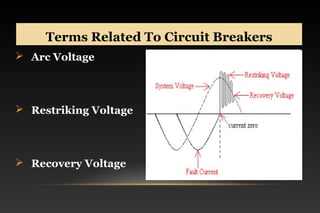
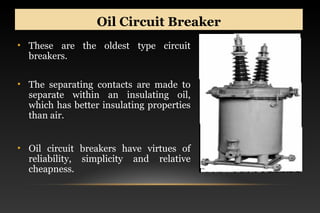
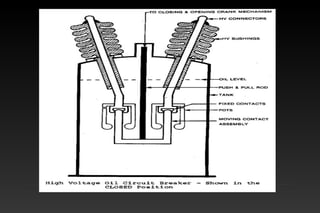
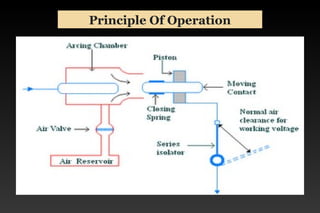
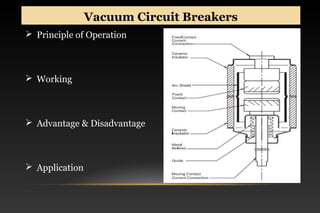
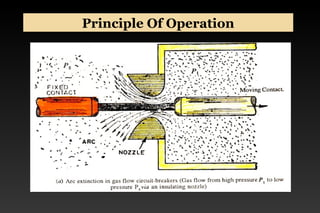
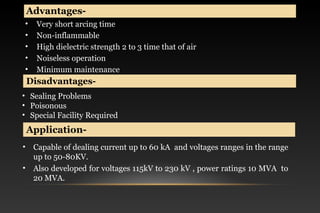
This document summarizes a seminar on circuit breakers. It discusses the working principles of circuit breakers, including arc phenomenon and methods of arc extinction. It also covers terms related to circuit breakers and different types of circuit breakers such as oil, air blast, sulfur hexafluoride, and vacuum circuit breakers. For each type, it provides details on principles of operation, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. The document concludes that the seminar helped gather new information about circuit breakers and their role in power systems.