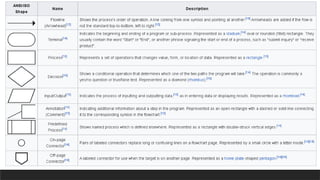
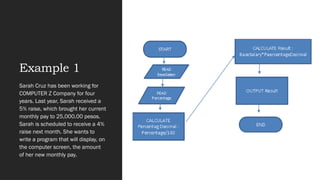
The document explains Program Logic Formulation (PLF), which consists of ordered instructions for programming tasks, emphasizing the role of logic in designing algorithms. It covers flowcharts for diagramming processes, pseudocode for documenting algorithms in plain language, and the use of conditional statements and loops in programming. Additionally, it discusses operators in programming languages that perform various functions, such as arithmetic and logical operations.