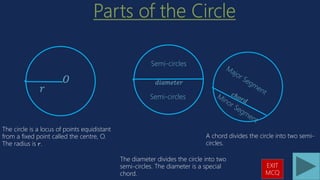
The document contains worked examples and multiple choice practice questions about properties of angles and circles. In the first example, the values of angles QPR and MQO are calculated using properties of isosceles triangles and angles in circles. The following examples involve calculating angle measures using properties such as angles in the same segment being equal, angles at the center being twice the angle at the circumference, and angles formed by tangents and chords.