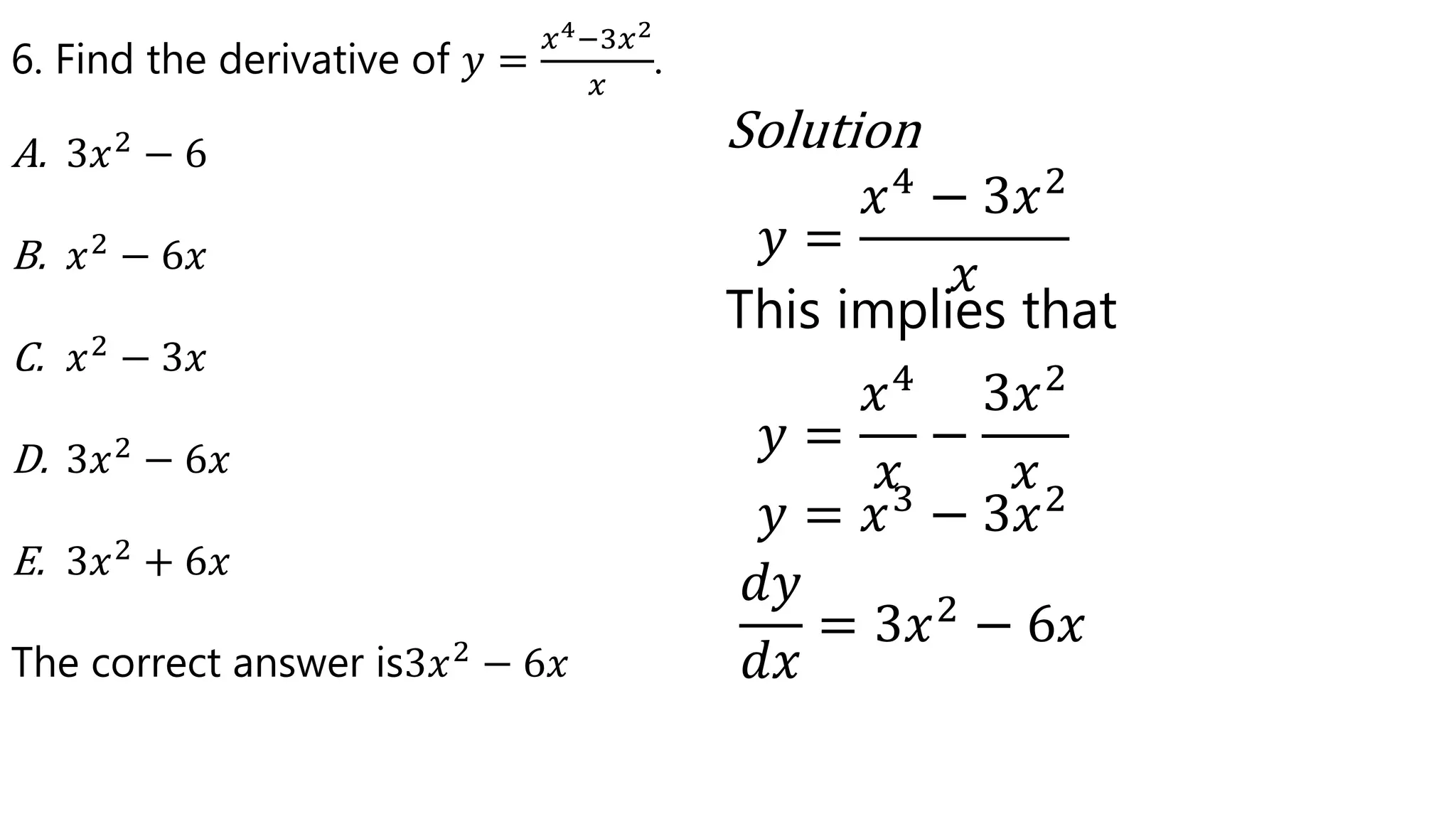- The document discusses differentiation and integration of algebraic functions.
- It provides rules for finding the derivatives of functions such as y = xn, y = axn, and the sum or difference of functions.
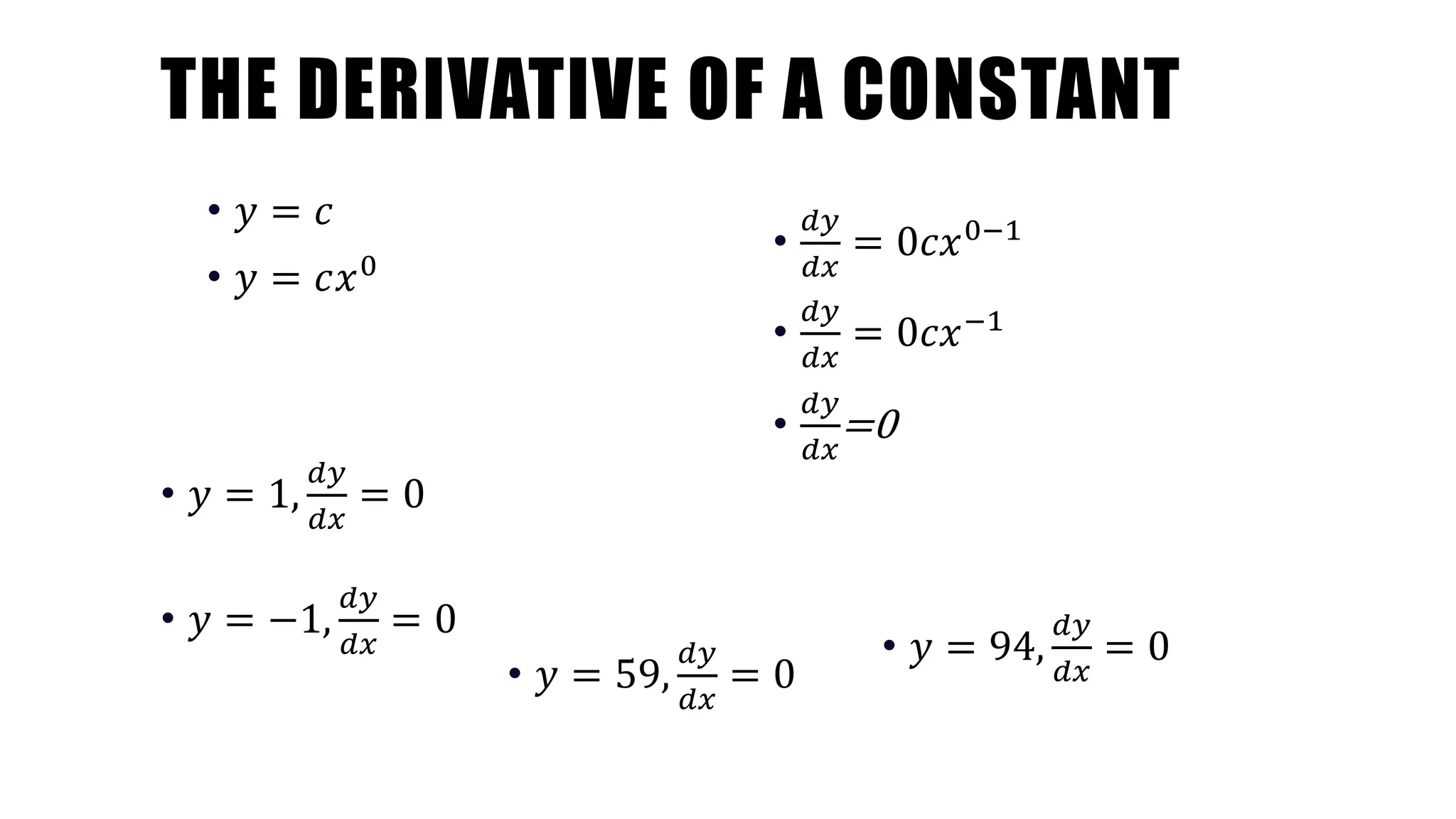
- It also discusses that the derivative of a constant is 0, and provides examples such as dy/dx = 0 for y = 1.
- Integration is discussed as the reverse process of differentiation, with rules provided for indefinite integrals of functions like xn and definite integrals over an interval.