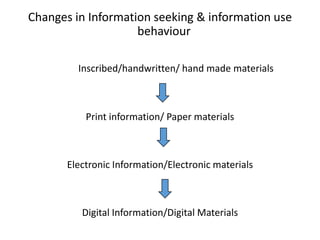
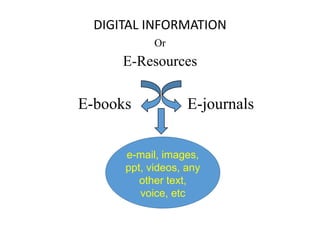
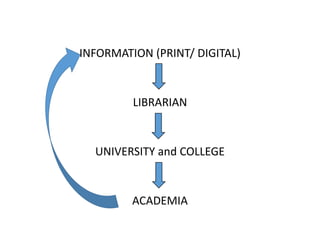
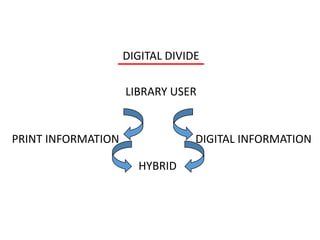
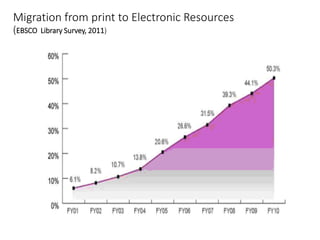
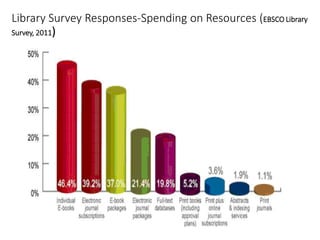
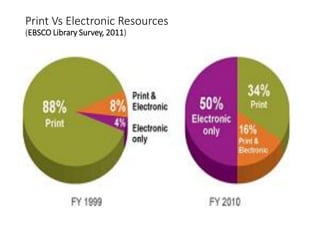
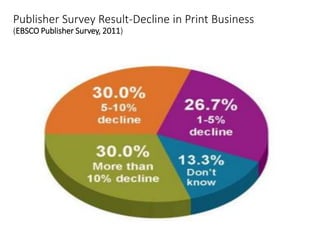
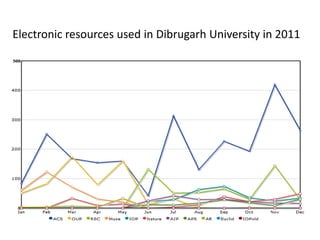
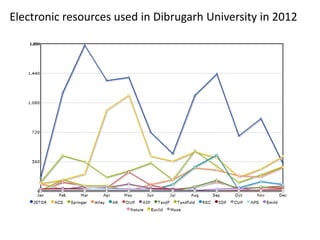
The document discusses how information seeking and use behaviors have changed with disruptive technologies over time. Specifically, it notes the paradigm shift brought about by digital transformation, which has significantly changed behaviors from print-based to online/electronic. This is due to factors like the extensive use of ICT, exponential growth of the internet and digital media, and the convenience of online accessibility. As a result, libraries have also had to change and now provide both print and electronic resources, as well as platforms for online access. Survey results show this trend towards electronic resources and decline in print materials. Overall, digital transformation has fundamentally changed how users seek and interact with information.