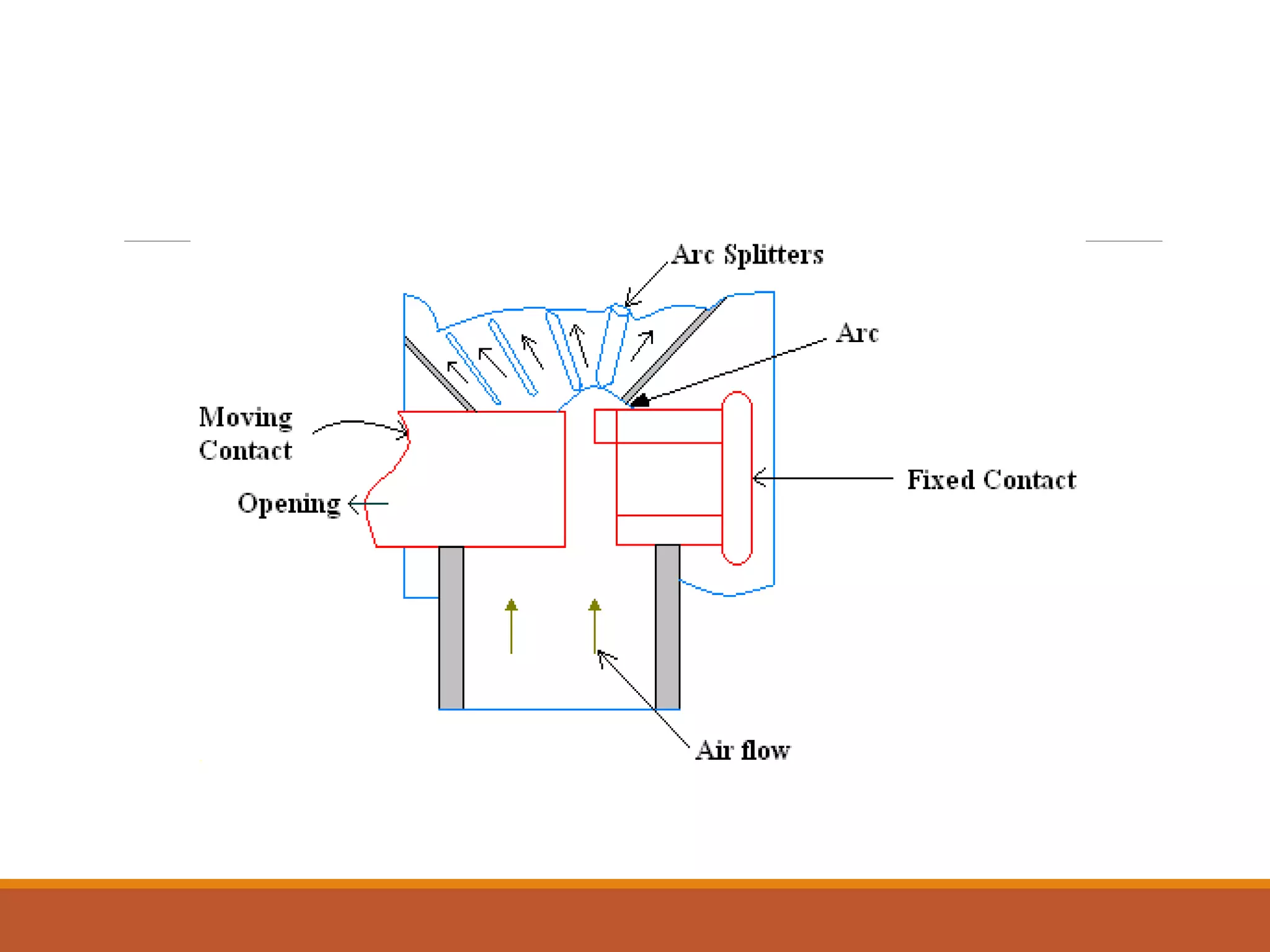
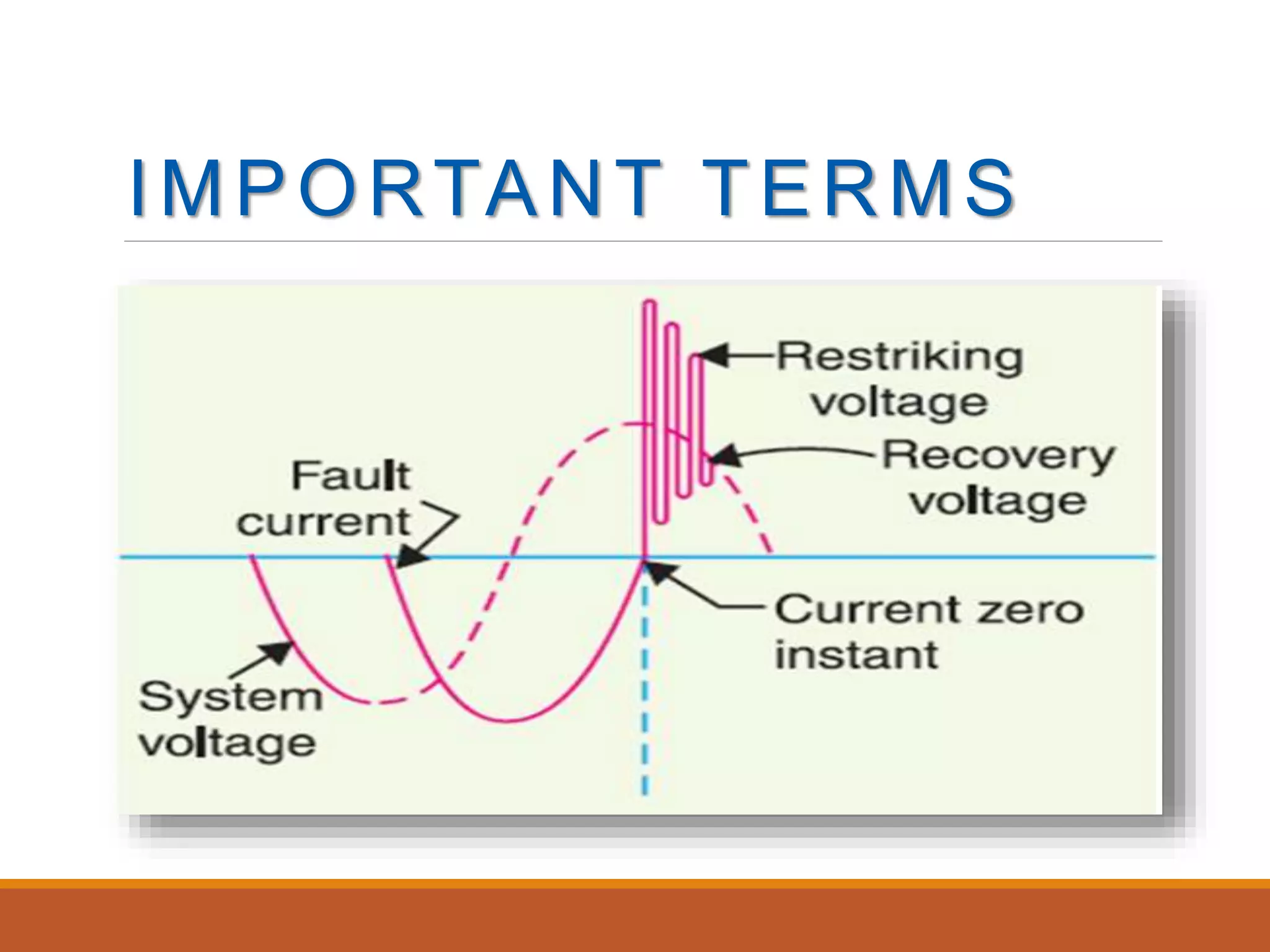
Circuit breakers are used to break electric circuits either manually or automatically during faults. When contacts open under a fault, an arc is produced which must be quickly extinguished. There are two main methods: the high resistance method increases arc resistance over time to reduce current below the level needed to sustain the arc, such as by lengthening, cooling, or splitting the arc. The low resistance or current zero method keeps arc resistance low until current reaches zero, then rapidly deionizes the medium between contacts to prevent the arc from restarting when voltage rises again.