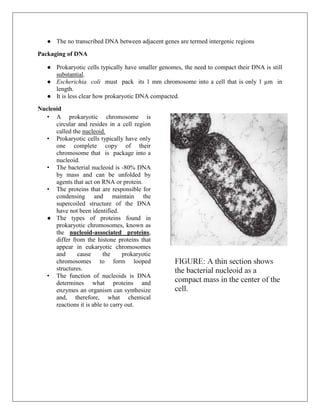
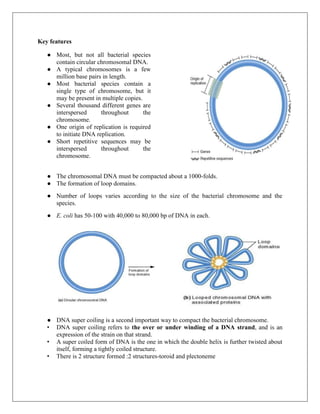
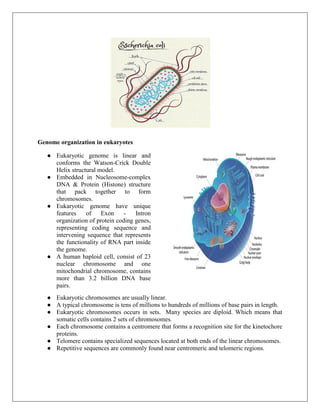
A genome is the complete set of DNA in an organism, including nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, and encompasses all hereditary material needed for building and maintaining the organism. Prokaryotic genomes are typically compact, circular DNA molecules found in the nucleoid region, often accompanied by plasmids that provide advantages like antibiotic resistance, while eukaryotic genomes are linear, organized into nucleosomes, and contain introns. The document also contrasts prokaryotic and eukaryotic genome characteristics, focusing on their structures, gene organization, and mechanisms of DNA packaging.