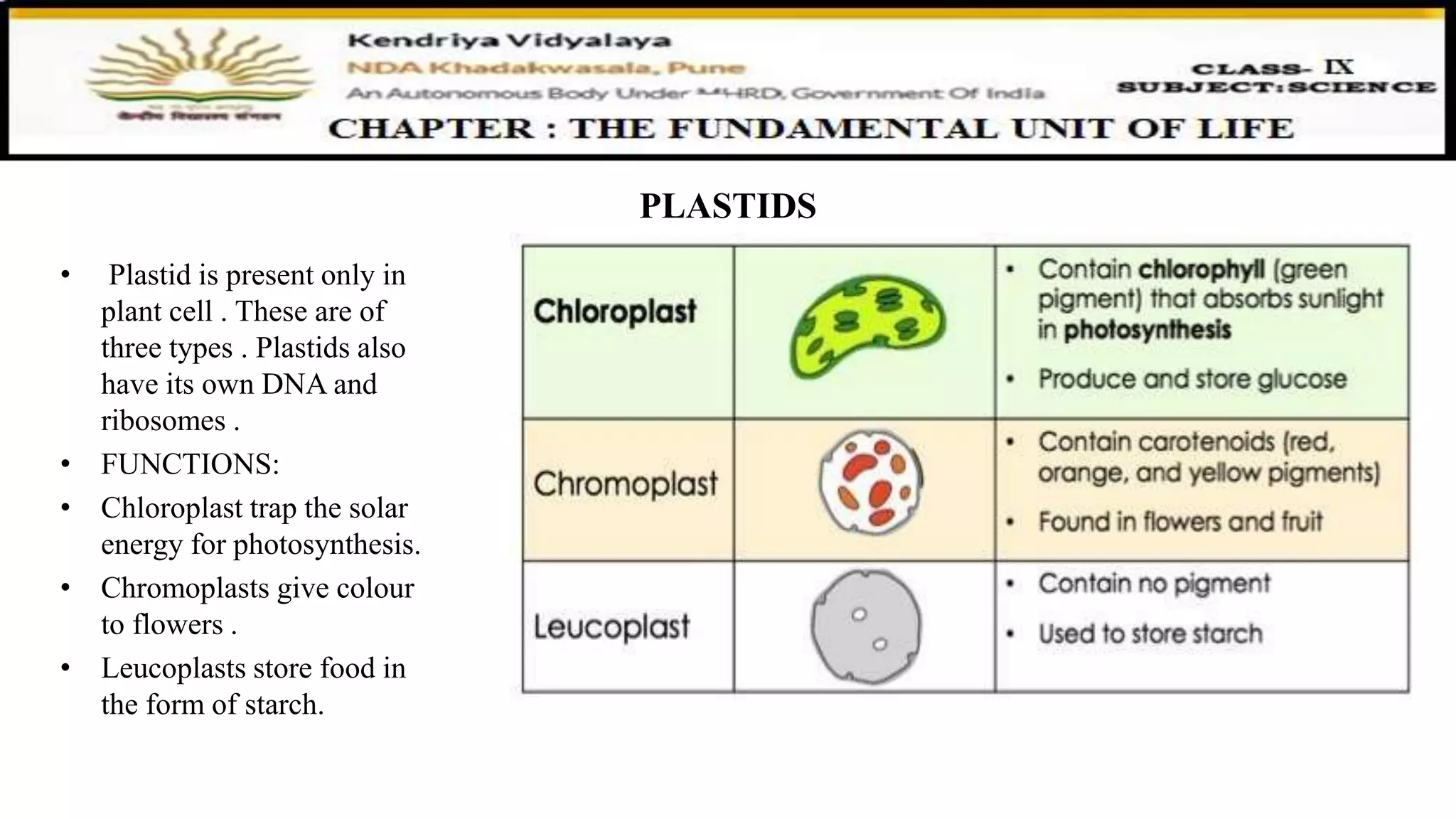
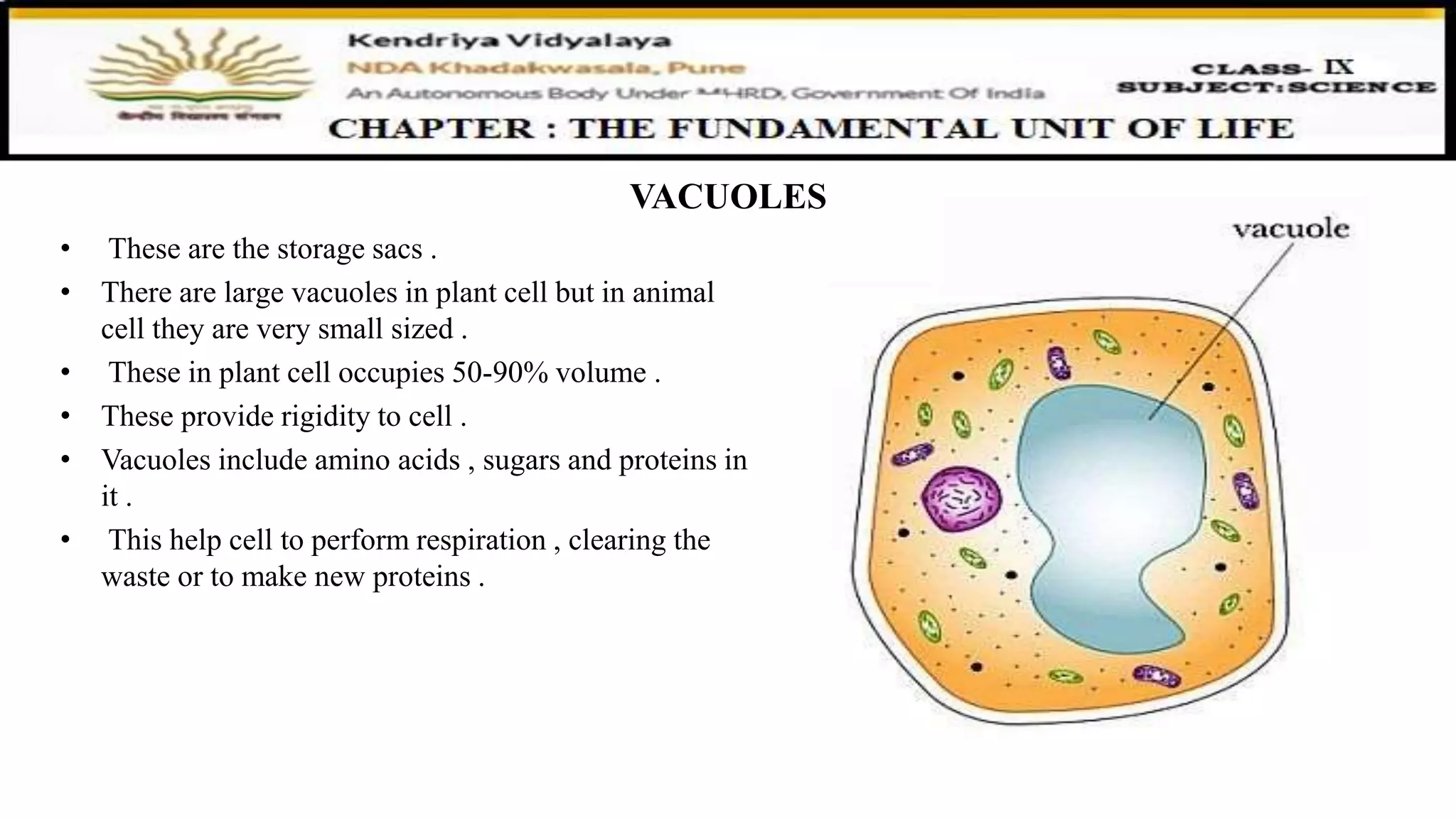
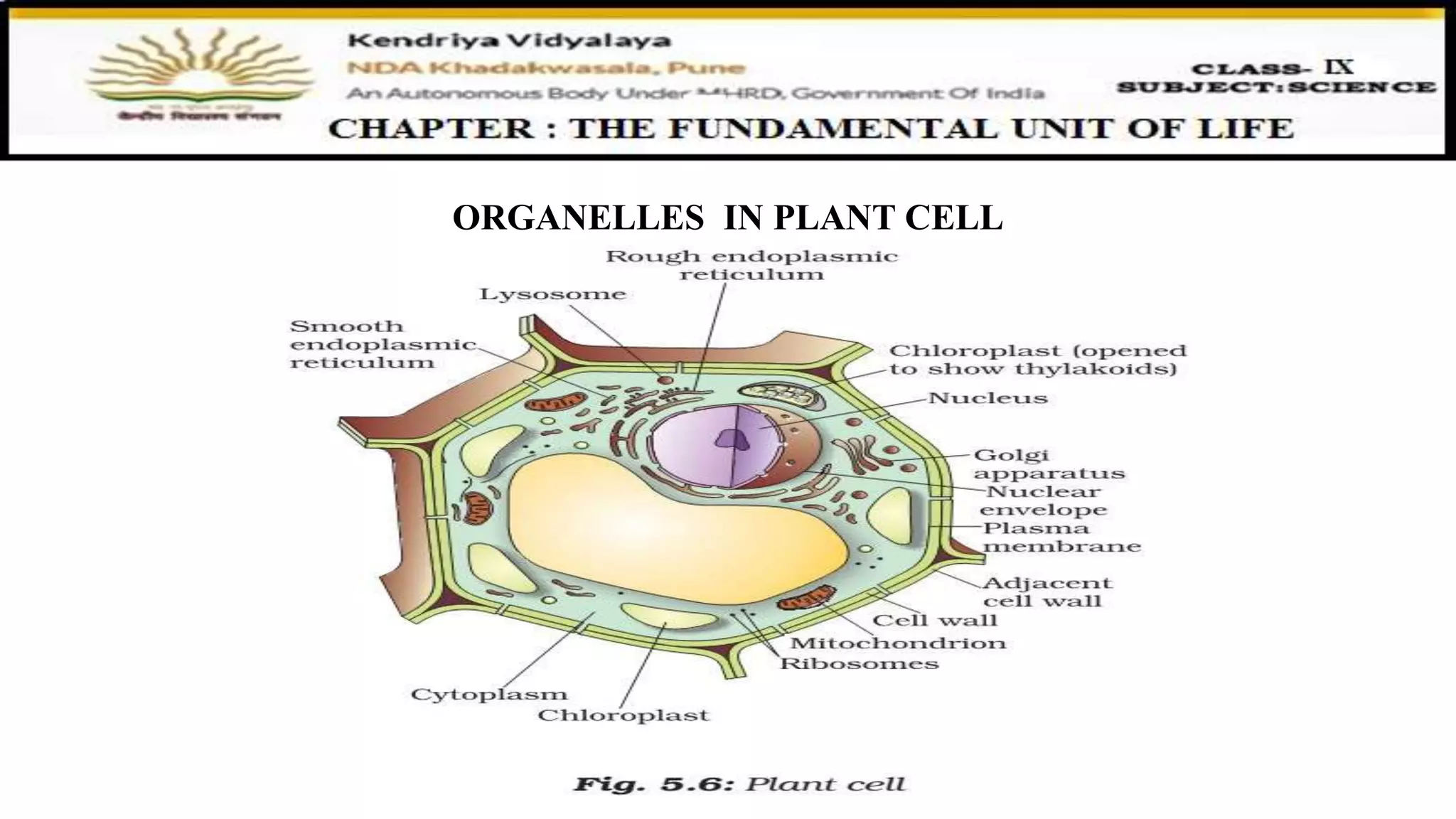
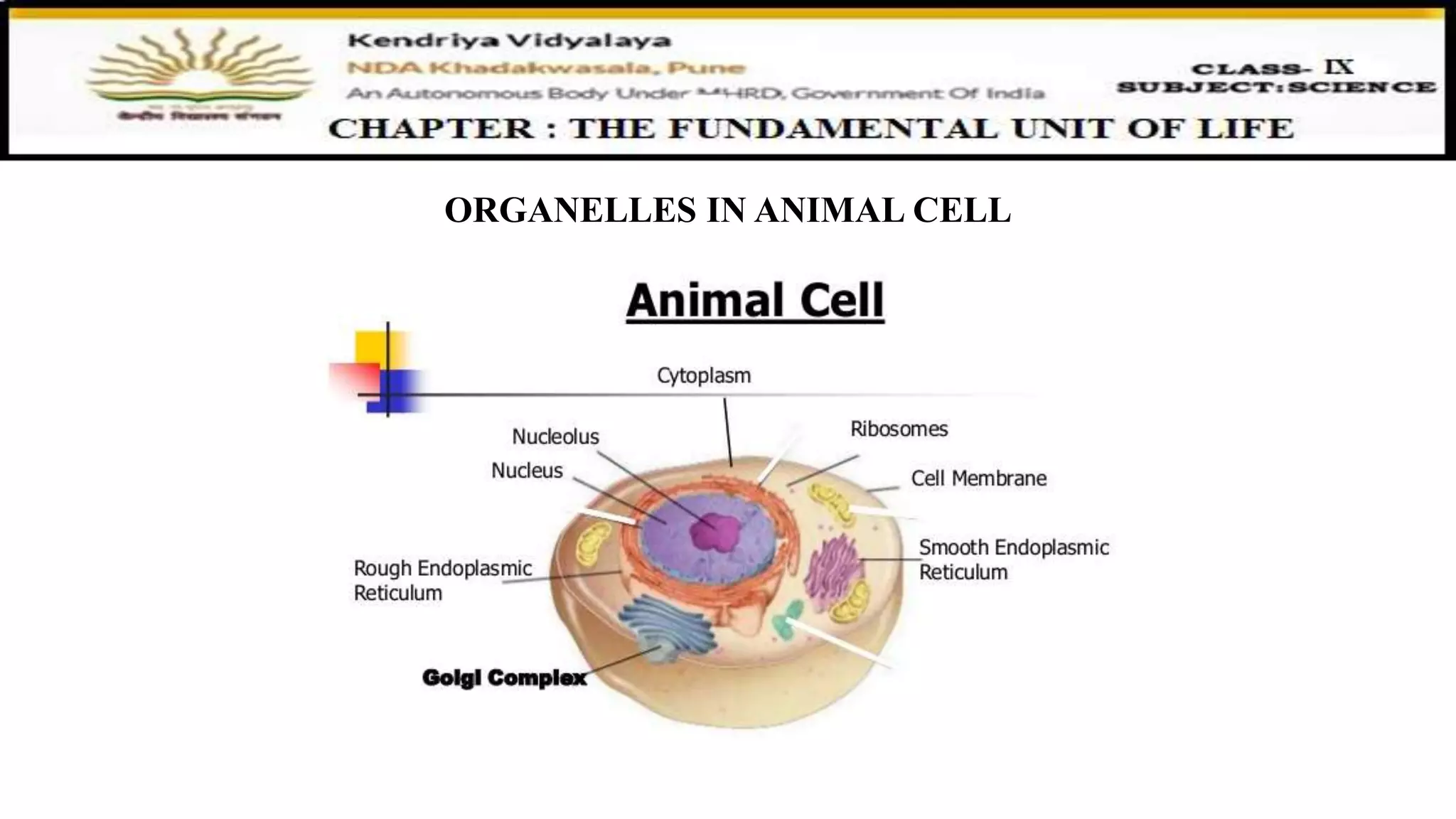
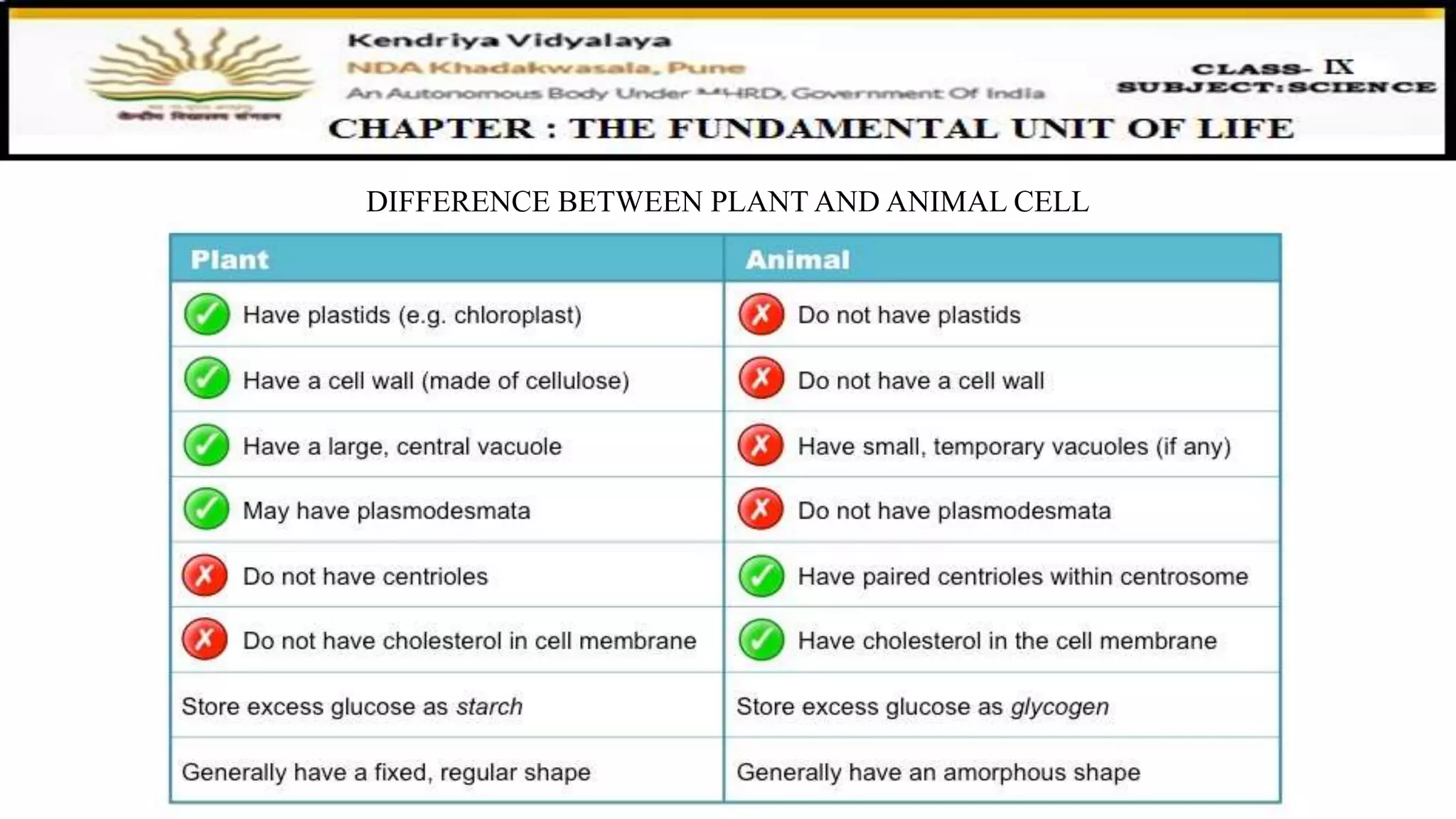
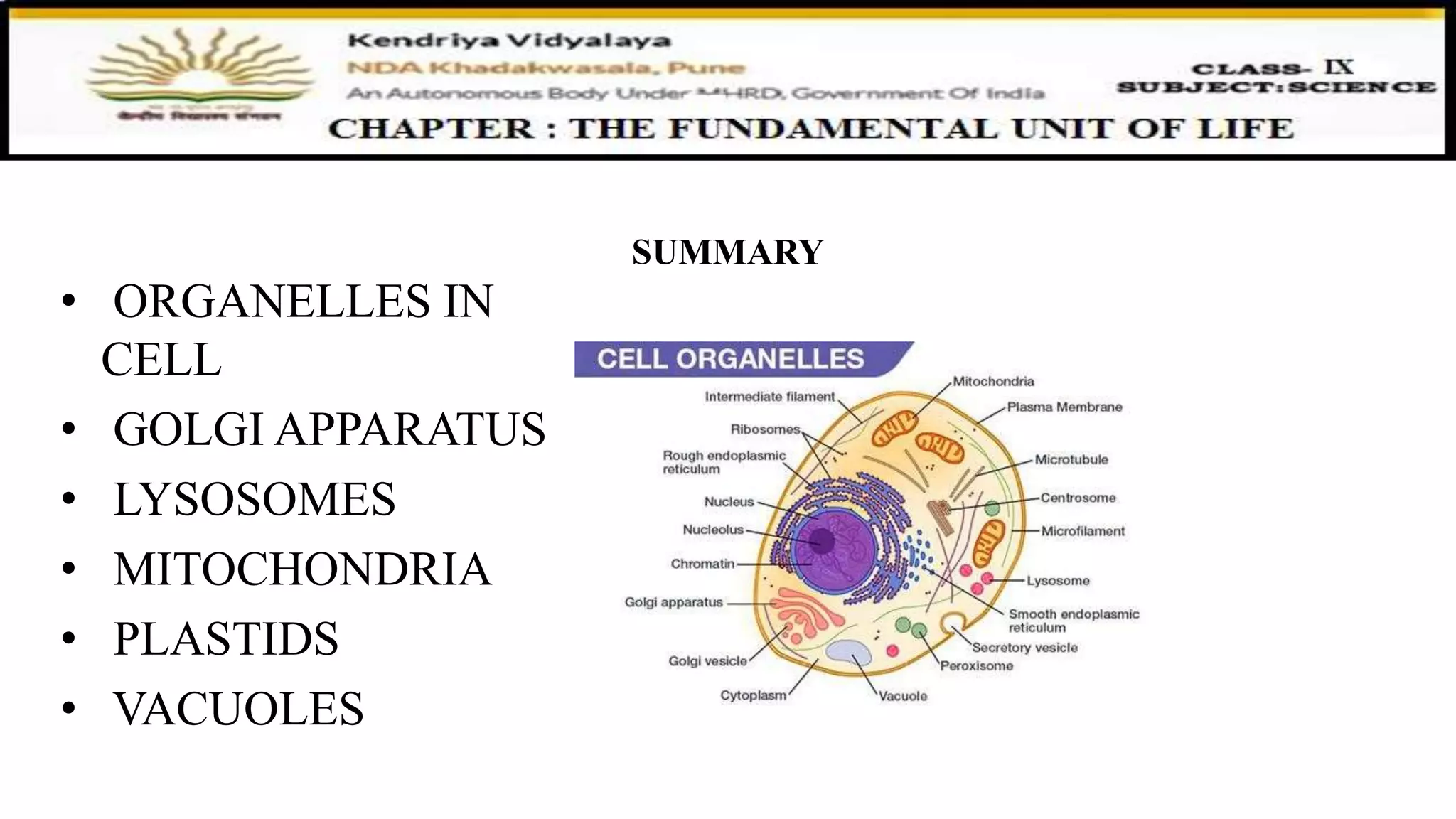
This document discusses various organelles found in plant and animal cells including the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and differences between plant and animal cells. The Golgi apparatus packages and transports proteins, lysosomes contain digestive enzymes, mitochondria generate energy, plastids aid photosynthesis in plants, and vacuoles provide storage. It also covers cell division and the process of mitosis and meiosis.