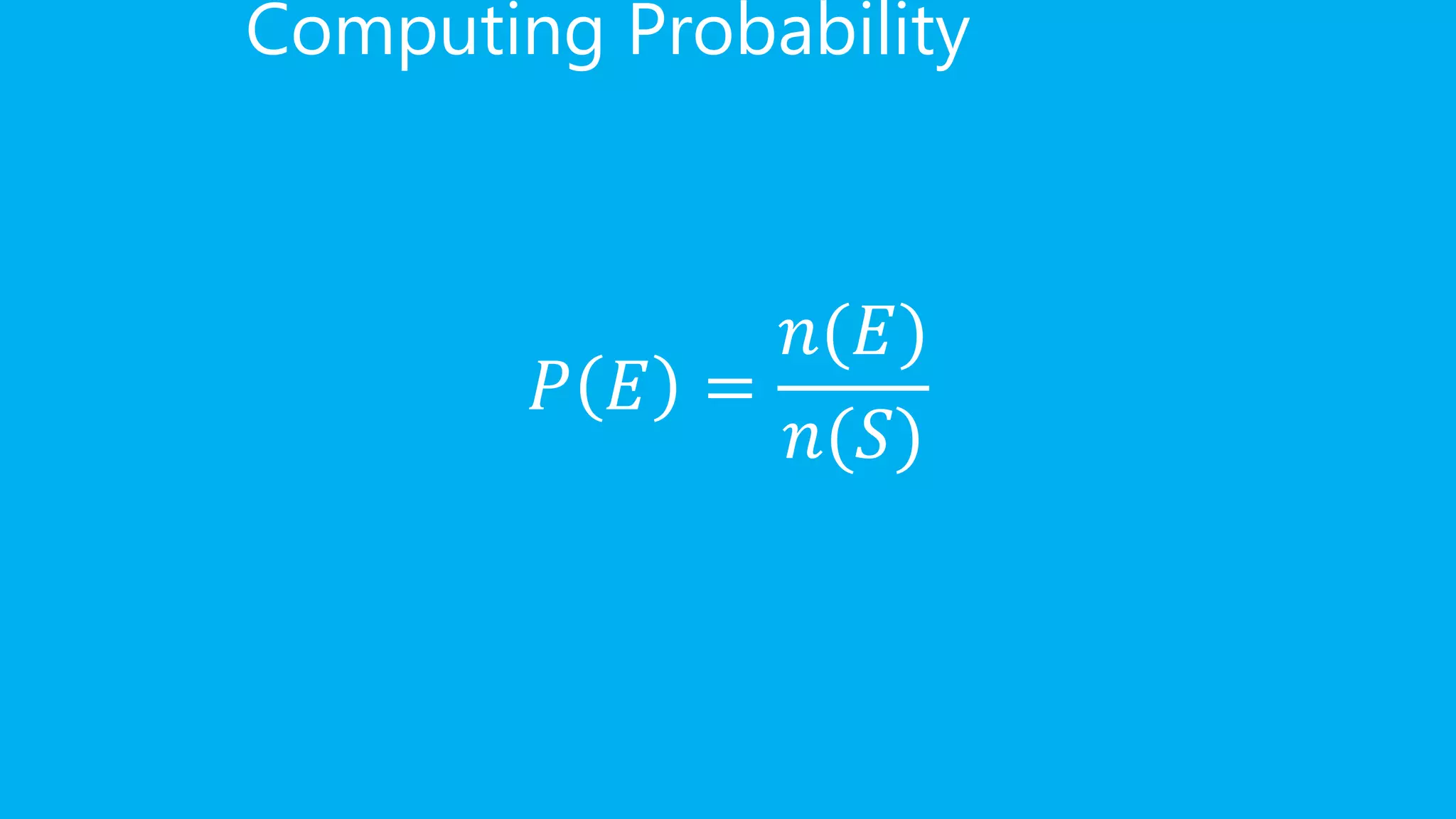
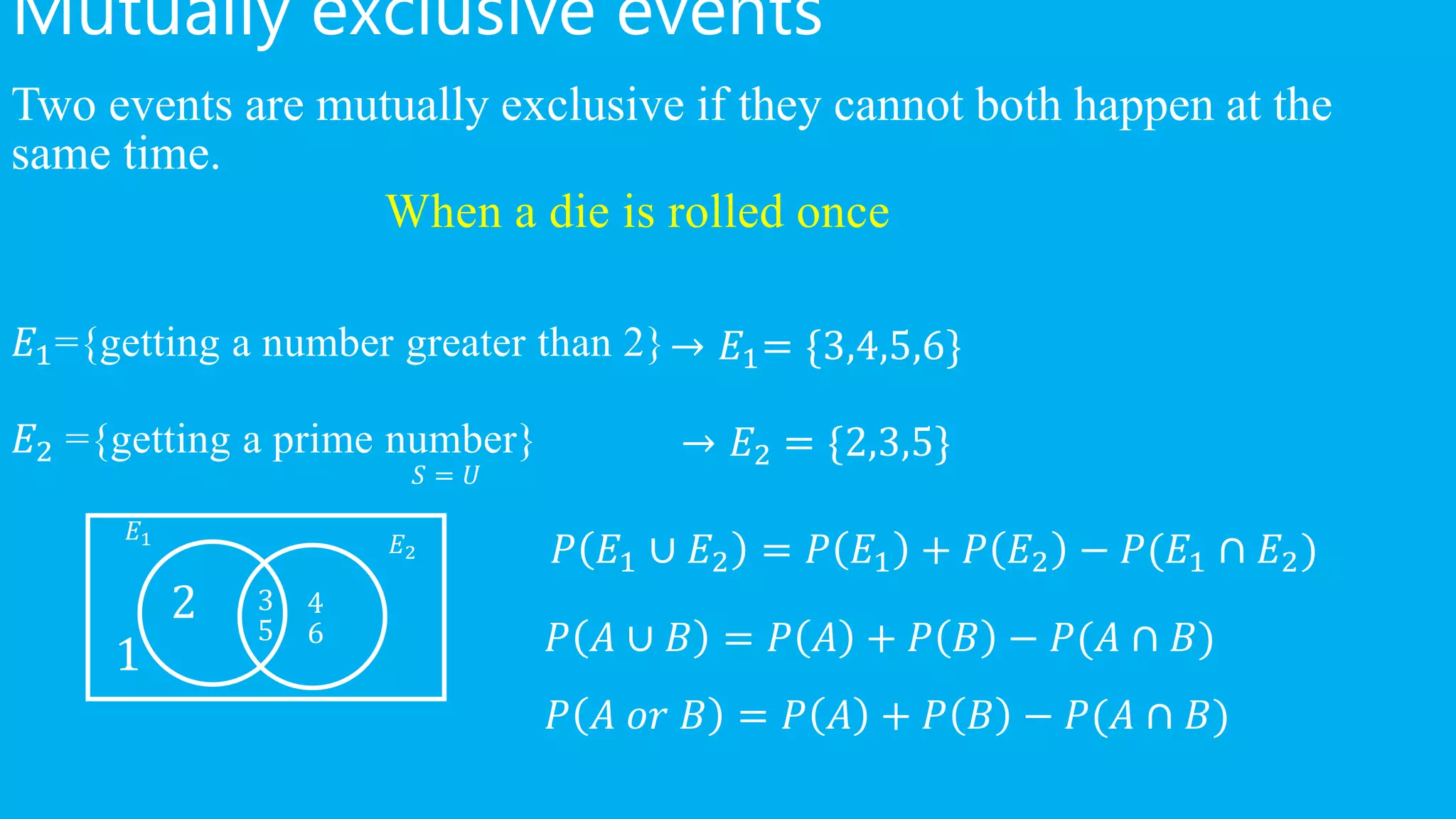This document provides formulas and examples for calculating probabilities of events. It defines mutually exclusive events as events that cannot occur at the same time. It gives the formulas for calculating the probability of the union or intersection of events. Examples include calculating probabilities of rolling dice, picking beads from a bag, and selecting fruits or students at random.