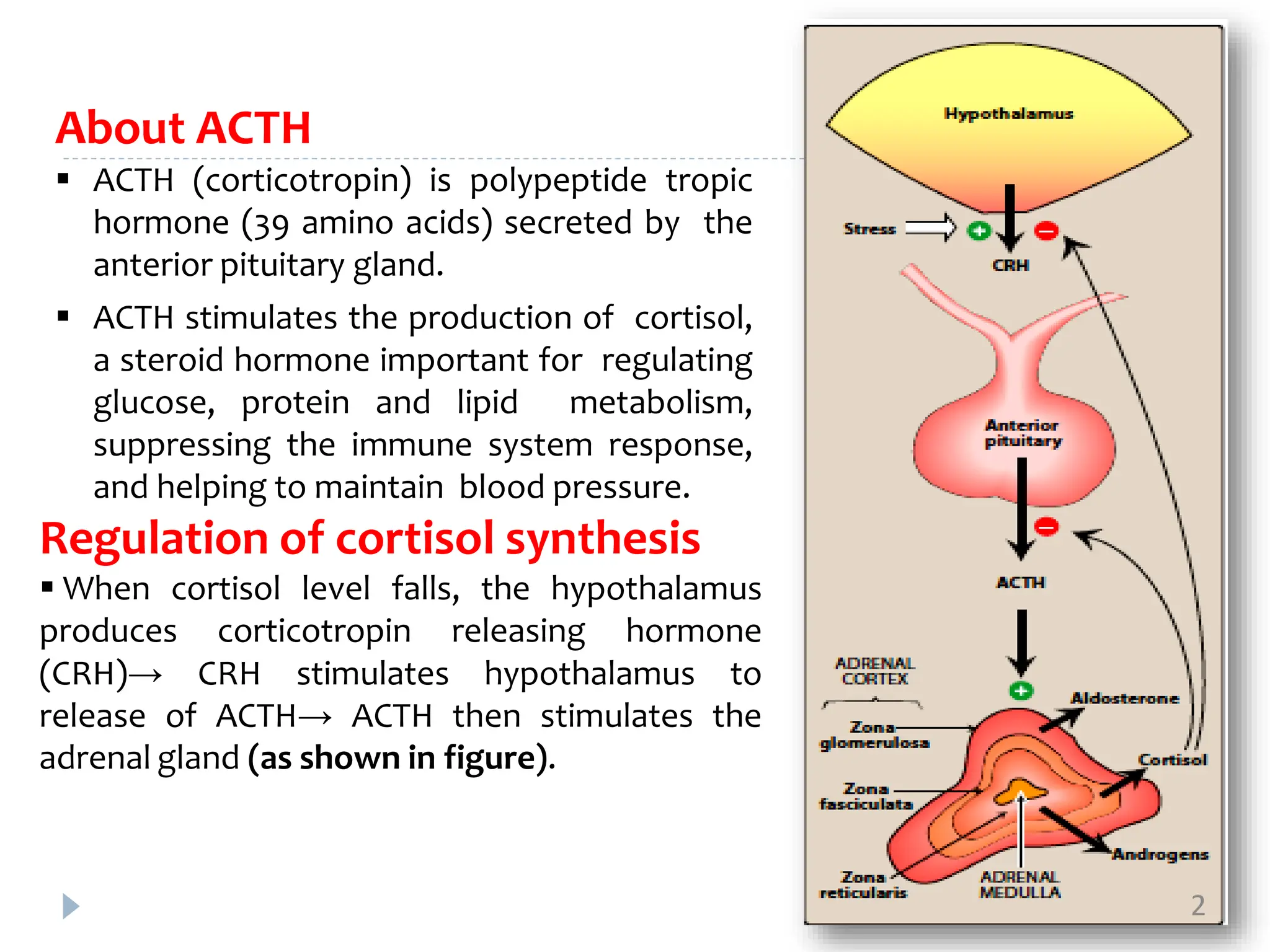
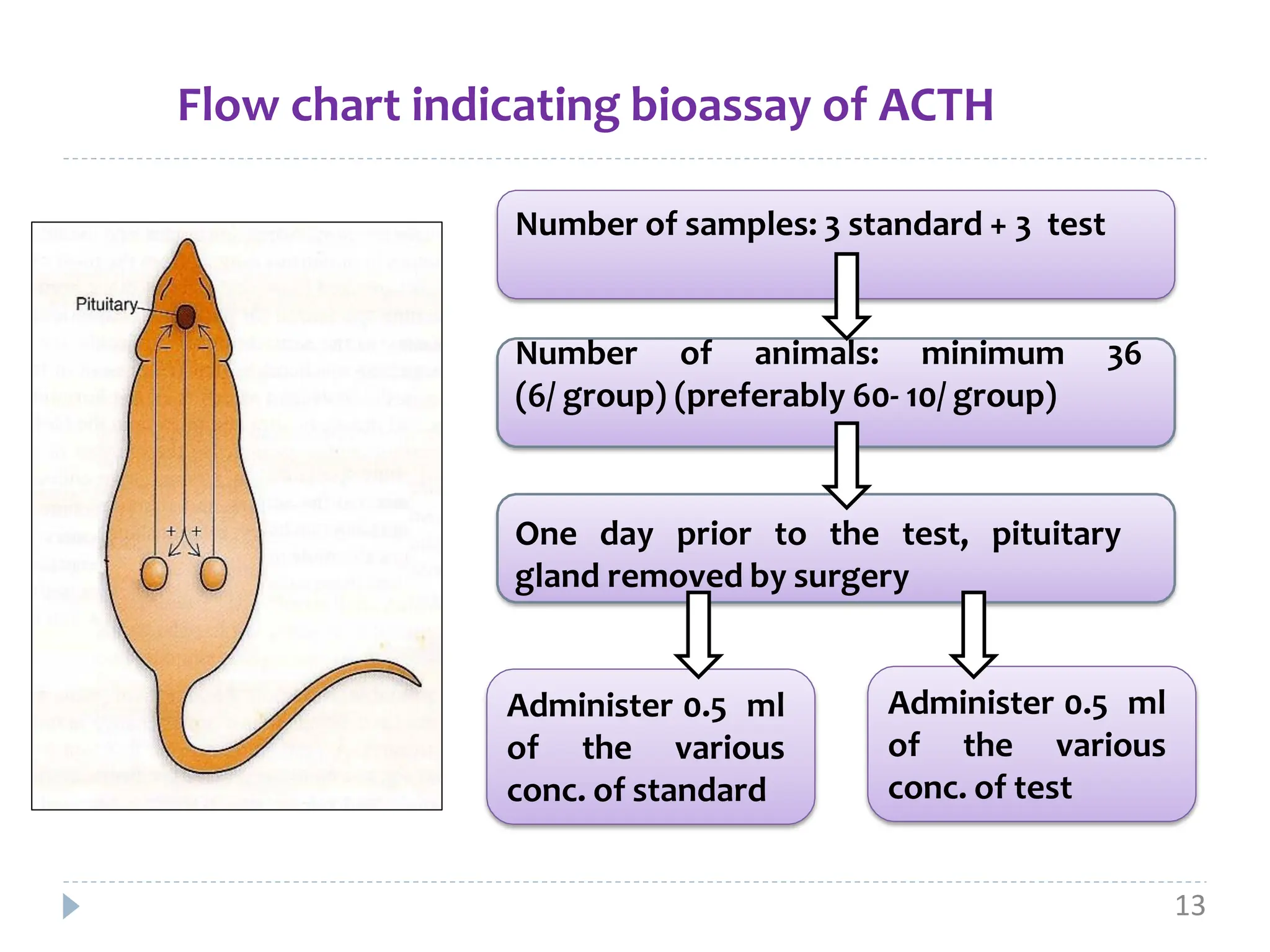
ACTH, also known as corticotropin, is a polypeptide hormone secreted by the pituitary gland that stimulates the production of cortisol by the adrenal glands. Two common bioassays are described for measuring ACTH activity. The first involves measuring ascorbic acid depletion in the adrenal glands of hypophysectomized rats after ACTH administration. The second measures corticosterone levels in the blood of dexamethasone-blocked rats at increasing time points after ACTH injection. Both assays involve administration of multiple doses of a standard ACTH preparation and test preparation to rats, followed by quantitative chemical analysis to determine potency ratios and confidence limits for the test preparation relative to the standard