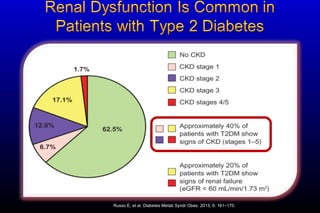
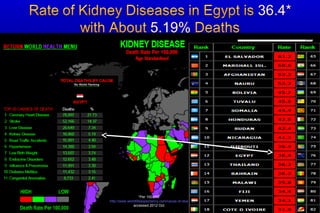
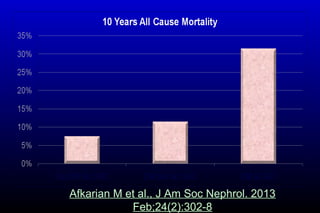
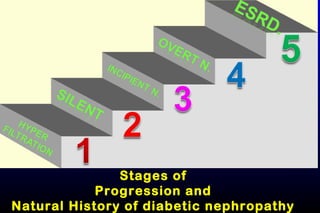
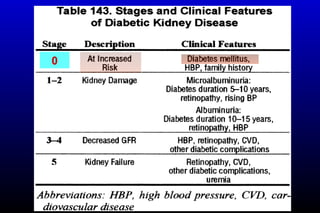
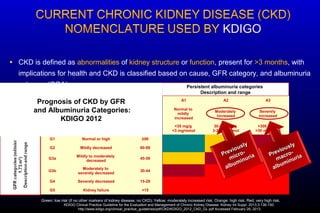
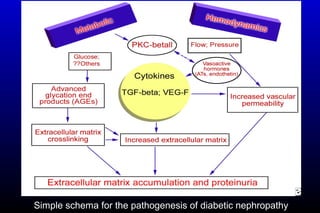
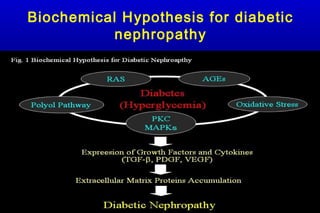
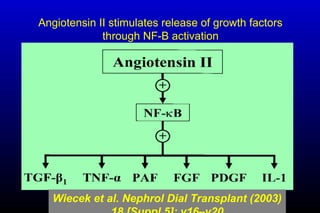
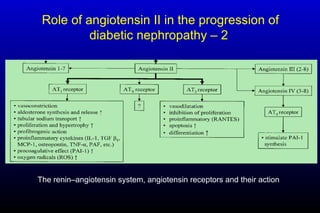
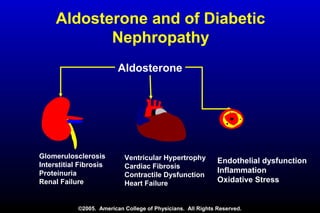
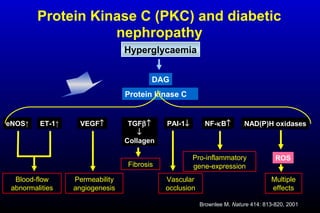
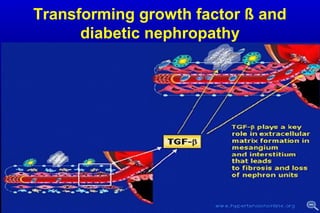
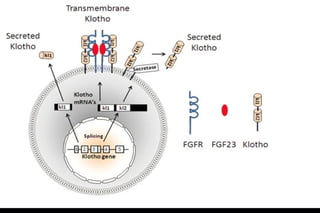
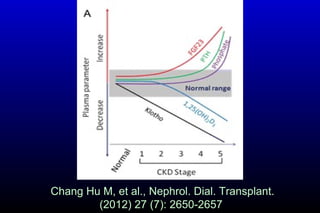
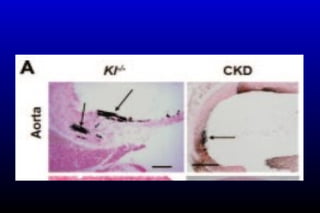
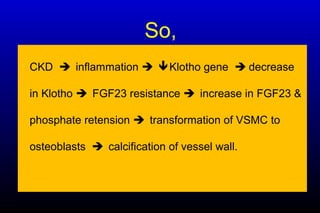
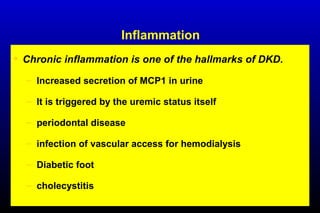
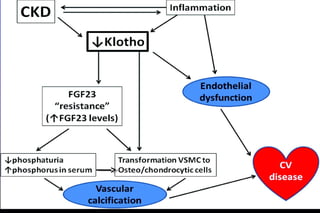
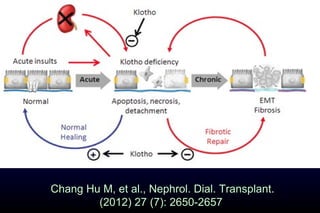
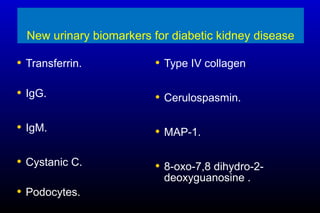
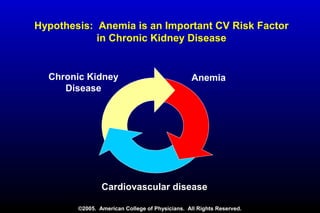
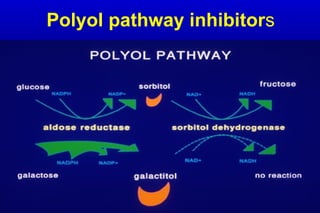
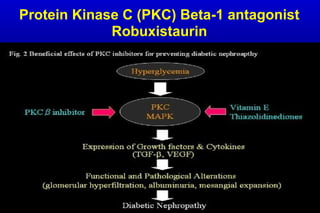
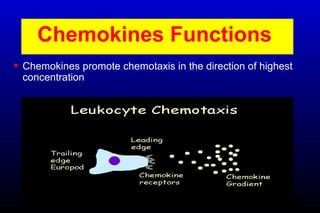
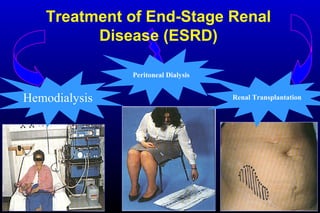
Diabetic nephropathy is a major complication of diabetes that can progress to kidney failure. The document discusses the pathophysiology, risk factors, stages of progression, biomarkers and pathology of diabetic nephropathy. Key factors that contribute to its development include genetic susceptibility, hypertension, activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, increased levels of growth factors like TGF-β, and chronic high blood glucose levels which can activate biochemical pathways like protein kinase C. Left untreated, diabetic nephropathy can progress through five stages and ultimately lead to end-stage renal disease.