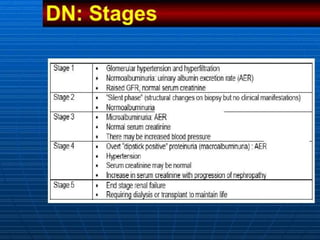
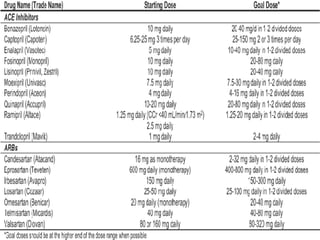
This document discusses the stages, diagnosis, prevention, and management of diabetic nephropathy. It begins with objectives and defining diabetic nephropathy as persistent albuminuria and declining kidney function. Risk factors include poor blood sugar and blood pressure control, smoking, and family history. Screening involves measuring the albumin-creatinine ratio annually after diagnosis. Prevention focuses on patient education, glycemic control, blood pressure management, and smoking cessation. Treatment includes ACE inhibitors or ARBs to slow progression even in normotensive patients, with referral to a nephrologist for advanced kidney disease.