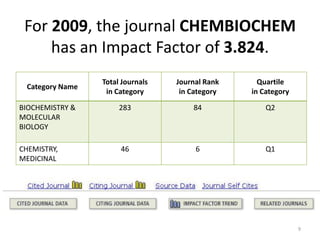
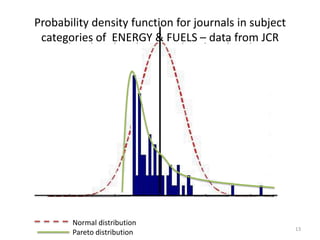
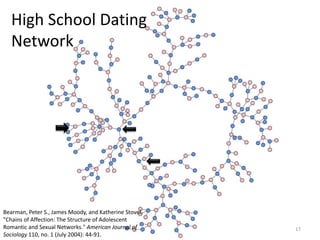
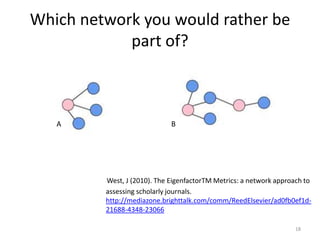
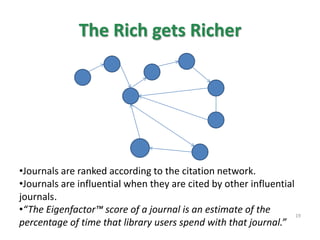
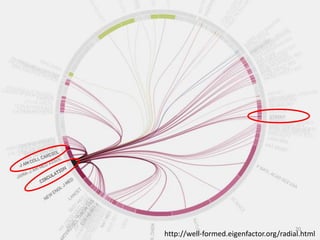
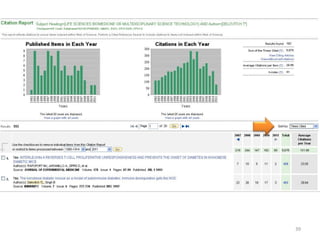
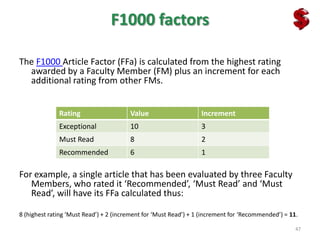
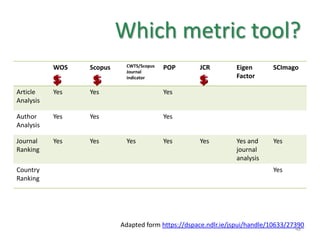
This document provides an overview of various bibliometric products and metrics that can be used to measure research impact, including journal impact factor, h-index, citation counts, and journal/article ranking tools from Journal Citation Reports, Scopus, and Google Scholar. It discusses the purpose and calculations of metrics like impact factor, eigenfactor, and source normalized impact per paper (SNIP). It also covers limitations of bibliometrics and recommends using multiple metrics and tools to evaluate research. Exercises are provided to help understand how to analyze journals, articles, and individual researchers using different bibliometric resources.