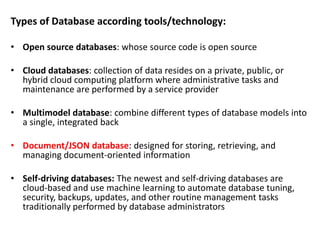
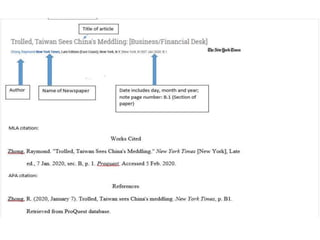
The document discusses databases and citation databases, explaining their structures, types, and functions. It highlights the importance of citation databases for accessing high-quality research outputs and the indexing mechanisms that enhance search precision. Additionally, it addresses challenges faced in database management, such as data volume, security, and scalability.