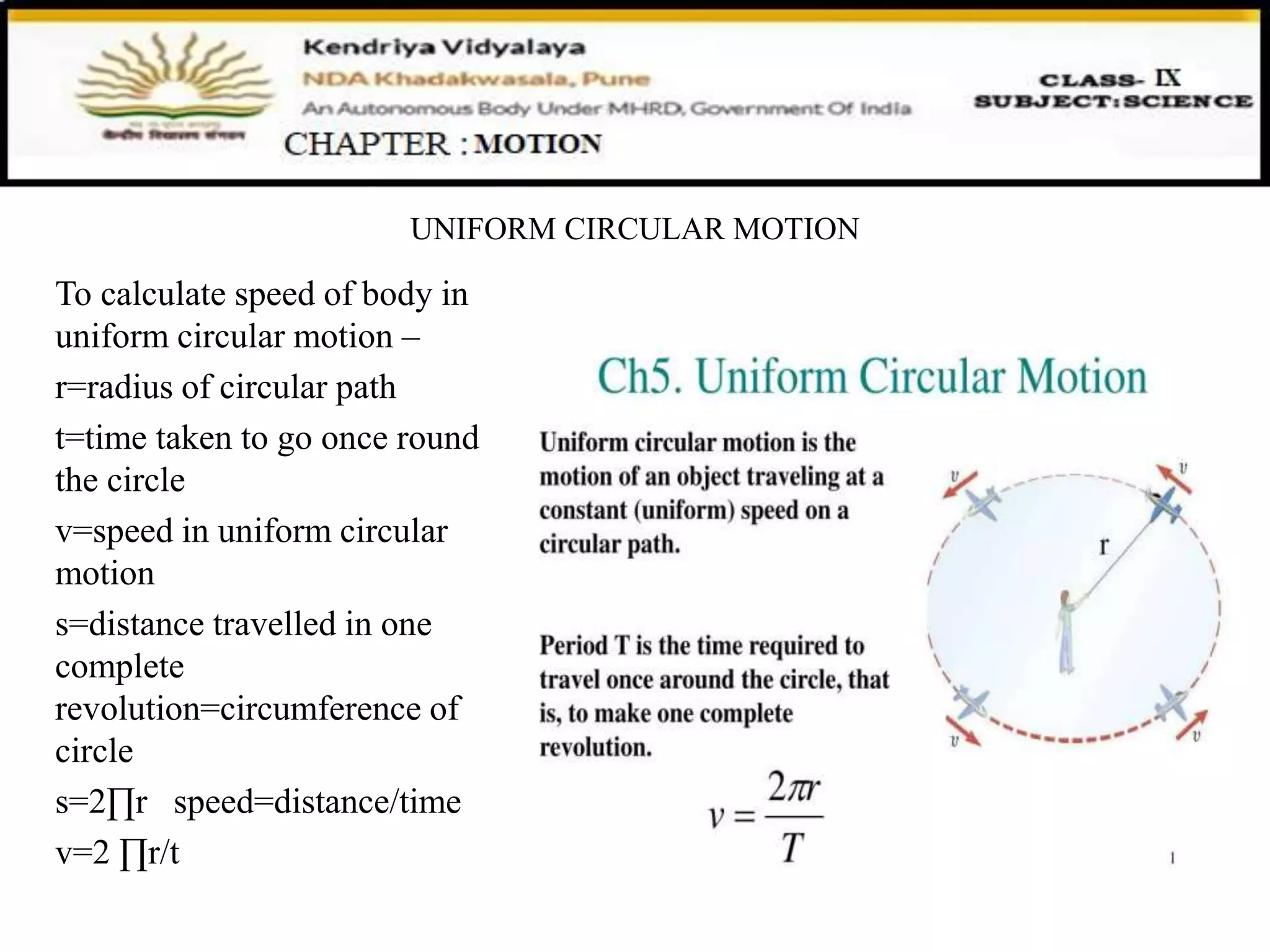
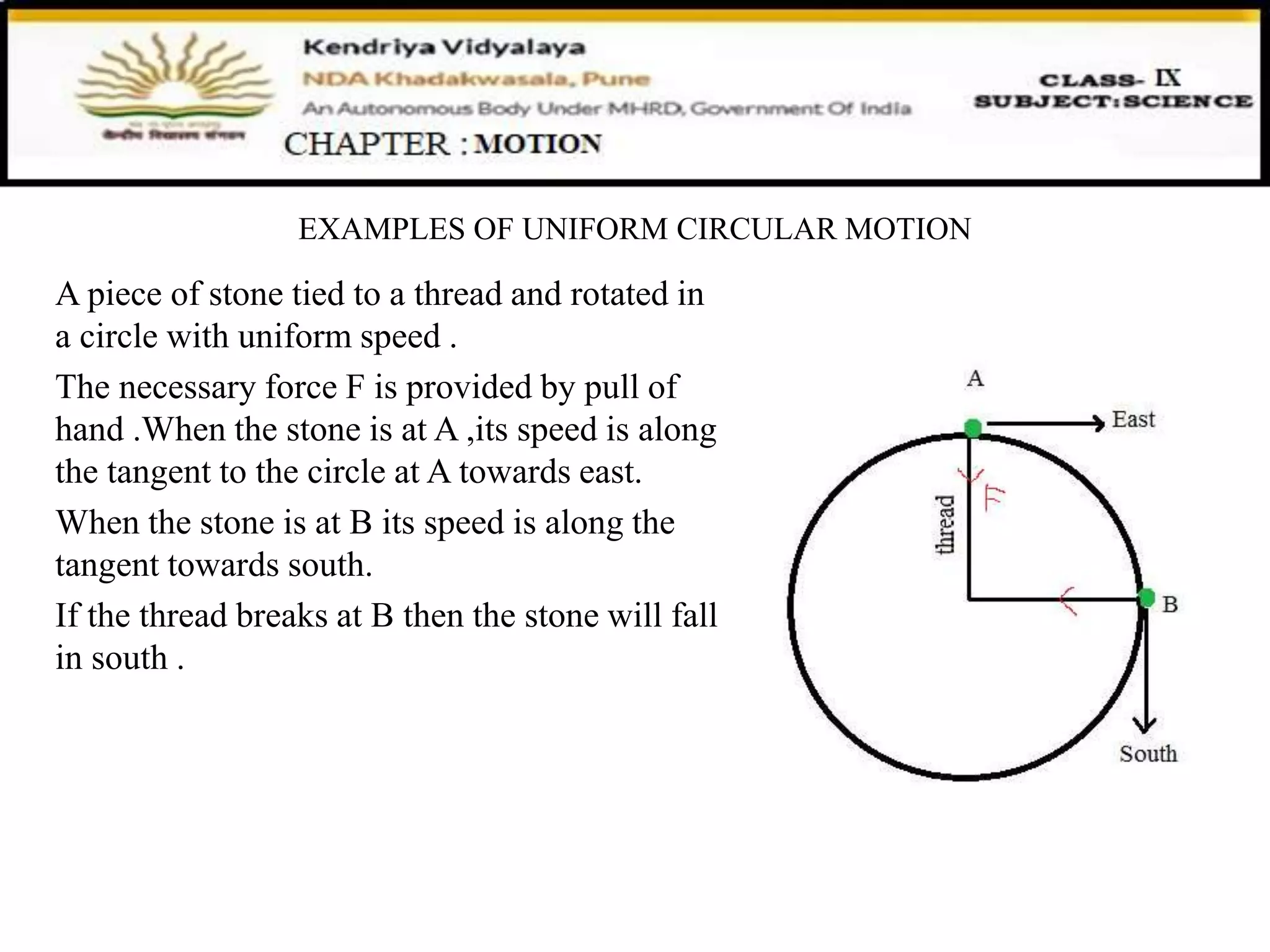
The document discusses uniform circular motion and the position-velocity relation equation. It defines uniform circular motion as motion where the speed is constant but the direction is continuously changing, requiring a centripetal force. It provides the equation for the position-velocity relation as v^2 - u^2 = 2as. Finally, it gives examples of uniform circular motion like a stone on a string being rotated in a circle and the moon orbiting the Earth.

![3.EQUATION FOR POSITION VELOCITY RELATION
As discussed ,distance travelled by a uniformly
Accelerated body in time t is given by area of
the space enclosed between velocity time graph
and time axis.
Distance travelled s=area of trapezium ODBE
=sum of parallel sides/2 * distance between
parallel sides
s=(OD+EB)/2 *OE
s=(u+v)/2 *t [v=u+at or v-u=at or t=v-u/a]
Putting value of t
s=(v+u)/2 *(v-u)/a
s=v2-u2/2a
v2-u2=2as position velocity relation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class9chmotionppt3-200707165553/75/Class-9-chapter-motion-ppt-3-2-2048.jpg)