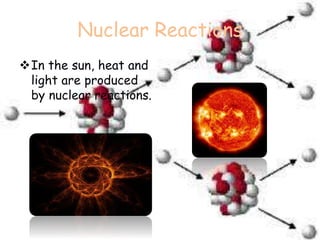
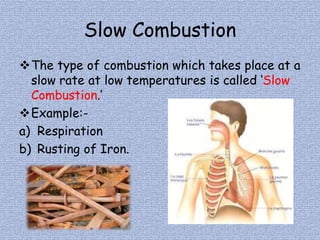
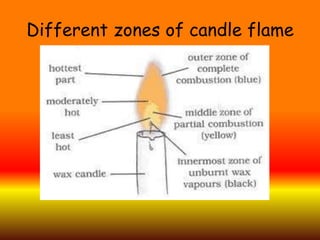
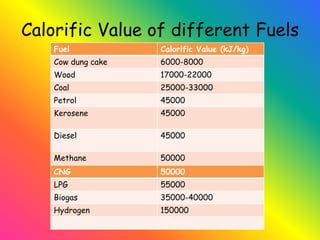
The document discusses combustion and different types of fuels. It defines combustion as a chemical reaction between a substance and oxygen that produces heat. Fuels can be solid, liquid or gas. Examples of different fuels are provided. The document also discusses flame, ignition temperature, fire extinguishers, types of combustion like rapid, spontaneous and slow combustion. It provides information on calorific values of different fuels and environmental disadvantages of fuel combustion.