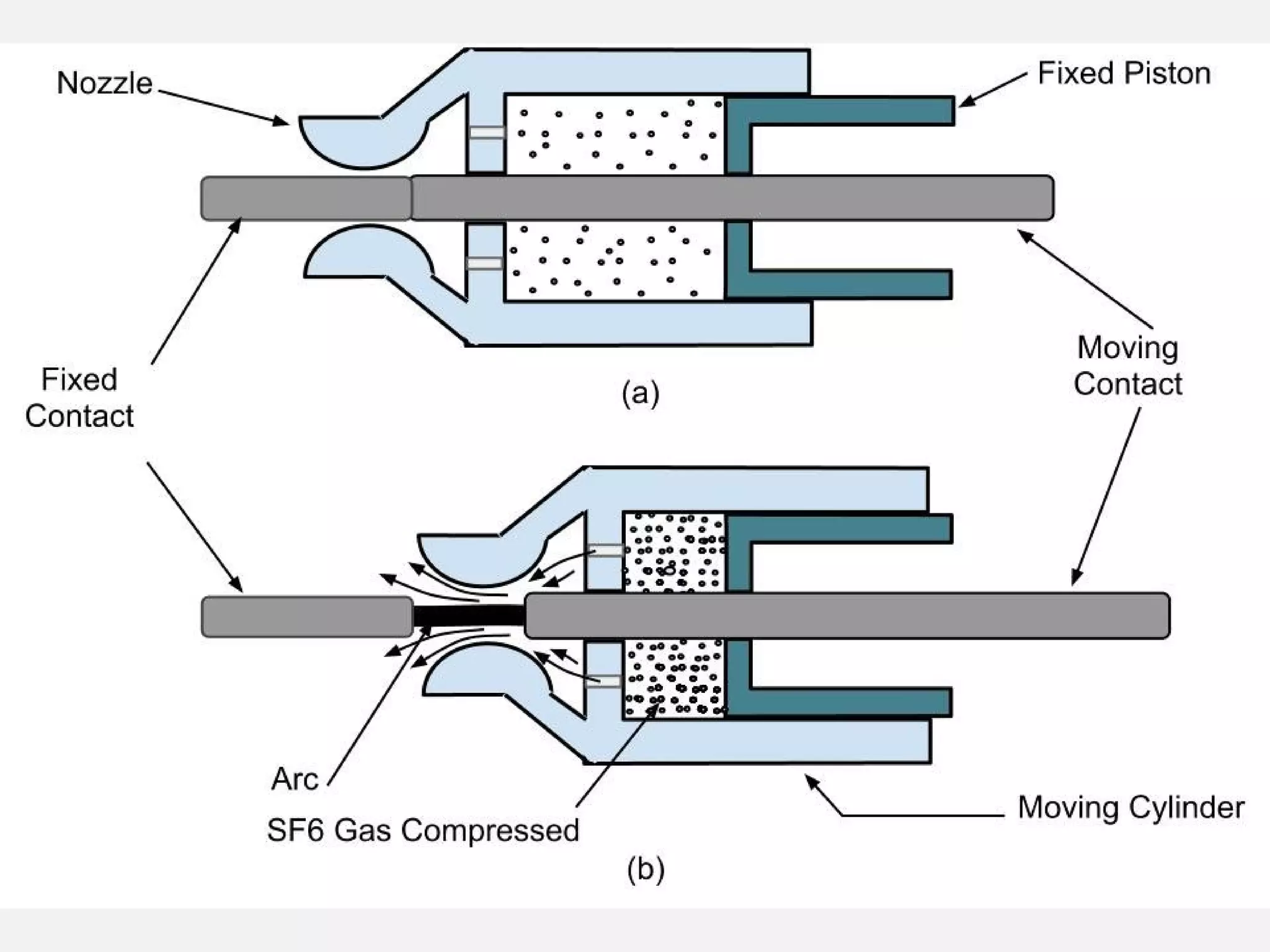
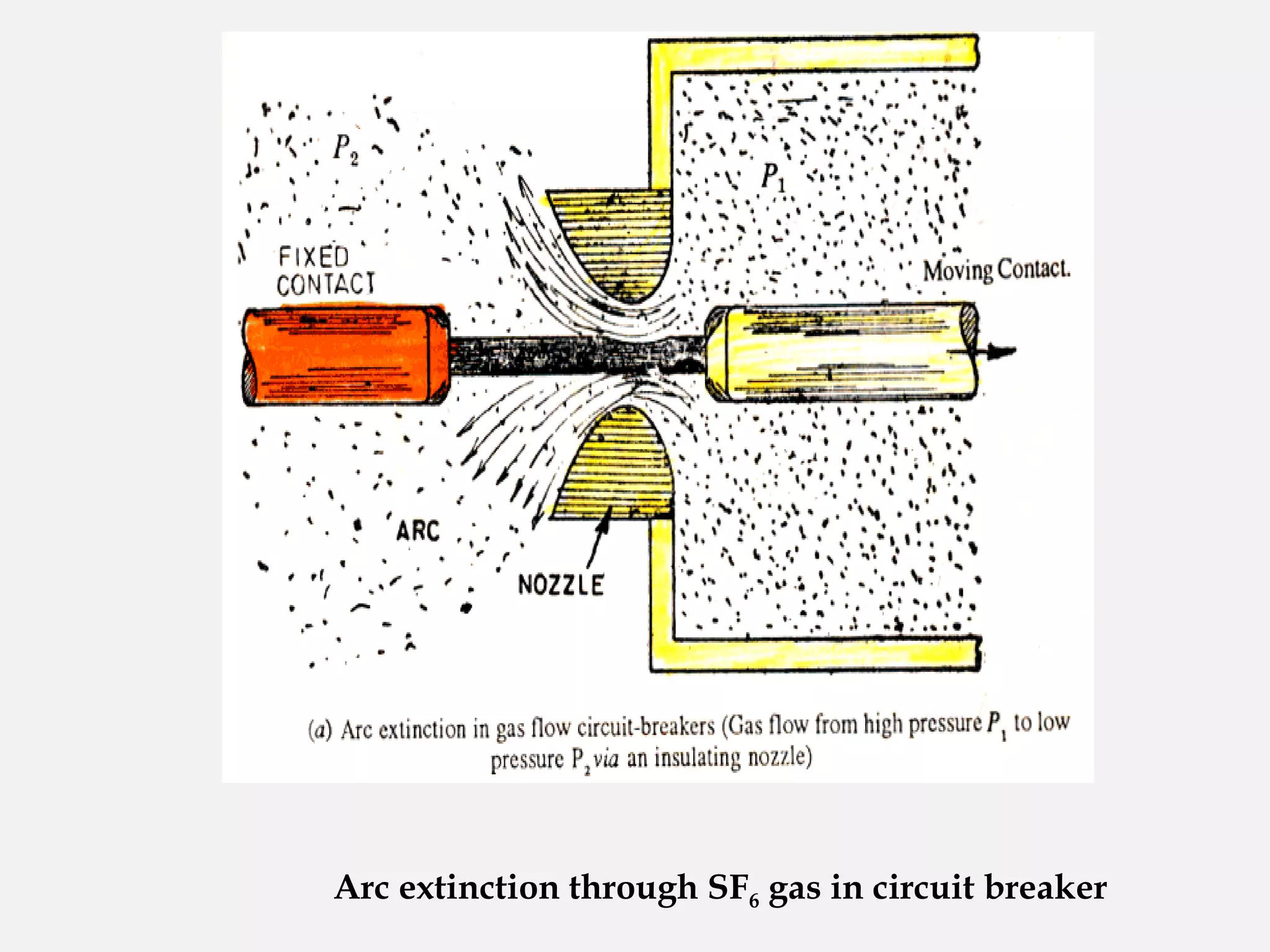
This document provides an overview of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breakers. It discusses that SF6 circuit breakers are commonly used in modern power systems for their safety and protection. The document describes the types and working principles of SF6 circuit breakers, including how the SF6 gas is able to quench arcs that form when contacts open or close under fault conditions. It also outlines the physical and chemical properties of SF6 that make it suitable for use in circuit breakers, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of SF6 circuit breakers. The document concludes by noting limitations in the use of SF6 and potential alternatives being researched.