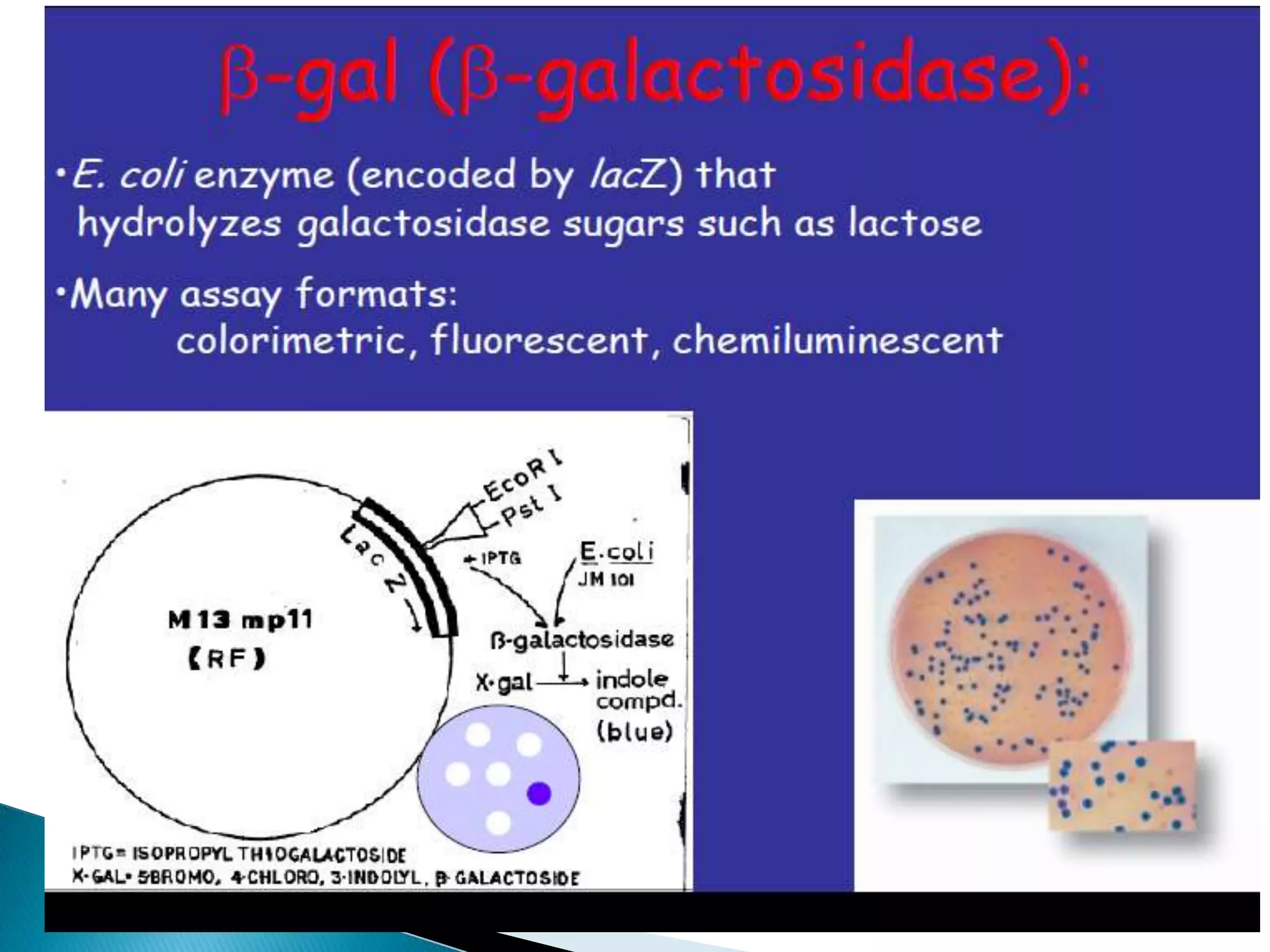
- β-glucuronidase (GUS) is a commonly used reporter gene in plant molecular biology and genetic engineering to indicate successful introduction of foreign DNA into cells.
- GUS expression can be detected through fluorometric or histochemical assays, allowing visualization of promoter activity, protein localization, and transgenic events.
- The GUS gene is fused to genes of interest, and GUS activity is used to study processes like tissue-specific expression, response to stresses, and transformation efficiency.
- While destructive, GUS is a stable and non-toxic reporter enabling versatile applications in fundamental and applied plant research.