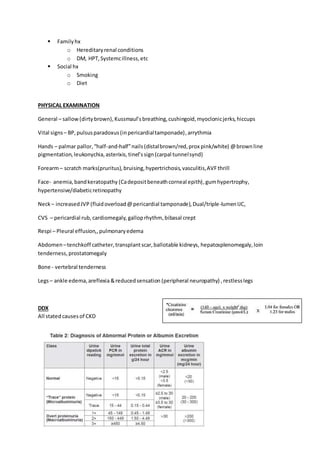
The document provides a comprehensive overview of chronic kidney disease (CKD), including its definition, stages, symptoms, and management strategies. It highlights the importance of early referral to nephrologists, treatment of underlying conditions, and monitoring of kidney function, with a focus on hypertension and proteinuria management. The document also outlines dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and potential complications associated with CKD, emphasizing the need for a multidisciplinary approach.
![CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE INFO & TEMPLATE
OVERVIEW
CPG = an irreversiblelossof renal functionforatleastthree months.
Oxford= kidneydamage >= 3 monthsbasedon findingof abnormal structure
or GFR <60 mL/min/1.73m2
for>= 3months withorwithoutevidenceof kidneydamage.
UM express= 1. Azotemia– accum of nitrogenousproduct(chieflyurea) inblood –raisedU & C
2. Uremia – manifestationof organdysfunctiona/w azotemia
3. CRF – permanentGFRreduction/ GFR sufficienttoproduce detectablealterations
inwell-being&organ fx
4. ESRF –final stage of CKD whenptcan’t survive w/otransplant@longtermdialysis
[NKF-KDOQIClassification]
basedon three factors:
1. GFR (level of kidneyfunction)
2. pathological changes(kidneydamage)
3. presence of the abnormalityforatleast
three months.
- MildCKD. Asymptomatic.
- Moderate CKD.Usually
asymptomatic.
- Anemiainsome ptat 3B.
- Most are non-progressive or
progressveryslowly.
- Severe CKD.Firstsymptom
usuallyatGFR <20.
- ElectrolytesproblemsasGFRfalls
- Kidneyfailure.Significant
symptoms& complications.
- Dialysisinitiationvariesbut
usuallyatGFR <10
The kidneydamage isdefinedaseither:
a. Persistentmicroalbuminuria
b. Persistentproteinuria
c. Persistenthaematuria
d. Radiological evidence of structural
abnormalitiesof the kidneys
e.Biopsyprovenglomerulonephritis
Asymptomatic.Only
biochemical abn.
Loss of excretory,
metabolic & endocrine fx
of kidney.Leadstosx & sx
(referred as uremia)
ESRD/ESRF = when death
is likely w/o RRT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckdtemplate-160330125124/75/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-INFO-AND-TEMPLATE-1-2048.jpg)

![ Identifycauses/riskfactorsforCKD
o CommoninMalaysia: long standingDM,HPT
o h/oautoimmune disorders (IgA nephropathymostcommon), systemicinfections,
drugs,neoplasia------[Glomerulardiseases]
o h/orepetitive urinarytractinfection,stones,drugtoxicity,autoimmune,
nephrocalcinosis ----- [Tubulointerstial disease]
o h/olarge vessel disease,hypertension,microangiopathy,vasculitis ----[ Vascular
diseases]
o h/oStones (lointogroinpain,dysuria,etc) oranatomical problemsof the urinary
tract --- [Urinarytract obstruction]
o Symptomsof SLE (malarrash, arthritisetc) & vasculitis ----- [systemicinflammatory
disease]
o Previousepisode of acute renal failure
o Historyof transplantedkidney –can have chronicrejection,drugtoxicity,transplant
glomerulopathy
o HereditaryKidneyDiseases, egPCKD
inchronic cases,alsoask about:
o Course & progression
Progressionof symptoms
Progressionof markers.Egproteinuria,creatinineetc(espeducatedpt)
Additionof medication, fluidrestrictions..
o Detailsaboutdialyisis
HD/CAPD,frequency,done at..,compliance
Int jugularcatheter/femoral catheter/AV Fistula/peritoneal dialysiscatheter
Complicationsof hemodialysis:
Hypotension,cardiacarrythmias,hemorrhage,airembolism, dialyser
hypersensitivity,pulmonaryedema,systemicsepsis
Complicationsof peritoneal dialysis:
CAPDperitonitis,catheterexitsite infection,sclerosingperitonitis
o Anyotherinterventionsdone:
Renal transplant,lagi..?
Functional impairment/status
o Change inqualityof life (espif starteddialysis)
o Psychosocial aspect
PMH
o Comorbids,eg:
DM - Glucose control,....
HPT - Strict bloodpressure control (understandtargetBPinCKD)...
Illnessleadingtochronicuse of NSAIDs& analgesics
o All followups&medications:
Currentlistof medications prescribed.Eg: ace-I,ARB,etc
OTC drugs – worsenCKD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckdtemplate-160330125124/85/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-INFO-AND-TEMPLATE-3-320.jpg)

![2. Monitoringof Renal Function
a. RP at 2 wksafterstart/adjustACE-I/ARB
b. reduce or discontinue ACEi/ARBif:
i. sustained rise increatinine levelsabove 30% frombaseline
ii. or eGFR reduces>25% from baseline
iii. or serumpotassiumis>5.6 mmol/l duringthe firsttwomonthsafter
commencementof ACEi/ARB
**after excludingotherprecipitatingfactorsandrefertoa nephrologist/physician.
3. Optimal GlycaemicControl
a. Target HbA1c ≤7% inDM but thisshould be individualisedaccordingtoco-
morbidities.
4. Preventionof CoronaryArteryDisease
a. Statinfor 1o
& 2o
prevention (startterusawal2)
b. Aspirinfor2o
prevention(avoidcombinationclopidogrel +aspirininCKDunless..)
5. DietaryIntervention
a. Referdietitian
b. Low proteindiet(0.6- 0.8 g/kg/day) withadequateenergyintake (30– 35
kcal/kg/day) forCKDStage 3 – 5
c. Sodiumrestriction(notmore than 1 level teaspoonof salt addedtofood/day)
6. Lifestyle Modification !!!
a. exercise,reduceexcessweightandavoidsmoking
7. Special Precautions
a. Reviewall prescribedmedicationregularlytoensure dose is appropriate
b. AvoidNSAIDsincludingCOX-2Inhibitors(such asmefenamicacid, diclofenac,
ibuprofen,naproxen,indomethacin,ketoprofen,salicylic acid[highdose],
meloxicam, celecoxibandetoricoxib)
c. Avoidradio-contrastagentsif possible(use alternativesmethod@contrasts)
d. AvoidFleet(oral NaPO) incolono forCKDstage 4-5 (use macrogol)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckdtemplate-160330125124/85/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-INFO-AND-TEMPLATE-6-320.jpg)
