This document provides an overview of basic statistical concepts including:
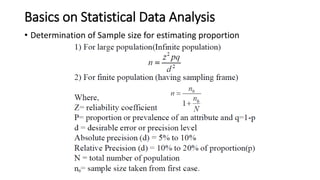
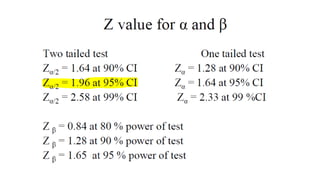
1. How to calculate sample size for estimating proportions based on a given population size, prevalence, confidence interval, and margin of error.
2. The different types of statistics - descriptive and inferential - and examples of each.
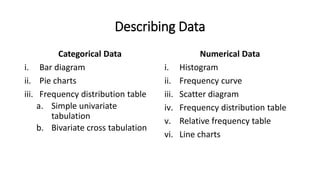
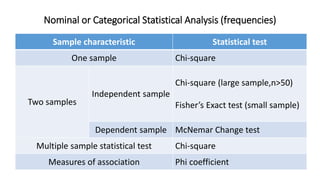
3. How to categorize and describe different types of statistical data - categorical vs. numerical - and appropriate analysis methods for each.