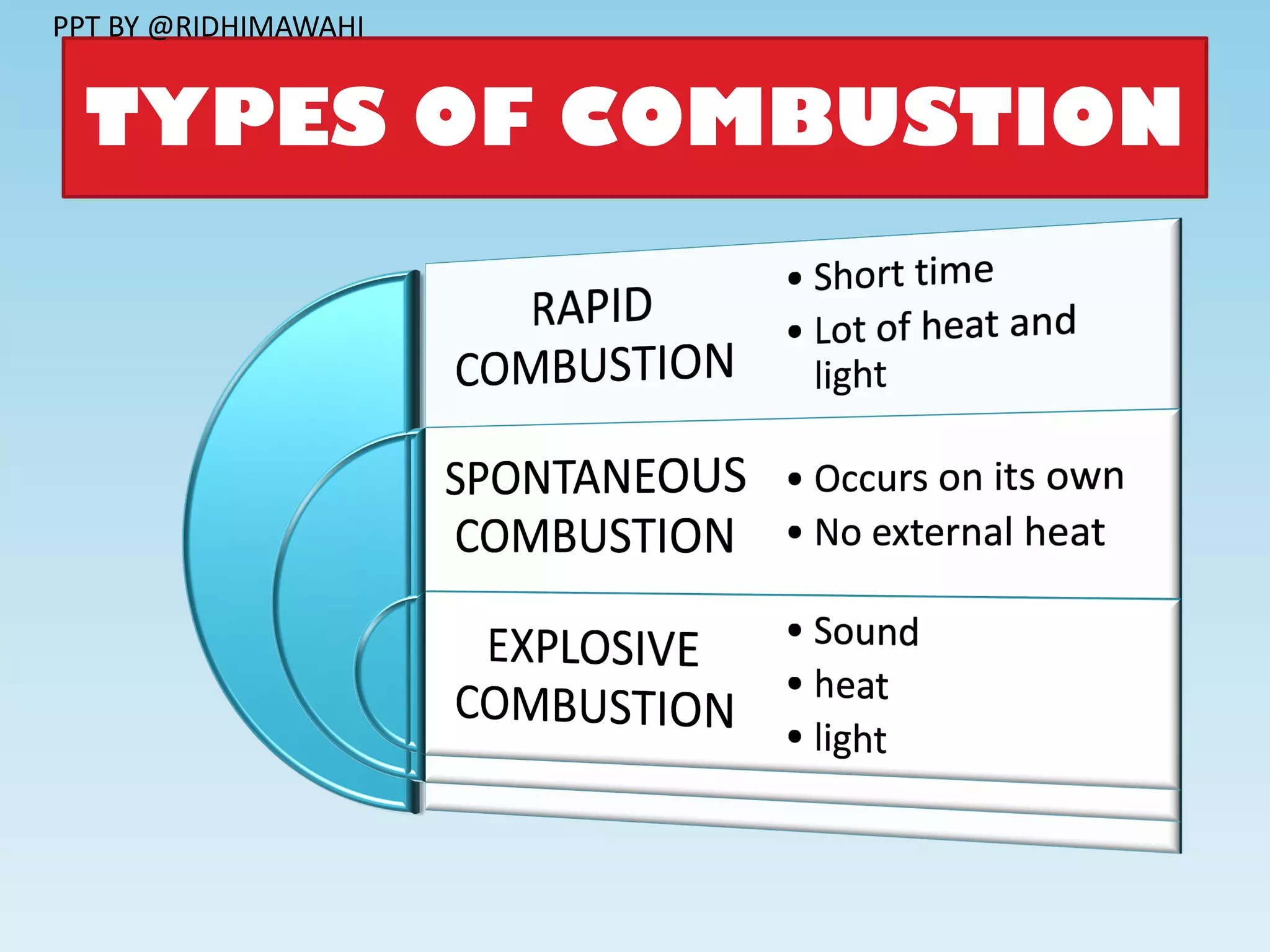
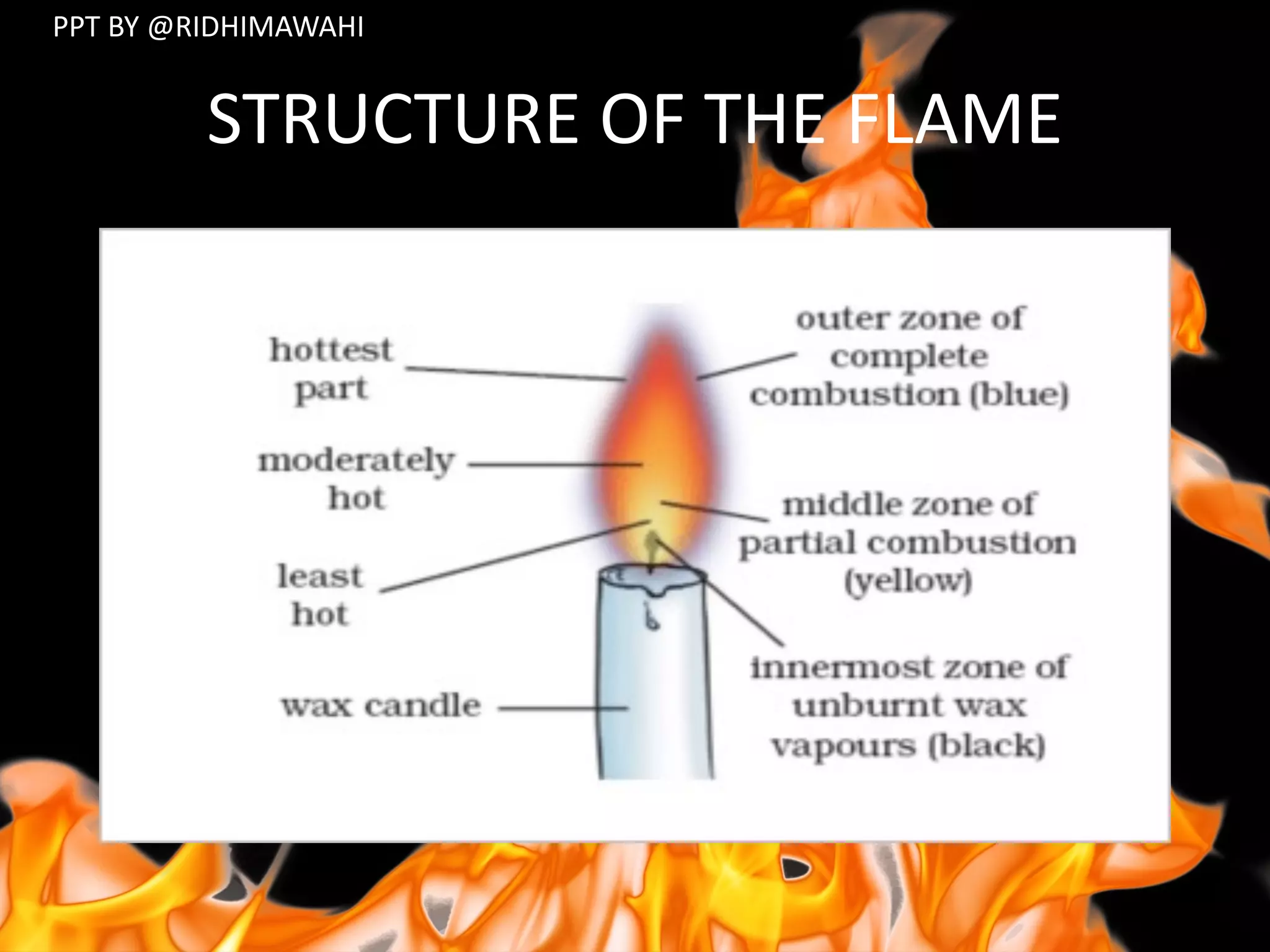
The document explains combustion as a chemical process involving the burning of a substance in the presence of oxygen, producing heat and light. It outlines types of substances (combustible and non-combustible), conditions required for combustion, ignition temperatures, and methods to control fire. Additionally, it differentiates between various combustion types, including rapid combustion, spontaneous combustion, and explosions, and describes the structure of flames.