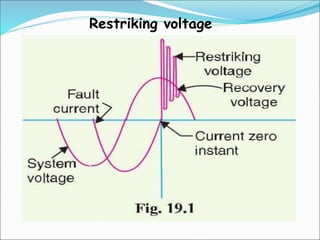
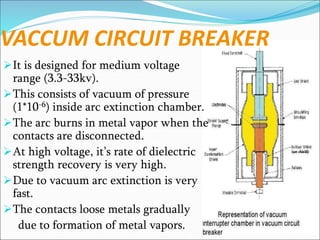
Circuit breakers are switching devices that can make, carry, and break electric currents under both normal and abnormal circuit conditions. They contain fixed and moving contacts that remain closed during normal operation but open automatically during faults to interrupt the fault current. When contacts open under fault conditions, an arc is produced that must be quickly extinguished. Different circuit breakers use various mediums like oil, air, vacuum, or SF6 gas to rapidly quench the arc through cooling and increasing dielectric strength between contacts. Common types of circuit breakers include oil, vacuum, air blast, and SF6 breakers that vary based on voltage level, switching speed, maintenance needs, and arc quenching method.