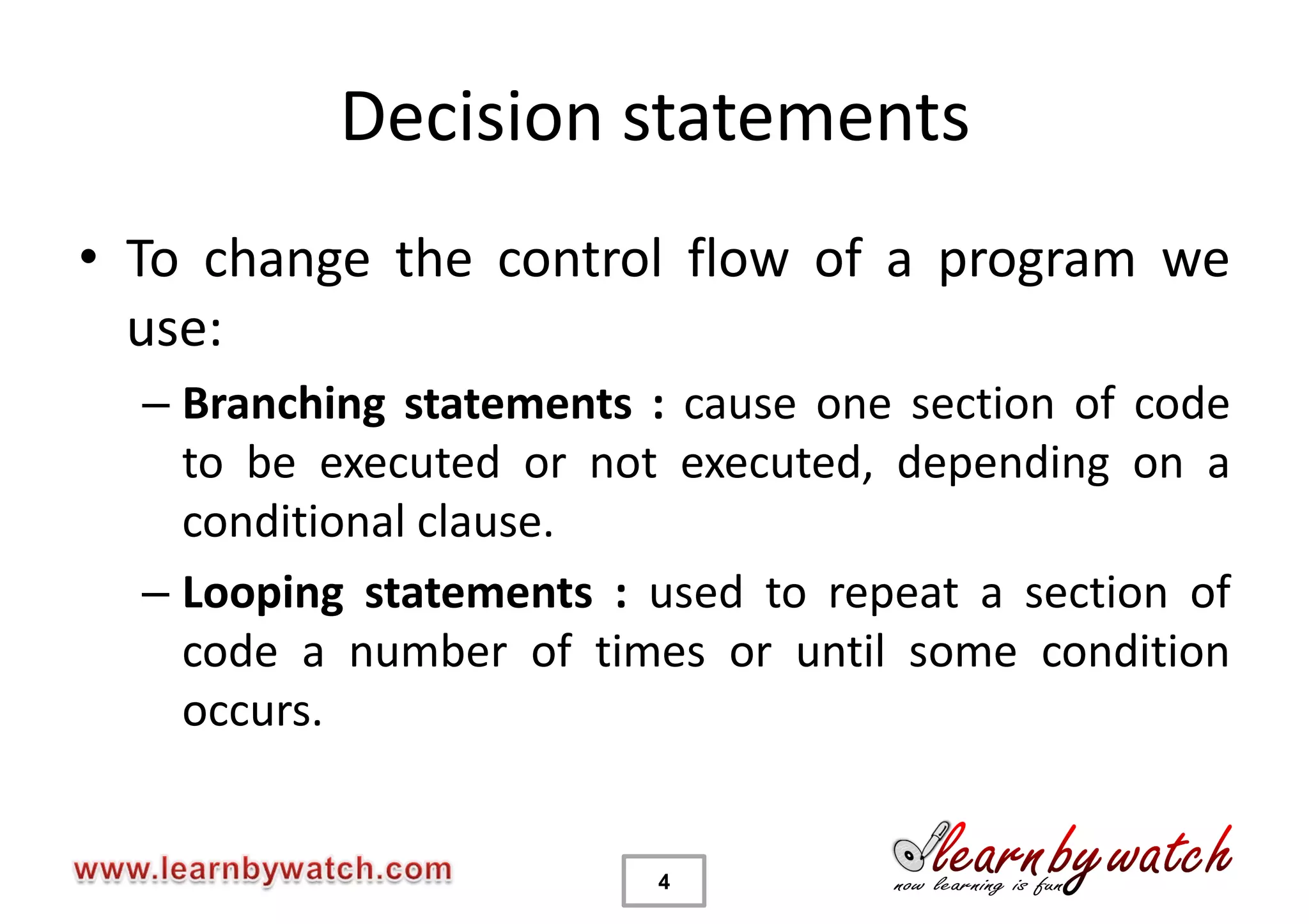
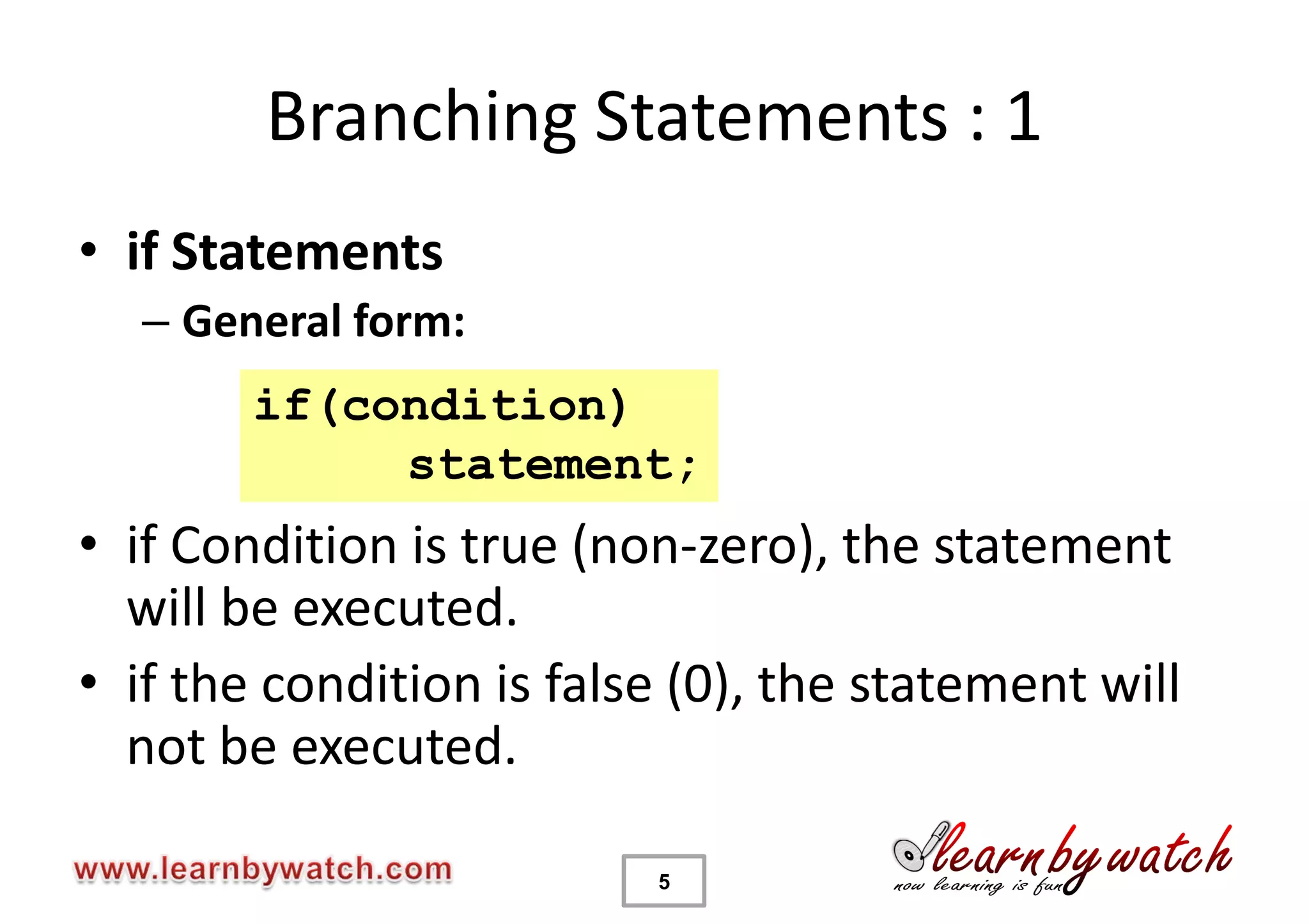
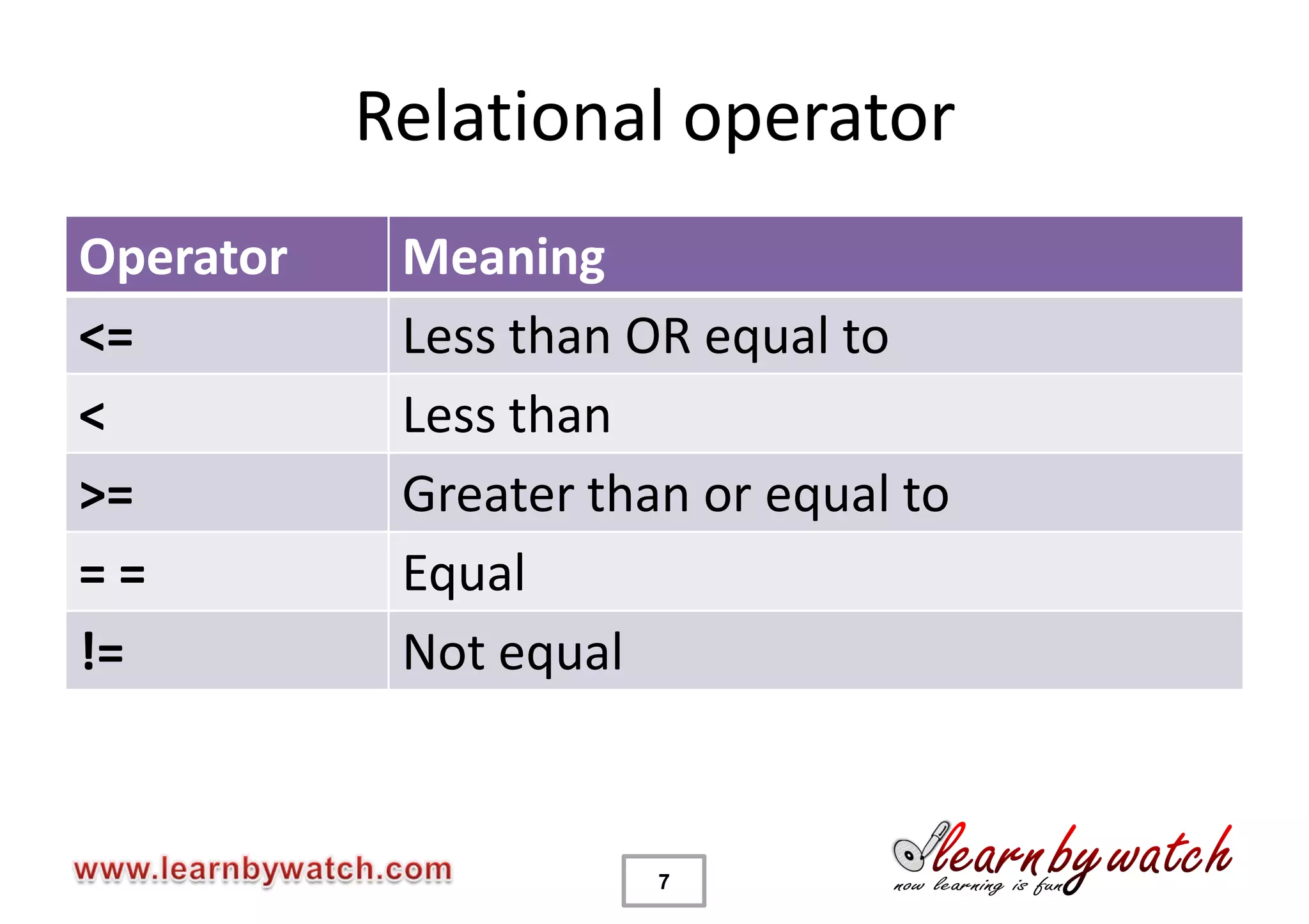
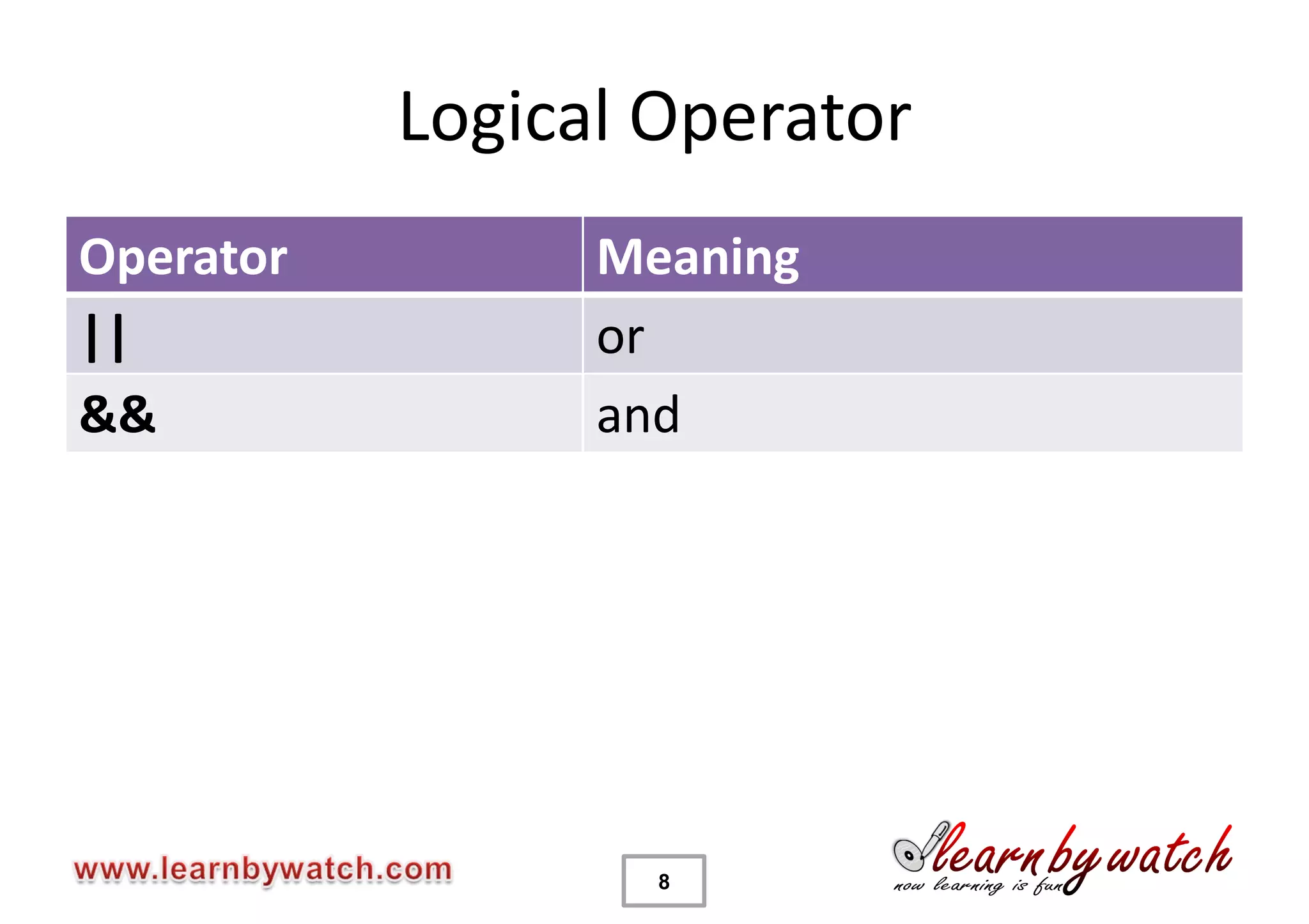
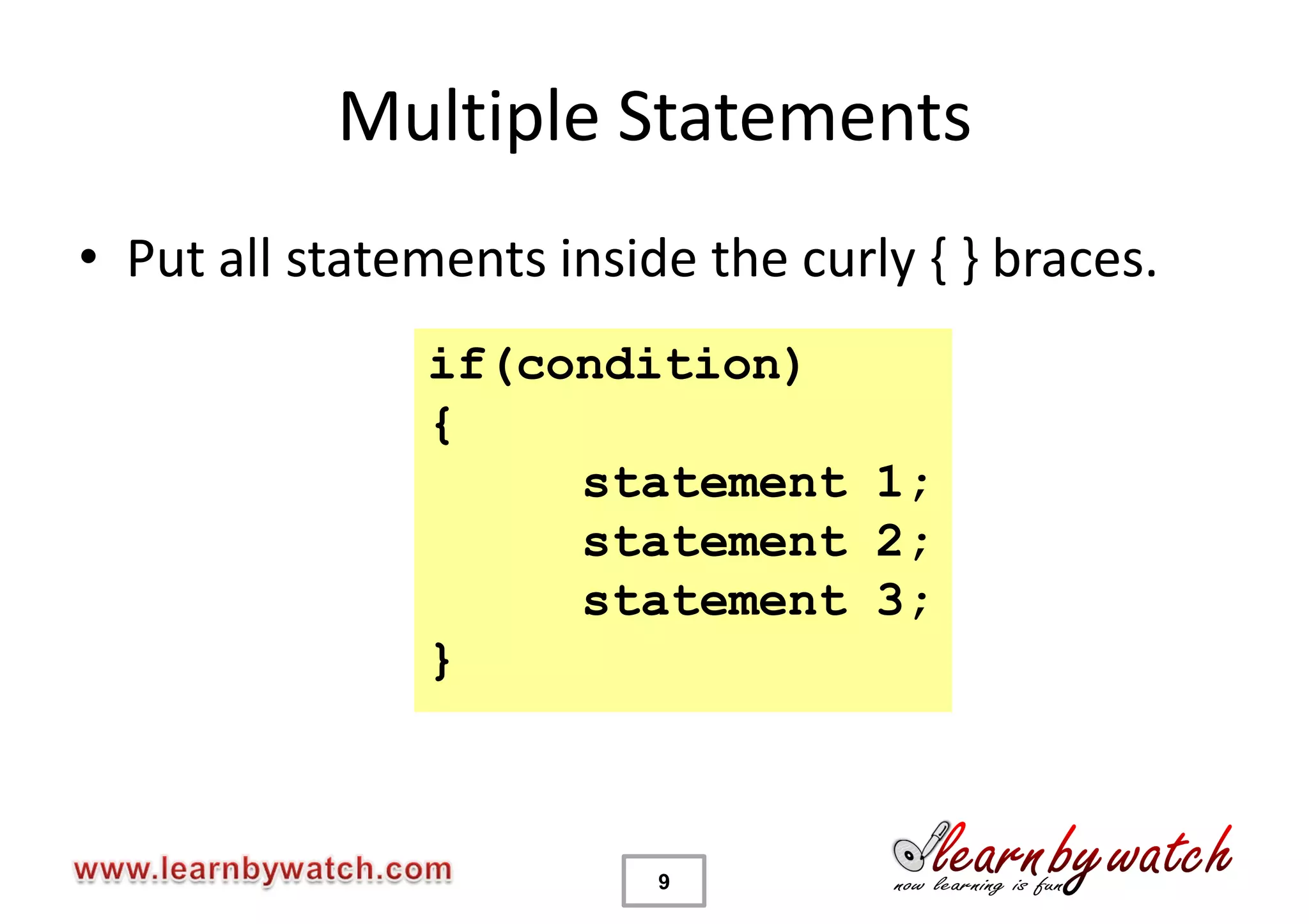
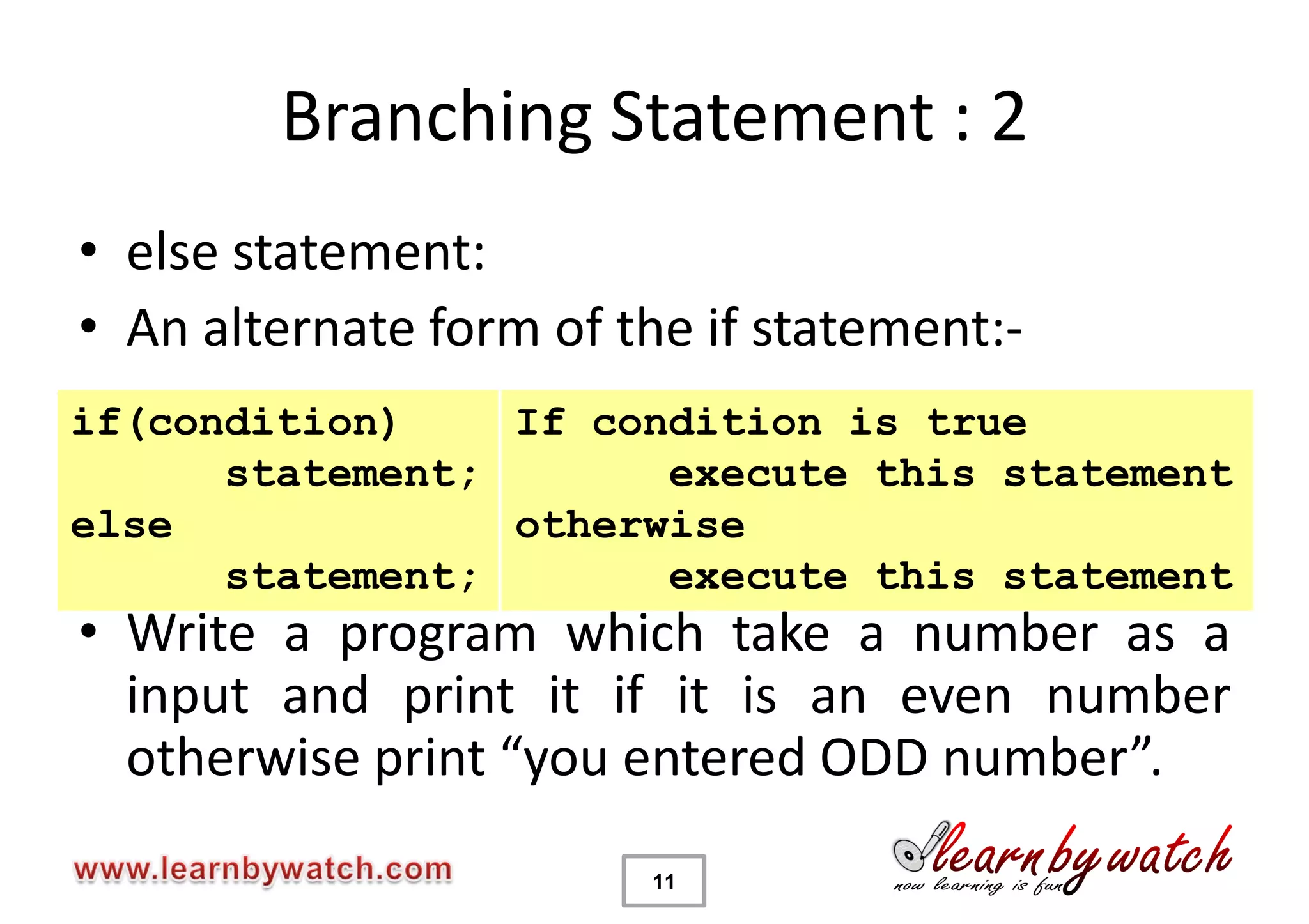
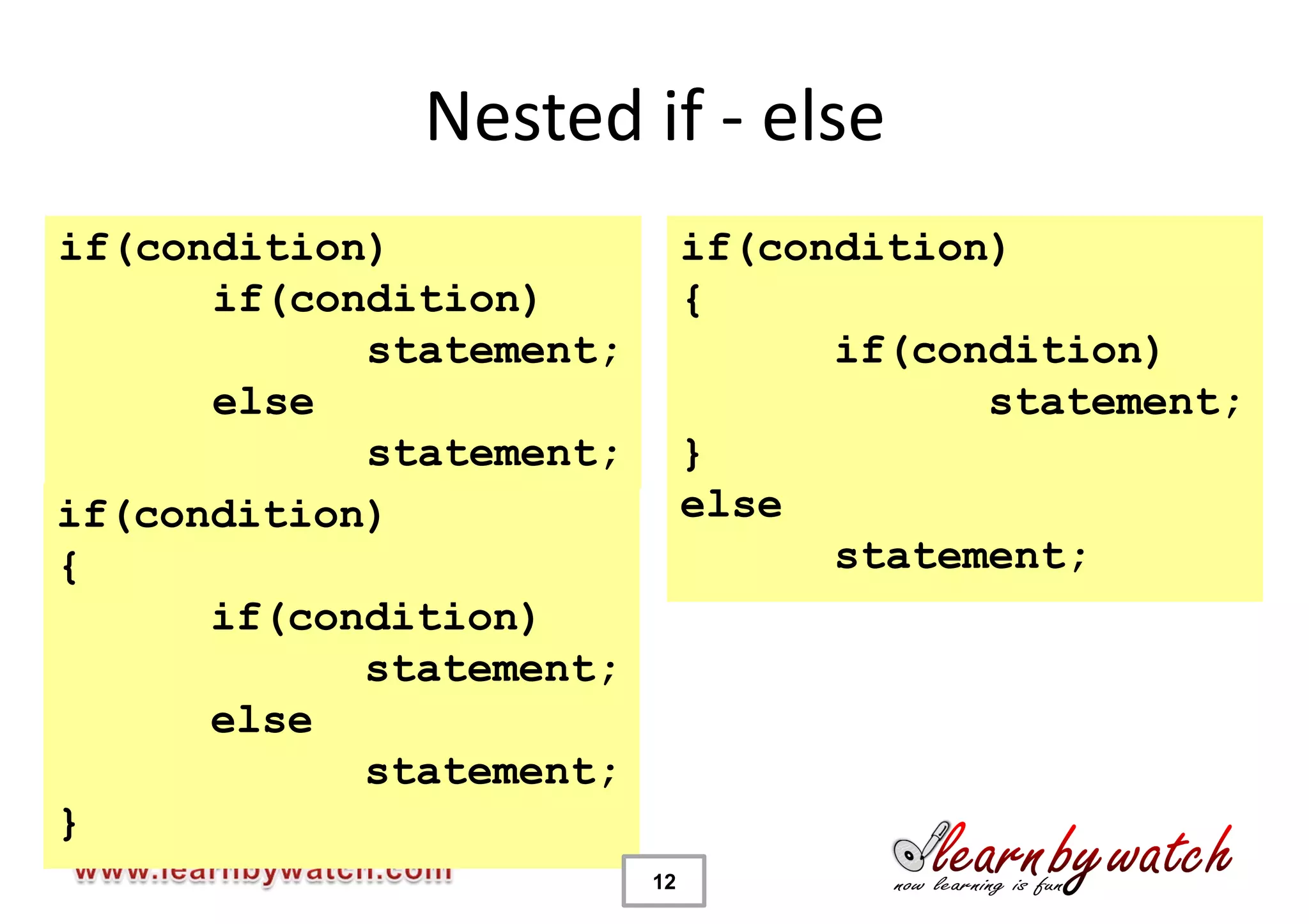
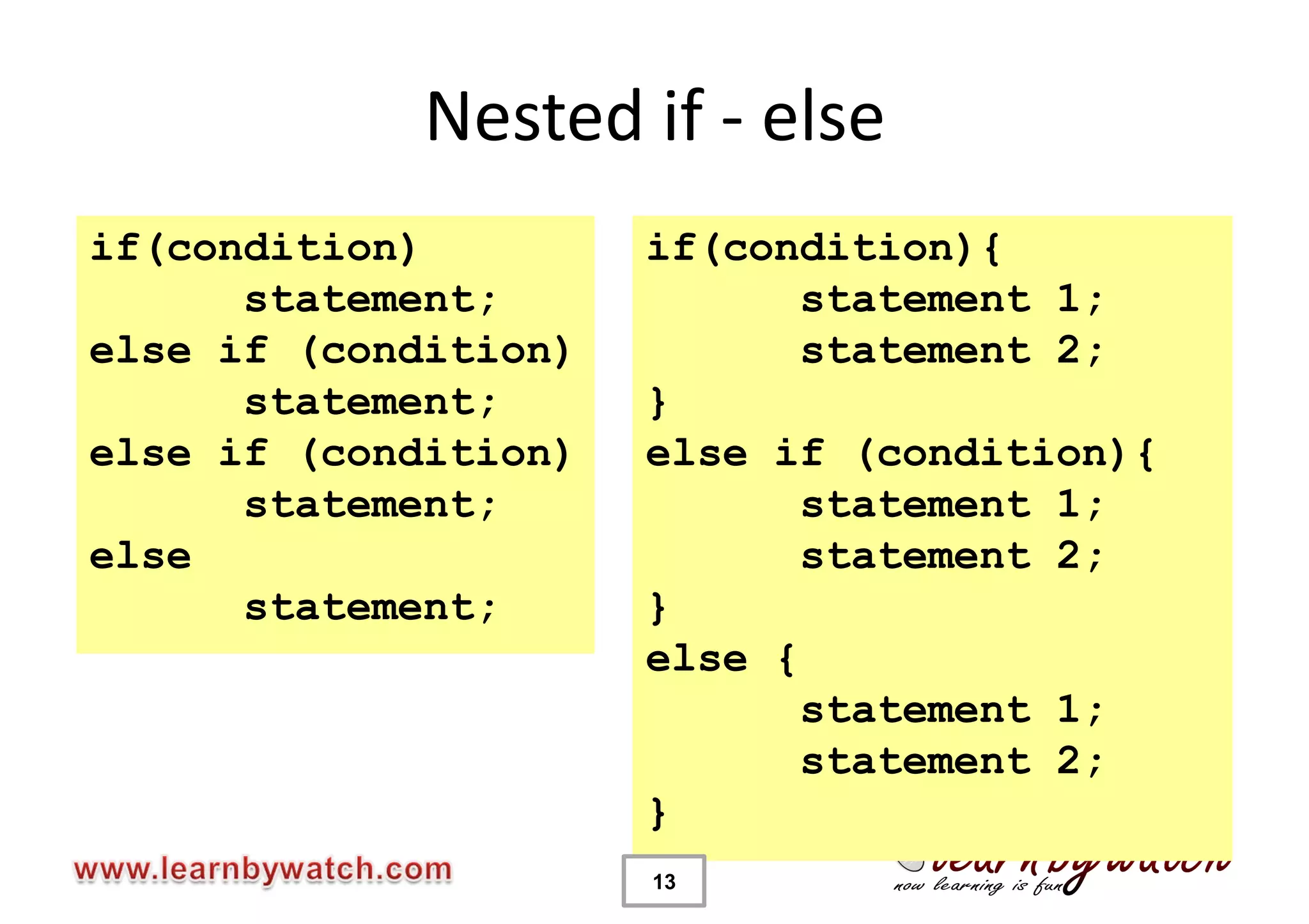
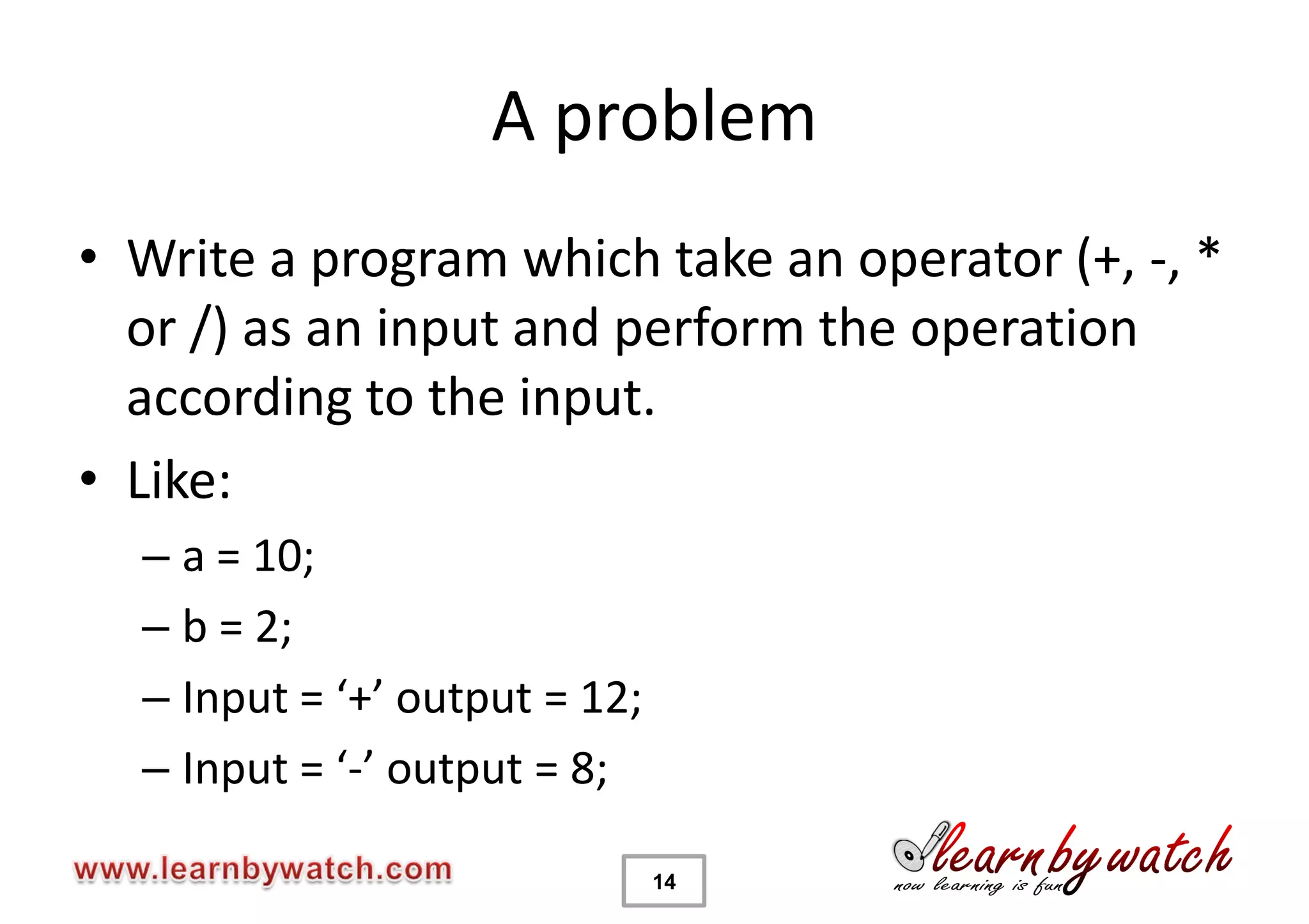
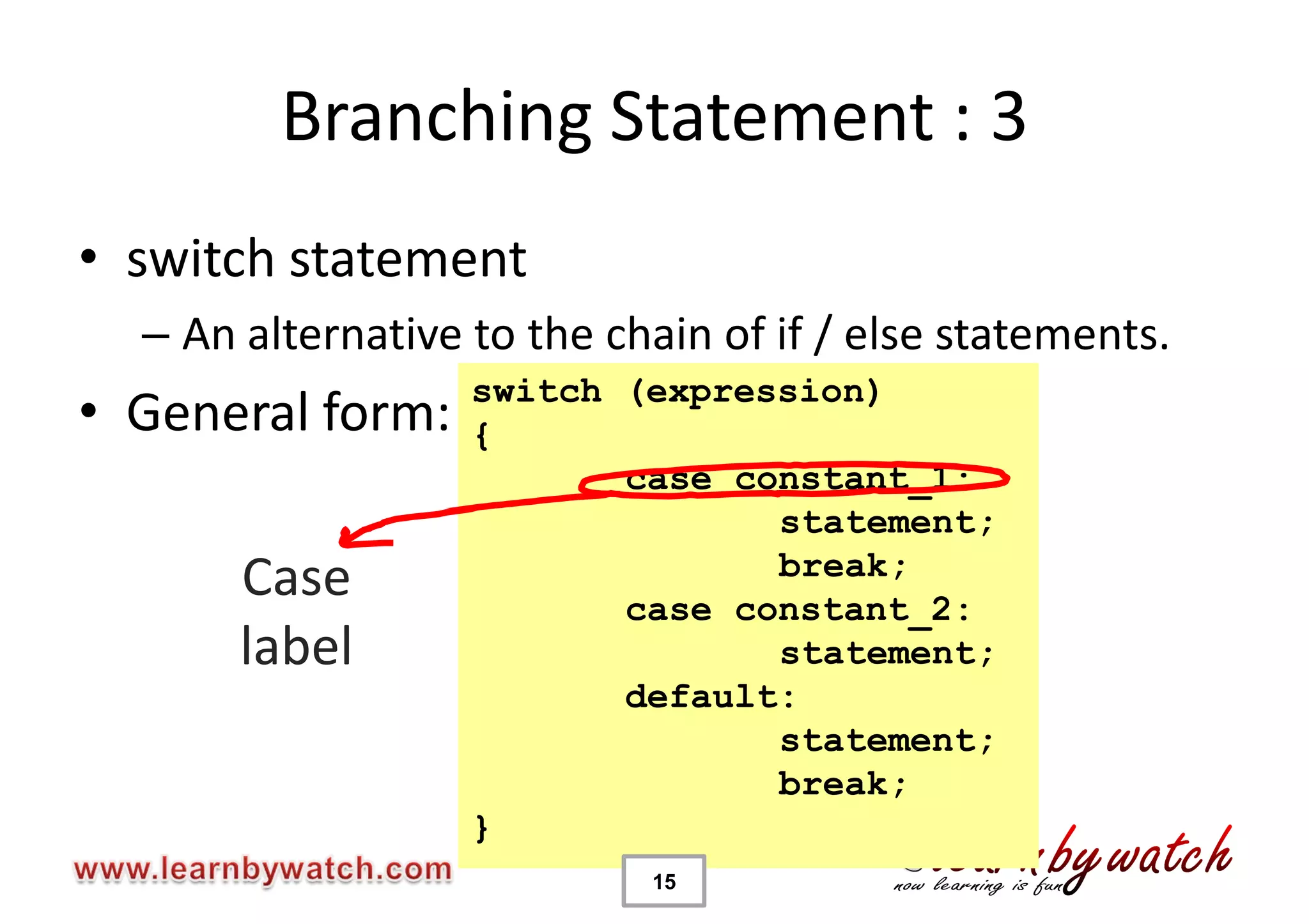
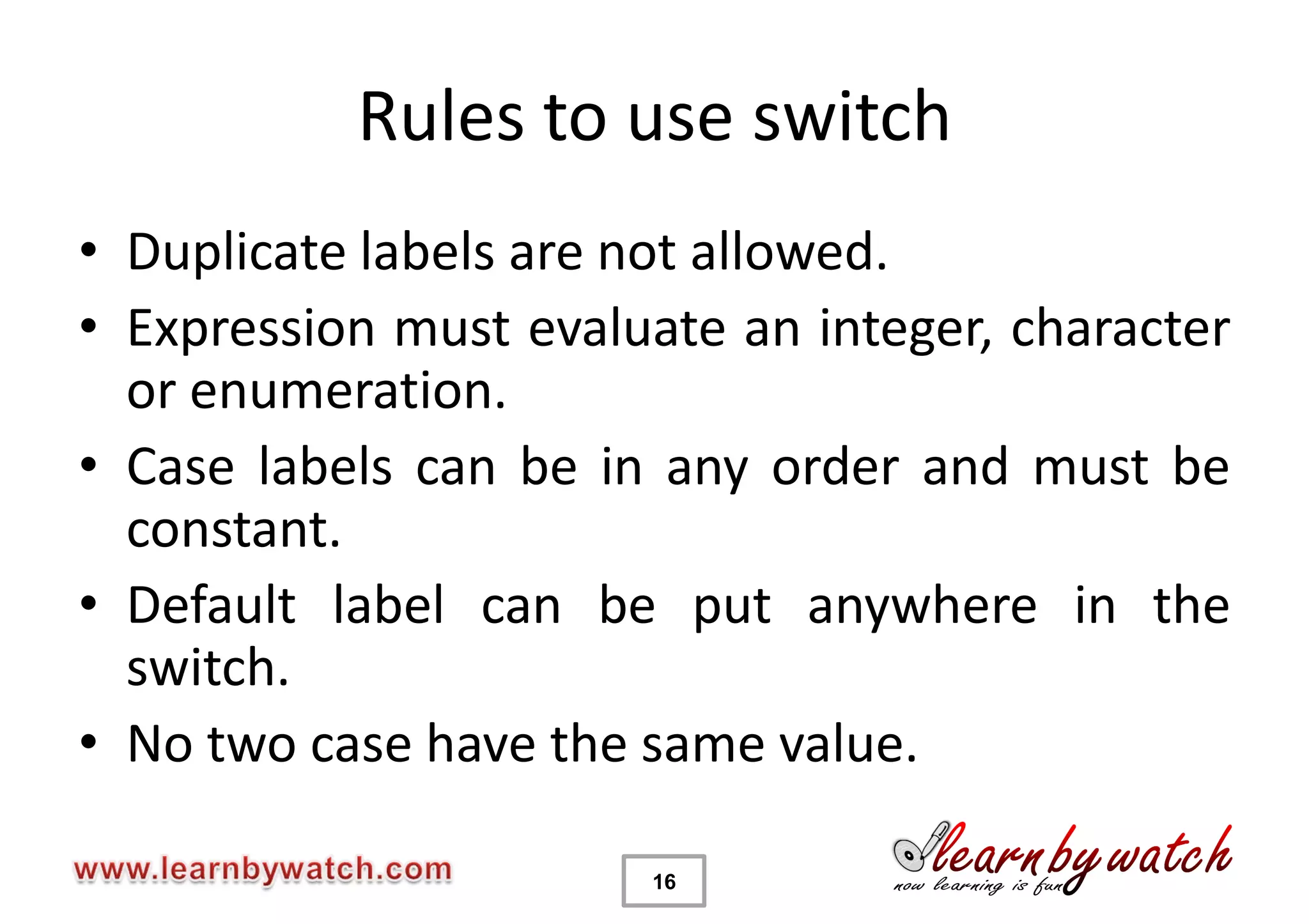
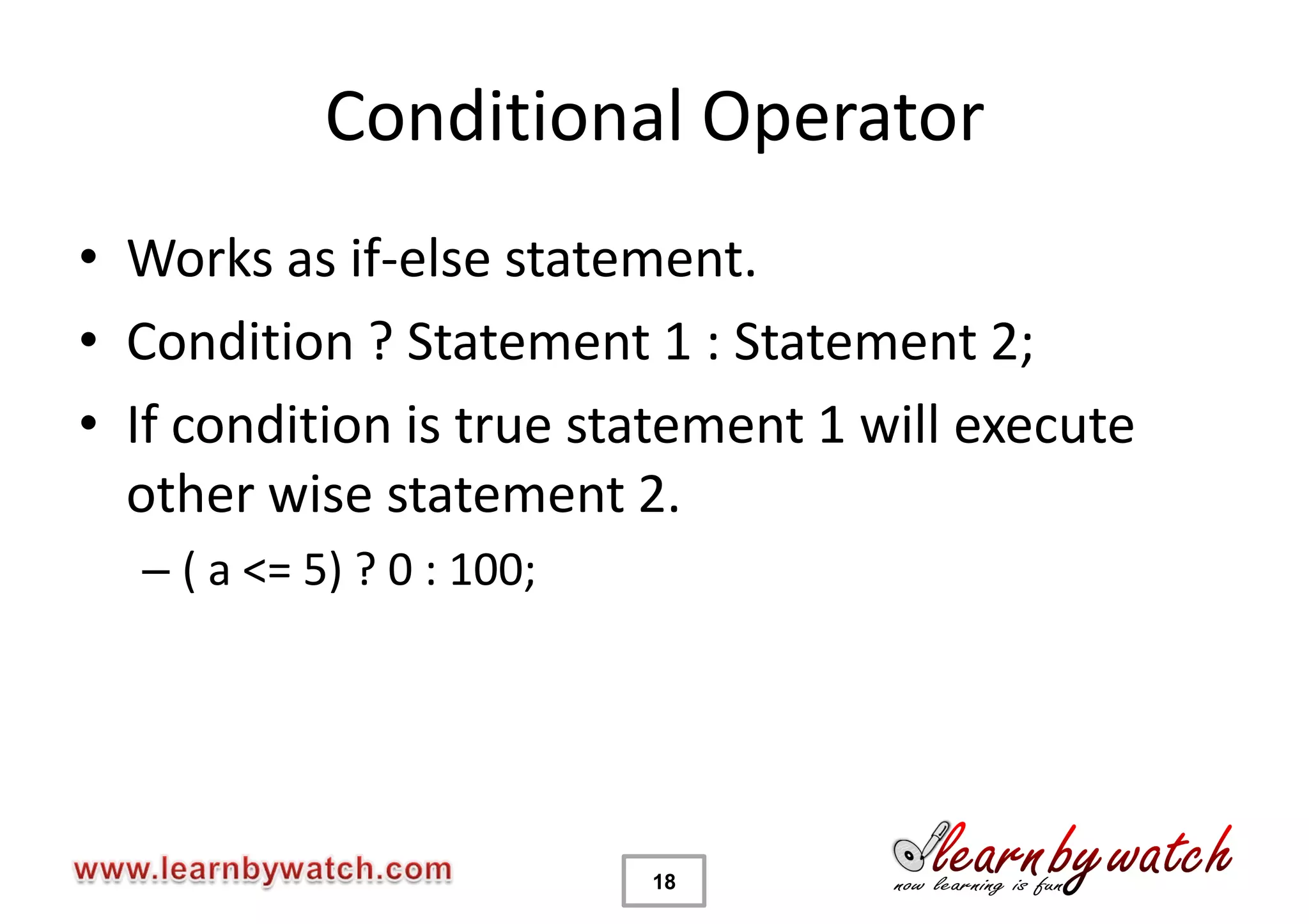
This document provides an introduction to decision statements in C programming. It discusses if, else if, else statements, switch statements, nested if/else, and conditional operators. Examples are given to check even/odd numbers, profit/loss calculation, and character classification. The importance of break statements in switch is explained. Operator precedence is also briefly covered.