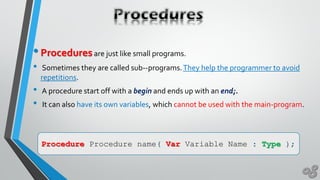
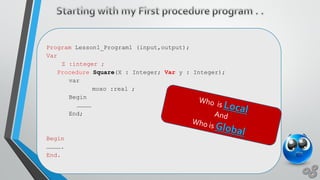
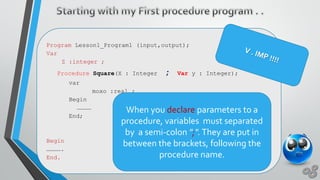
This document discusses Pascal programming language concepts like procedures, functions, variables, and built-in functions. It explains that procedures and functions are types of subprograms that can take parameters. Procedures do not return a value while functions return a single value. It also discusses global and local variables as well as function and procedure signatures, prototypes, and how to declare and call them.