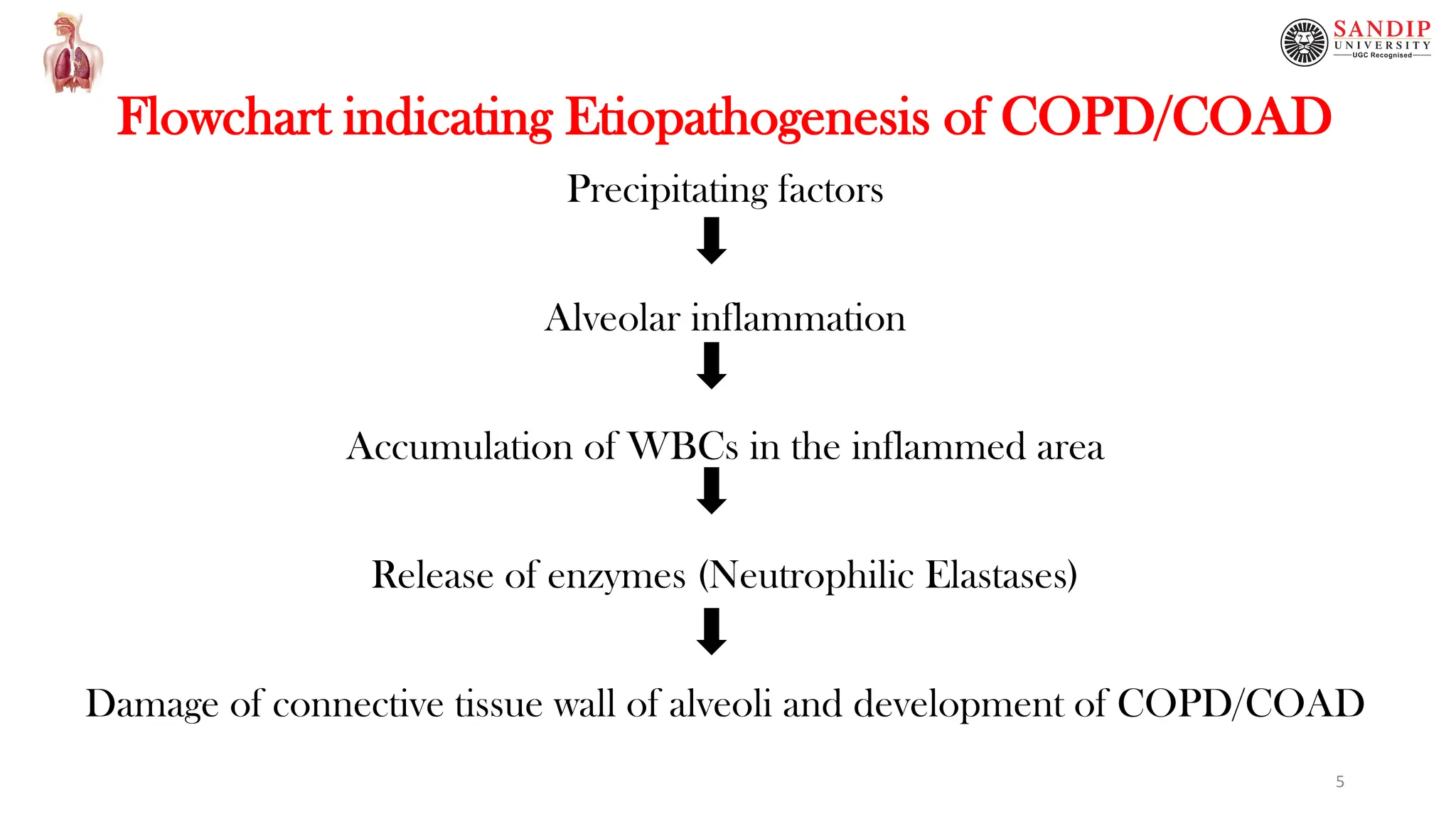
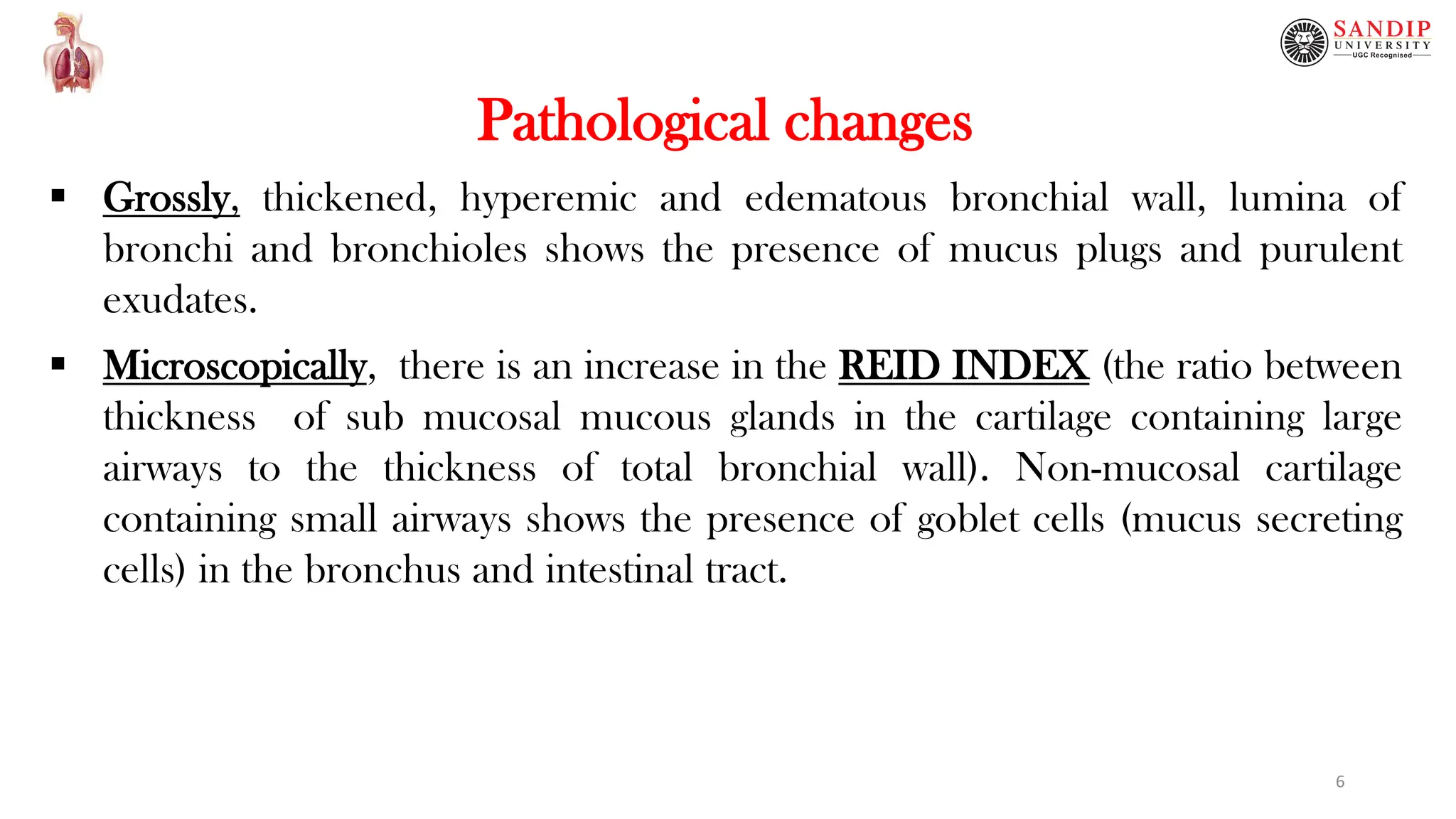
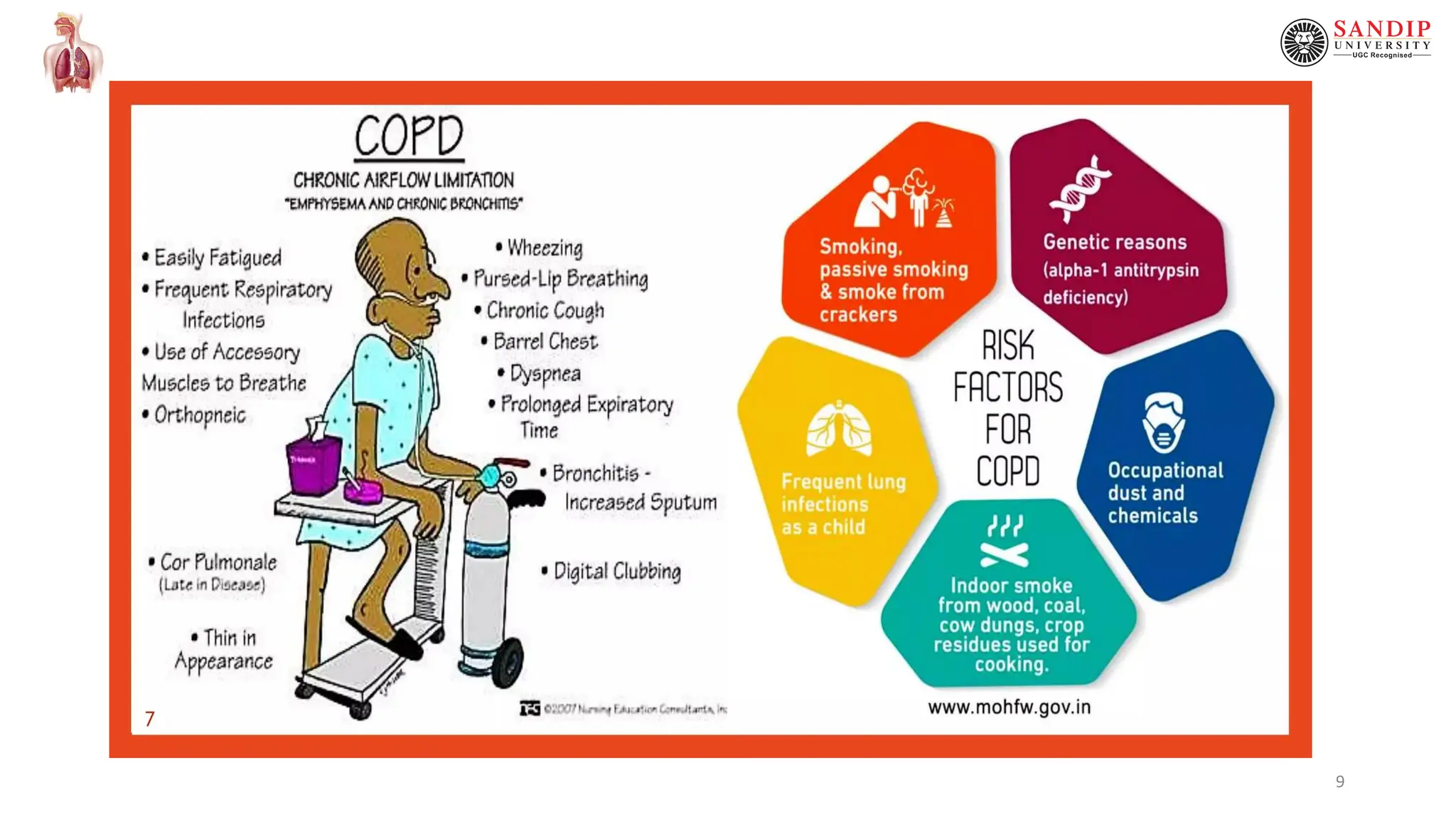
This document provides an overview of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including definitions, causes, pathophysiology, clinical features, and complications. COPD is a persistent obstruction of the airways caused by chronic bronchitis or emphysema. Chronic bronchitis involves persistent cough and mucus production, while emphysema involves destruction of lung tissue. Cigarette smoking is the primary cause of COPD by impairing mucociliary clearance. Other risk factors include air pollution, infections, and genetic conditions like alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Pathological changes include thickened bronchial walls, mucus plugs, and increased mucus gland size. Clinical features consist of cough, sputum production, dys